NASA’s James Webb House Telescope has many various observing modes to check planets orbiting different stars, referred to as exoplanets. A technique particularly is that Webb can instantly detect a few of these planets. Straight detecting planets round different stars is not any simple feat. Even the closest stars are nonetheless so far-off that their planets seem like separated by a fraction of the width of a human hair held at arm’s size. At these tiny angular scales, the planet’s faint mild is misplaced within the glare of its host star when making an attempt to watch it.
Fortuitously, Webb has the best instruments for the job: the Close to-Infrared Digicam (NIRCam) and Mid-Infrared Instrument (MIRI) coronagraphic modes. Webb’s coronagraphs block the sunshine from a distant star, whereas permitting the faint planet mild by to succeed in its sensors. This isn’t in contrast to how we use our automobile’s visor throughout sundown or dawn to see the automobiles in entrance of us, albeit Webb makes use of a a lot fancier “visor.” Associated analysis on MIRI is printed in Astronomy & Astrophysics.

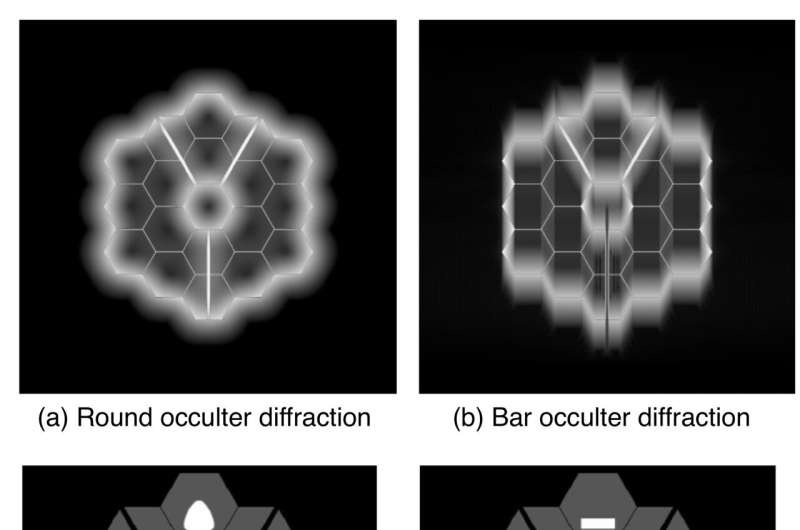
Alongside the trail mild takes by Webb’s optics, there are a number of necessary areas known as “planes.” The “picture airplane” is the place the distant sky is in focus, together with all astrophysical objects. The “pupil airplane” permits the floor of the first mirror to be in focus, which was used to make Webb’s “selfie.” All of Webb’s coronagraphs bodily masks out undesirable starlight in each the picture and pupil planes to optimize efficiency. Most of Webb’s picture airplane masks, resembling opaque spots or bars, take away starlight just by blocking it within the picture. The exception to this are MIRI’s “four-quadrant phase masks,” which shift the wave-tops of 1 a part of the wave of sunshine, so it cancels out with one other half by a course of known as “harmful interference.”
Nevertheless, because of the wave nature of sunshine, the picture airplane masks cannot utterly block the star. So Webb makes use of extra pupil airplane masks, additionally known as Lyot stops, to take away a lot of the remaining starlight. These pupil airplane masks look very totally different from the hexagonal main mirror (the telescope “pupil”). In consequence, objects imaged with the coronagraphs don’t exhibit Webb’s hallmark six-spiked diffraction sample, as proven within the observations above.
Webb’s NIRCam instrument has 5 coronagraphic masks, every of which may every be configured to watch at totally different wavelengths starting from 1.7 to five microns. Webb’s MIRI instrument has 4 coronagraphic masks that function at fastened wavelengths between 10 and 23 microns. The coronagraphs can observe objects as shut as 0.13 arcseconds from the star, and as distant as about 30 arcseconds from the star, which roughly interprets to circumstellar distances starting from a couple of Astronomical Items (au) to a whole lot of au round close by stars. One AU is equal to the space between the Earth and the sun.
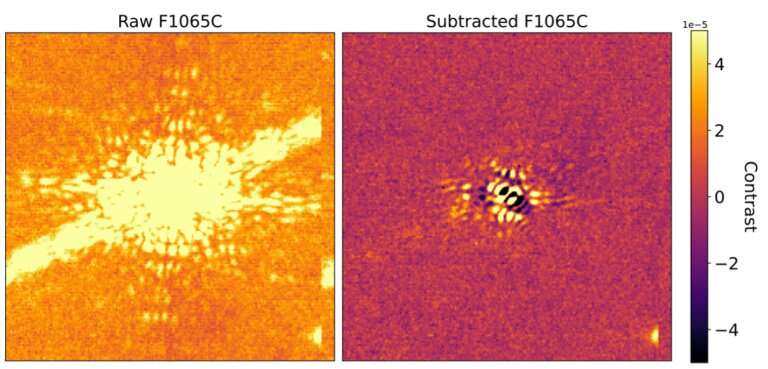
Regardless of the masks, Webb’s coronagraphs do not completely take away a star’s mild. To take away the final remnants of sunshine, Webb’s astronomers will fastidiously use a wide range of “level unfold operate (PSF) subtraction strategies.” Merely put, this implies measuring the sample of the residual starlight, after which subtracting it from the science picture. In the long run, what stays is a noisy-looking sample, which in the end limits the faintest detectable exoplanet. This restrict is expressed when it comes to “distinction,” the ratio in brightness between the faintest detectable planet and the star. Throughout commissioning, Webb’s NIRCam and MIRI coronagraphs demonstrated contrasts higher than 10-5 and 10-4 at 1 arcsecond separation, respectively.
Webb’s giant main mirror and infrared capabilities imply that its coronagraphs are uniquely suited to check faint objects within the infrared and can complement different devices at the moment observing at different wavelengths, together with Hubble’s STIS coronagraph and a number of devices on ground-based observatories. Exoplanet astronomers will primarily use Webb’s coronagraphs to detect big extrasolar planets which are nonetheless heat from being fashioned, like these proven above, that are the primary photographs of an exoplanet at wavelengths longer than 5 microns.
Webb may also excel at imaging dense circumstellar disks of particles generated by the asteroids and comets in these exoplanetary programs, in addition to protoplanetary disks through which planets are nonetheless forming. Webb’s coronagraphs may even be used for extragalactic astronomy, to check host galaxies that comprise vibrant lively galactic nuclei.
Webb’s coronagraphs will not be capable of reveal all of the secrets and techniques of a planetary system. To picture planets like our personal round close by sun-like stars, we’ll want to watch even nearer to the star and be capable of detect planets only one ten billionth the brightness of the star. It will require a future mission absolutely optimized round next-generation coronagraphs.
Fortuitously, NASA is already trying into it. The company’s upcoming Nancy Grace Roman House Telescope will carry a expertise demonstration instrument to check next-generation coronagraph expertise. And, following the suggestions of the 2020 Astrophysics Decadal Survey, NASA is laying the groundwork for additional expertise improvement for a Liveable Worlds Observatory mission idea, a telescope that will be as giant as Webb, working in the identical wavelengths as Hubble, however designed to seek out really Earth-like exoplanets round different stars and search them for indicators of life.
Extra data:
A. Boccaletti et al, JWST/MIRI coronagraphic performances as measured on-sky, Astronomy & Astrophysics (2022). DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361/202244578
Quotation:
How Webb’s coronagraphs reveal exoplanets within the infrared (2023, March 27)
retrieved 27 March 2023
from https://phys.org/information/2023-03-webb-coronagraphs-reveal-exoplanets-infrared.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any honest dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for data functions solely.




