Researchers observing with NASA’s James Webb Area Telescope have pinpointed silicate cloud options in a distant planet’s environment. The environment is continually rising, mixing, and transferring throughout its 22-hour day, bringing hotter materials up and pushing colder materials down.
The ensuing brightness adjustments are so dramatic that it’s the most variable planetary-mass object recognized so far. The staff, led by Brittany Miles of the College of Arizona, additionally made terribly clear detections of water, methane and carbon monoxide with Webb’s knowledge, and located proof of carbon dioxide. That is the biggest variety of molecules ever recognized suddenly on a planet exterior our solar system.
Cataloged as VHS 1256 b, the planet is about 40 light-years away and orbits not one, however two stars over a ten,000-year interval. “VHS 1256 b is about 4 instances farther from its stars than Pluto is from our sun, which makes it a terrific goal for Webb,” Miles mentioned. “Meaning the planet’s gentle is just not blended with gentle from its stars.”
Greater up in its environment, the place the silicate clouds are churning, temperatures attain a scorching 1,500 levels Fahrenheit (815 levels Celsius).
Inside these clouds, Webb detected each bigger and smaller silicate dust grains, that are proven on a spectrum. “The finer silicate grains in its environment could also be extra like tiny particles in smoke,” famous co-author Beth Biller of the College of Edinburgh in Scotland. “The bigger grains is perhaps extra like highly regarded, very small sand particles.”
VHS 1256 b has low gravity in comparison with extra huge brown dwarfs, which signifies that its silicate clouds can seem and stay larger in its environment the place Webb can detect them. Another excuse its skies are so turbulent is the planet’s age. In astronomical phrases, it is fairly younger. Solely 150 million years have handed because it fashioned—and it’ll proceed to vary and funky over billions of years.
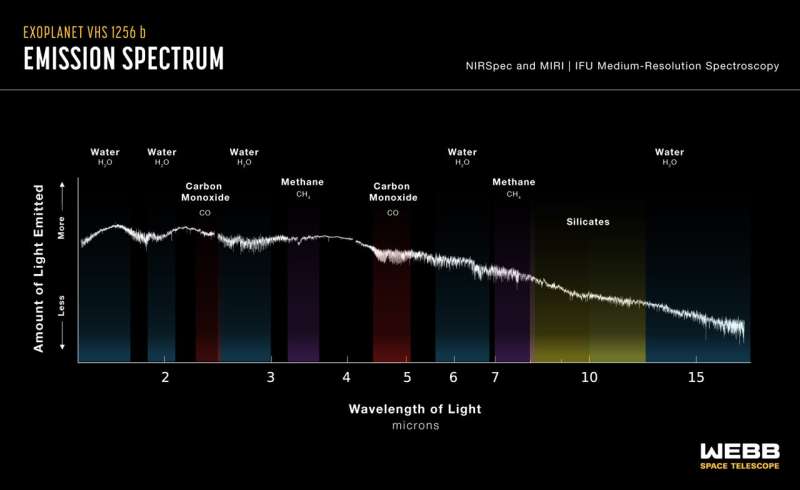
In some ways, the staff considers these findings to be the primary “cash” pulled out of a spectrum that researchers view as a treasure chest of knowledge. In some ways, they’ve solely begun figuring out its contents. “We have recognized silicates, however higher understanding which grain shapes and sizes match particular forms of clouds goes to take lots of further work,” Miles mentioned. “This isn’t the ultimate phrase on this planet—it’s the starting of a large-scale modeling effort to suit Webb’s advanced knowledge.”
Though all the options the staff noticed have been noticed on different planets elsewhere within the Milky Way by different telescopes, different analysis groups sometimes recognized solely one after the other. “No different telescope has recognized so many options without delay for a single goal,” mentioned co-author Andrew Skemer of the College of California, Santa Cruz. “We’re seeing lots of molecules in a single spectrum from Webb that element the planet’s dynamic cloud and climate programs.”
The staff got here to those conclusions by analyzing knowledge referred to as spectra gathered by two devices aboard Webb, the Close to-Infrared Spectrograph (NIRSpec) and the Mid-Infrared Instrument (MIRI). For the reason that planet orbits at such a terrific distance from its stars, the researchers have been in a position to observe it straight, relatively than utilizing the transit method or a coronagraph to take this knowledge.
There shall be lots extra to find out about VHS 1256 b within the months and years to come back as this staff—and others—proceed to sift via Webb’s high-resolution infrared knowledge. “There’s an enormous return on a really modest quantity of telescope time,” Biller added. “With just a few hours of observations, we now have what appears like endless potential for added discoveries.”
What may change into of this planet billions of years from now? Since it is so removed from its stars, it’s going to change into colder over time, and its skies could transition from cloudy to clear.
The researchers noticed VHS 1256 b as a part of Webb’s Early Launch Science program, which is designed to assist remodel the astronomical neighborhood’s capability to characterize planets and the disks the place they type.
The staff’s paper, entitled “The JWST Early Launch Science Program for Direct Observations of Exoplanetary Programs II: A 1 to twenty Micron Spectrum of the Planetary-Mass Companion VHS 1256-1257 b,” shall be revealed in The Astrophysical Journal Letters.
The work is at present revealed on the arXiv preprint server.
Extra data:
Brittany E. Miles et al, The JWST Early Launch Science Program for Direct Observations of Exoplanetary Programs II: A 1 to twenty Micron Spectrum of the Planetary-Mass Companion VHS 1256-1257 b, arXiv (2022). DOI: 10.48550/arxiv.2209.00620
Quotation:
James Webb spots swirling, gritty clouds on distant planet (2023, March 22)
retrieved 22 March 2023
from https://phys.org/information/2023-03-james-webb-swirling-gritty-clouds.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any honest dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for data functions solely.




