A world analysis workforce led by Professor Lengthy Xiao from the Faculty of Earth Sciences of China College of Geosciences (Wuhan) has found the presence of marine sedimentary rocks on the floor of Mars for the primary time by comprehensively analyzing the scientific knowledge obtained by the multispectral digicam (MSCam) carried by the Zhurong rover. The related analysis outcomes have been printed within the journal Nationwide Science Evaluate below the title “Proof for Marine Sedimentary Rocks in Utopia Planitia: Zhurong Rover Observations.”
At present Mars is chilly and dry, missing water and traces of life, however the Martian surroundings billions of years in the past might have been very completely different. Previous research have confirmed that there was a considerable amount of liquid water on Mars within the early days, and the paleo-ocean speculation was proposed by means of landform evaluation of satellite photos and numerical simulation.
It has been proposed that the paleo-ocean space within the northern lowlands fashioned a particular marine sedimentary geological unit, referred to as the Vasitas Borealis Formation (VBF), however this proposition has lacked the help of in-situ knowledge. Due to this fact, whether or not there was an ocean within the northern plain of Mars has been the main focus of controversy for many years.
In 2021, the Zhurong rover carried by China’s Tianwen-1 Mars mission efficiently landed on the southern fringe of the Utopia Plain within the jap a part of the northern plain of Mars. A part of the mission was to seek for any attainable proof for or towards the existence of an historical ocean, which can have hosted adolescence on Mars.
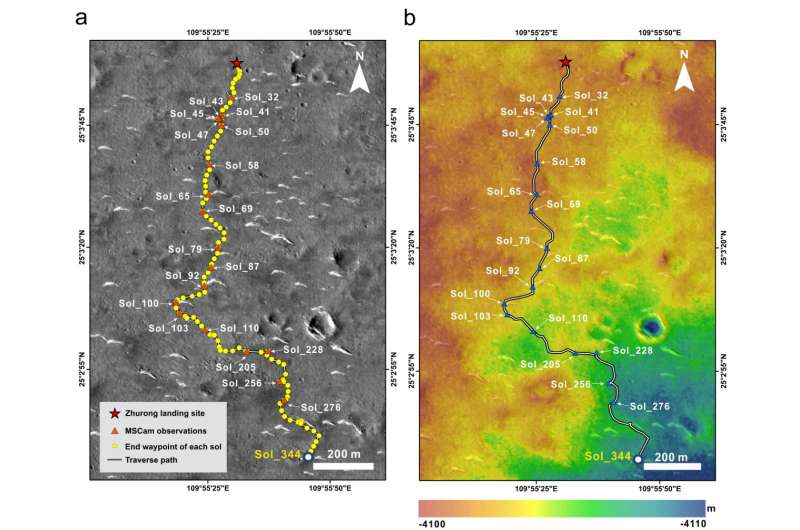
After touchdown, the Zhurong rover headed south in direction of potential shoreline areas, observing the uncovered Vasitas Borealis Formation alongside the way in which. Zhurong traveled about 1,921 meters, and used completely different imaging and evaluation methods to conduct detailed in-situ observations of outcrops and floor rocks. The navigation and terrain cameras obtained 106 units of panoramic photos, which recorded intimately the floor morphology and structural traits of many rocks close to the route of the Zhurong rover.
The analysis workforce examined the pictures despatched again by the rover’s on-board digicam and located that the uncovered rocks featured bedding buildings, that are considerably completely different from the frequent volcanic rocks on the floor of Mars, and in addition completely different from the bedding buildings fashioned by aeolian sand deposition. The buildings indicated bidirectional movement traits per low-energy tidal currents in Earth’s littoral-shallow marine surroundings.
Based mostly on the rock photos obtained by MSCam, the analysis workforce analyzed intimately the floor construction of the rocks within the inspection space of the Zhurong rover. For the reason that noticed rocks are all positioned within the Zhurong inspection space, the analysis workforce named the geological unit it represents the Zhurong Member. Through the research, the analysis workforce discovered that the rocks within the part sometimes retained native lens-shaped cross-bedding materials, primarily composed of quite a lot of small-scale cross-bedding, accompanied by a small quantity of lens-shaped flaser bedding and sedimentary buildings of small channel buildings.
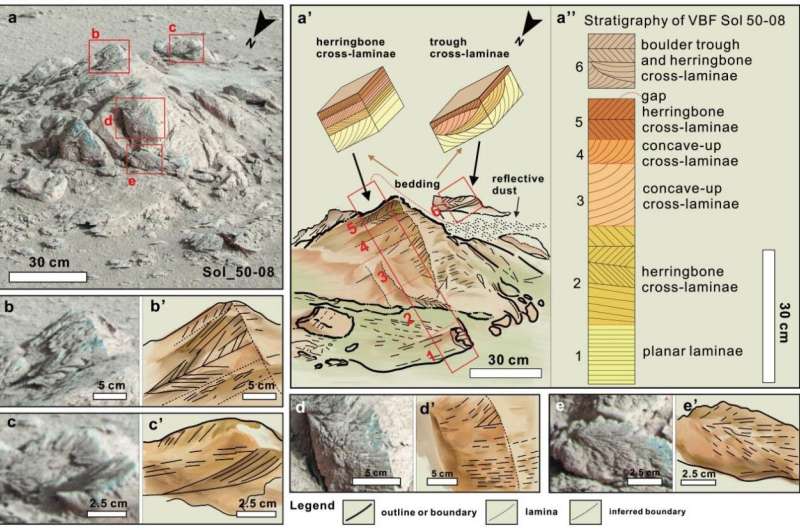
Amongst them, the layers that make up the cross-bedding overlap and tilt in two reverse instructions, indicating a bidirectional paleocurrent surroundings. As well as, for the reason that thickness and grain dimension of the strata are largely completely different in several instructions, it signifies that there are variations within the depth of paleocurrents within the two instructions.
This bidirectional water movement sample is normally fashioned by the fluid motion with periodic movement course adjustments, which isn’t frequent in eolian and fluvial environments, however is frequent within the littoral-shallow sea surroundings of Earth. In contrast with Earth, Mars has solely two small satellites, which makes its floor have a low-energy tidal system, and solely small-scale bedding buildings could be fashioned on this tidal surroundings.
As well as, the bedforms and sedimentary buildings recognized within the research embody proof supporting aqueous movement slightly than eolian deposition.
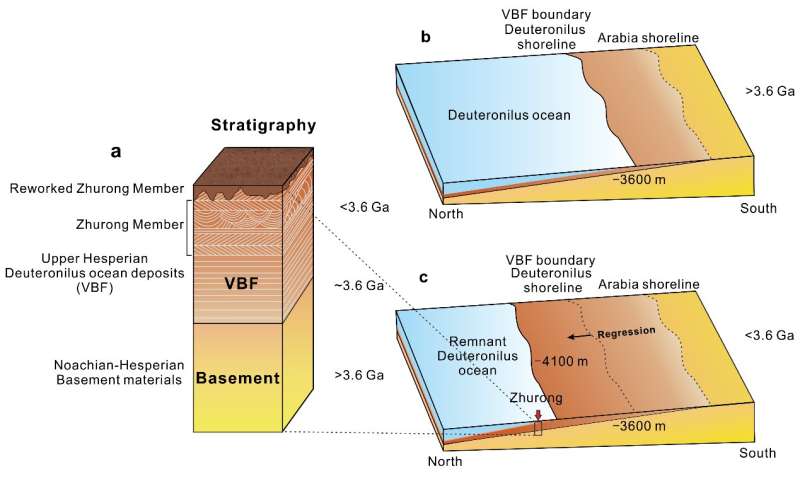
The workforce’s observational outcomes of the Zhurong Member rocks on this research are the primary direct in-situ proof detected to help the existence of historical oceans within the northern plains of Mars. The situation of the touchdown website of Zhurong signifies that the noticed sedimentary buildings might have fashioned throughout the regression of the northern plain paleo-ocean.
The sedimentary structures discovered within the Vasitas Borealis Formation present new insights into the early historical past of Mars. The in-depth exploration by Zhurong on this space and future pattern return will deepen our understanding of the habitability of Mars and the preservation of microbial life traces.
Extra info:
Lengthy Xiao et al, Proof for marine sedimentary rocks in Utopia Planitia: zhurong rover observations, Nationwide Science Evaluate (2023). DOI: 10.1093/nsr/nwad137
Supplied by
Science China Press
Quotation:
In-situ observations of marine sedimentary rocks counsel historical northern ocean on Mars (2023, Could 22)
retrieved 22 Could 2023
from https://phys.org/information/2023-05-in-situ-marine-sedimentary-ancient-northern.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any honest dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for info functions solely.




