Are these the first darkish stars?
Astrophysicists on the College of Texas at Austin stated on July 14, 2023, that they’ve now recognized three vivid objects that is likely to be “darkish stars.” Wait. Stars shine, don’t they? It’s the actual fact of their shining – by way of fusion reactions of their interiors – that differentiates stars from planets. These new objects have existed thus far solely in idea. And so they do, certainly, shine. In reality, they’re stated to be a lot larger and brighter than our sun. However they don’t shine as stars do. As an alternative, if this new examine is right – if these really are darkish stars – then these three objects are product of the mysterious substance referred to as dark matter. And so they’re powered by collisions between dark matter particles. The scientists stated:
If confirmed, darkish stars may reveal the character of dark matter, one of many deepest unsolved issues in all of physics.
The scientists published the analysis within the peer-reviewed Proceedings of the Nationwide Academy of Sciences.
Darkish matter stars?!
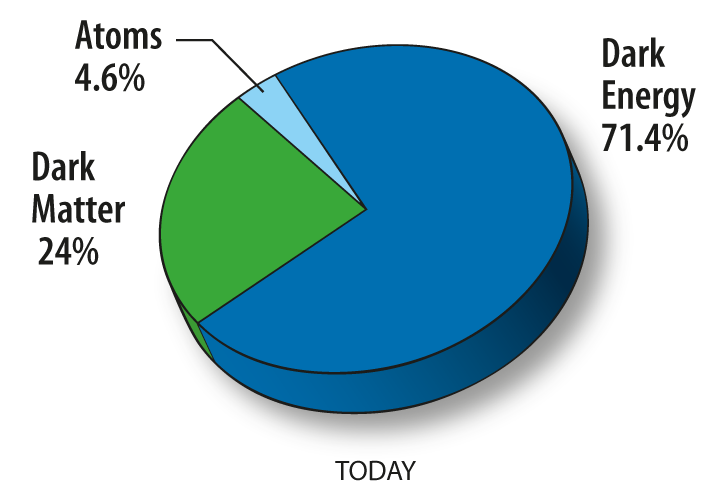
In fashionable cosmology, dark matter makes up about 25% of the universe. And roughly 70% of the universe is dark energy. Atypical matter – like our sun and Earth and all that we all know – makes up solely 5% of the universe, based on the scientists’ theories.
Darkish matter has been elusive. Scientists imagine it exists, however don’t know what it’s. However dark matter stars? That’s a brand new thought. Katherine Freese, director of the Weinberg Institute for Theoretical Physics at UT Austin, is lead writer on the brand new examine. She commented:
Discovering a brand new sort of star is fairly fascinating all by itself, however discovering it’s dark matter that’s powering this … that may be enormous.
Meet the darkish star candidates
The three candidate darkish stars are JADES-GS-z11-0, JADES-GS-z12-0 and JADES-GS-z13-0. Astronomers taking part within the James Webb House Telescope Superior Deep Extragalactic Survey (JADES) noticed them in December 2022. They thought, initially, these objects have been galaxies, or collections of odd stars, not in contrast to our personal Milky Way.
And so they have been very distant, inserting them within the extraordinarily early universe. The scientists’ assertion stated:
The JADES workforce confirmed the objects have been noticed at occasions starting from about 320 million to 400 million years after the Large Bang, making them a few of the earliest objects ever seen.
Freese stated:
After we take a look at the James Webb information, there are two competing prospects for these objects. One is that they’re galaxies containing tens of millions of odd, population-III stars.
The opposite is that they’re darkish stars. And imagine it or not, one darkish star has sufficient gentle to compete with a complete galaxy of stars.
Darkish stars could be enormous!
Darkish stars may theoretically develop to be a number of million occasions the mass of our sun, these scientists stated, and as much as 10 billion occasions as vivid because the sun. However do they exist?
Thus far, the concept for darkish stars existed solely in idea. The scientists’ assertion stated:
[It] originated in a collection of conversations between Freese and Doug Spolyar, on the time a graduate pupil on the College of California, Santa Cruz. They puzzled: What does dark matter do to the primary stars to kind within the universe?
Then they reached out to Paolo Gondolo, an astrophysicist on the College of Utah, who joined the workforce. After a number of years of improvement, they printed their first paper on this idea within the journal Bodily Assessment Letters in 2008.
And now, it appears, darkish stars would possibly in reality exist.
What’s dark matter?
The UT Austin scientists’ assertion stated:
Scientists imagine [dark matter] consists of a brand new sort of elementary particle. And the hunt to detect such particles is on. Among the many main candidates are Weakly Interacting Massive Particles. After they collide, these particles annihilate themselves, depositing warmth into collapsing clouds of hydrogen and changing them into brightly shining darkish stars.
The identification of supermassive darkish stars would open up the potential of studying in regards to the dark matter based mostly on their noticed properties.
The scientists plan follow-up observations with the Webb telescope.

Backside line: Scientists say they’ve discovered the first darkish stars – larger and brighter than our sun – powered by dark matter particles that collide and annihilate themselves.
Source: Supermassive Dark Star candidates seen by JWST




