What’s a secure distance from a supernova?
A supernova is a spectacular explosion of an enormous star. If our sun exploded as a supernova, the ensuing shock wave in all probability wouldn’t incinerate your entire Earth, however the facet of Earth dealing with the sun would boil away. Scientists estimate that the planet as an entire would improve in temperature to roughly 15 instances hotter than our sun’s regular floor temperature.
What’s extra, Earth wouldn’t keep put in orbit. The sudden lower within the sun’s mass may free the planet to wander off into space. Clearly, the sun’s distance – 8 light-minutes away – isn’t secure if it have been to blow up in a supernova. Luckily, our sun isn’t the form of star destined to blow up as a supernova. However different stars, past our solar system, will.
What’s the closest secure distance? In response to a recent study based mostly on knowledge from the Chandra X-Ray Observatory , a supernova must be inside 160 light-years of Earth earlier than we might really feel its damaging results. Previously, it was believed a supernova must be inside 50 light-years of Earth to impression our planet. One other research discovered proof a supernova within 300 light-years reached Earth hundreds of thousands of years in the past, but it surely wouldn’t trigger an extinction occasion. So, the reply varies and the analysis continues.
What would occur if a supernova exploded close to Earth?
Let’s contemplate the explosion of a star that’s at an unsafe distance to Earth. Say, the supernova is 30 light-years away. Mark Reid, a senior astronomer on the Harvard-Smithsonian Heart for Astrophysics, said:
… have been a supernova to go off inside about 30 light-years of us, that might result in main results on the Earth, possibly mass extinctions. X-rays and extra energetic gamma rays from the supernova could destroy the ozone layer that protects us from solar ultraviolet rays. It additionally may ionize nitrogen and oxygen within the environment, resulting in the formation of enormous quantities of smog-like nitrous oxide.
What’s extra, if a supernova exploded inside 30 light-years, phytoplankton and reef communities would be particularly affected. Such an occasion would severely deplete the bottom of the ocean meals chain.
Suppose the explosion have been barely extra distant. An explosion of a close-by star may go away Earth and its floor and ocean life comparatively intact. However any comparatively close by explosion would nonetheless bathe us with gamma rays and different high-energy radiation. This radiation may trigger mutations in earthly life. Additionally, the radiation from a close-by supernova may change our local weather.
Luckily, there aren’t any stars inside 30 light-years of Earth poised to go supernova.
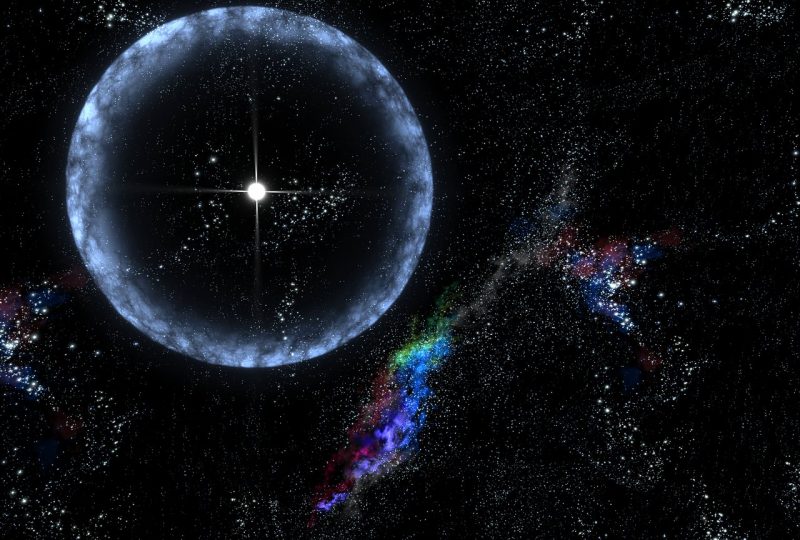

Shut supernovas within the not-so-distant previous
No supernova has been recognized to erupt inside 100’s of light-years within the recognized historical past of humankind. The newest supernova seen to the attention was Supernova 1987A, within the 12 months 1987. It was roughly 168,000 light-years away.
Earlier than that, the final supernova seen to the attention was was documented by Johannes Kepler in 1604. At about 20,000 light-years, it shone extra brightly than any star within the night time sky. It was even seen in daylight! However it didn’t trigger earthly results, so far as we all know.
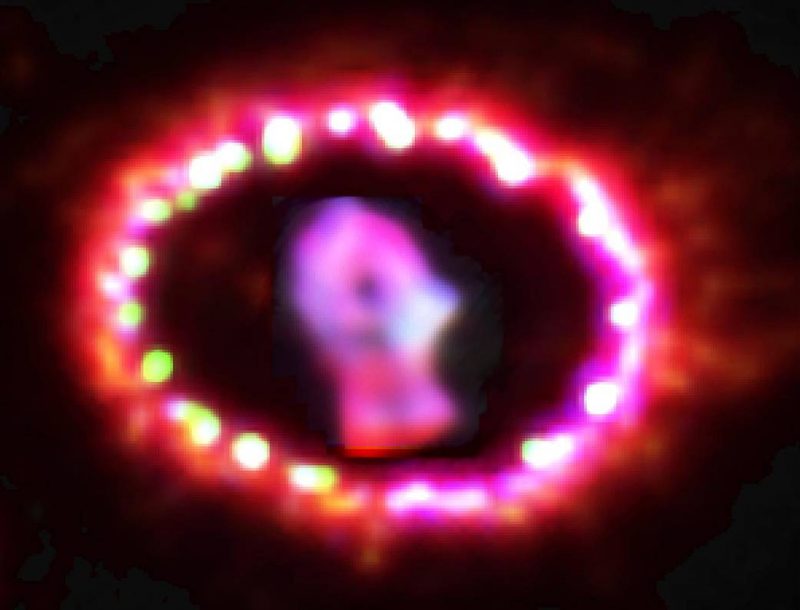
A brand new, shut supernova in M101
A brand new supernova within the Pinwheel Galaxy, aka M101, is the closest to Earth in a decade. Nonetheless, at 21 million light-years, it gained’t impression us on Earth. Novice astronomer Koichi Itagaki found it on Might 19, 2023. The supernova brightened for a number of days. It ought to stay seen to newbie astronomers with yard telescopes for a number of months. The supernova – named 2023ixf – lies within the route of the constellation Ursa Major, close to the tip of the deal with of the Big Dipper.
How distant are the closest supernova candidates?
First, there are two completely different sorts of supernovas. A Type II supernova is an growing older large star that collapses. There aren’t any stars large sufficient to do that situated inside 160 light-years of Earth. A Sort I supernova occurs when a small, faint white dwarf star collapses as a result of infalling materials of a companion. These stars are dim and arduous to search out, so we are able to’t be certain simply what number of are round. There are in all probability a number of hundred of those stars inside 160 light-years, however we don’t know of any able to explode.
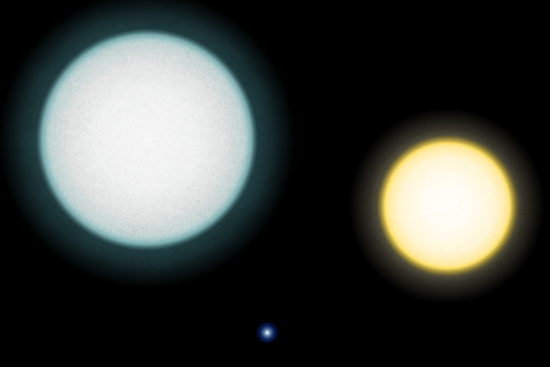
The star IK Pegasi B is the closest recognized supernova progenitor candidate. It’s a part of a binary star system, situated about 150 light-years from our sun and solar system.
The principle star within the system – IK Pegasi A – is an atypical main sequence star, not in contrast to our sun. The potential Sort I supernova is the opposite star – IK Pegasi B – an enormous white dwarf that’s extraordinarily small and dense, orbiting nearer to IK Pegasi A than Mercury is to our sun. When the A star begins to evolve right into a crimson large, it’s anticipated to develop to a radius the place the white dwarf can accrete, or tackle, matter from A’s expanded gaseous envelope. When the B star will get large sufficient, it would collapse on itself, within the course of exploding as a supernova.
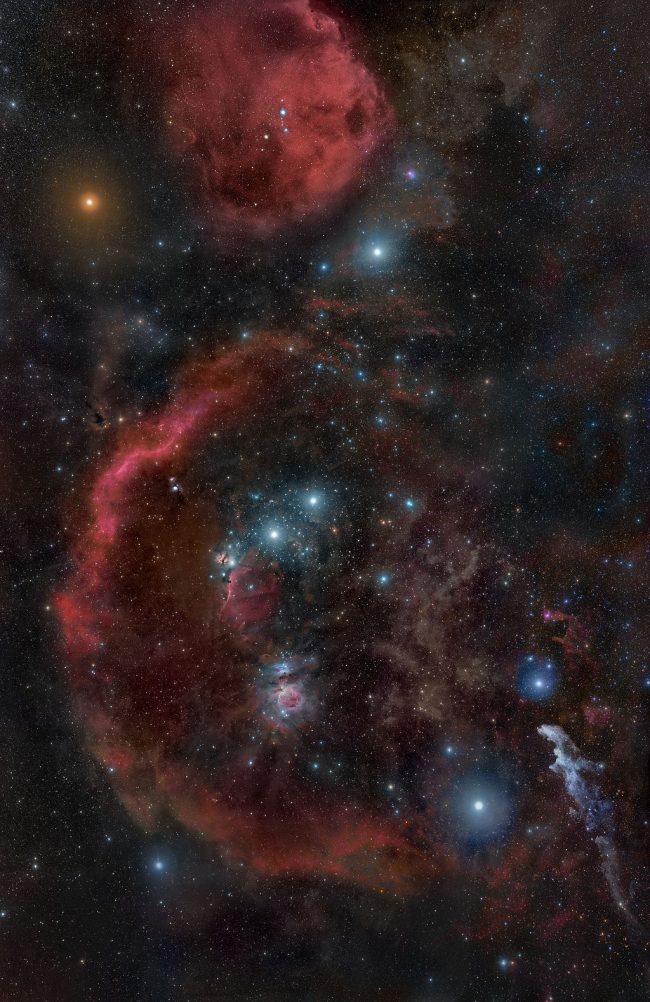
What about Betelgeuse?
One star that comes up every time the topic turns to supernovas is Betelgeuse, one of many brightest stars in our sky, a part of the well-known constellation Orion. Betelgeuse is a supergiant star. It’s intrinsically very sensible.
Such brilliance comes at a value, nonetheless. Betelgeuse is likely one of the most well-known stars within the sky as a result of it’s as a result of explode sometime. Betelgeuse’s monumental power requires that the gasoline be expended rapidly (comparatively, that’s), and actually, Betelgeuse is now close to the tip of its lifetime. Sometime quickly (astronomically talking), it’s going to run out of gasoline, collapse below its personal weight, after which rebound in a spectacular Sort II supernova explosion. When this occurs, Betelgeuse will brighten enormously for a number of weeks or months, maybe as brilliant because the full moon and visual in broad daylight.
When will it occur? Most likely not in our lifetimes, however nobody actually is aware of. It may very well be tomorrow or one million years sooner or later. When it does occur, any beings on Earth will witness a spectacular occasion within the night time sky, however earthly life gained’t be harmed. That’s as a result of Betelgeuse is 430 light-years away.

How typically do supernovas erupt in our galaxy?
Nobody is aware of. Scientists have speculated that the high-energy radiation from supernovas has already induced mutations in earthly species, possibly even human beings.
One estimate suggests there may be one harmful supernova occasion in Earth’s neighborhood each 15 million years. One other says that, on common, a supernova explosion happens inside 10 parsecs (33 light-years) of Earth each 240 million years. So that you see we actually don’t know. However you may distinction these numbers to the few million years people have existed on the planet and 4 1/2 billion years for the age of Earth itself.
And, in case you do this, you’ll see {that a} supernova is definite to happen close to Earth … however in all probability not within the foreseeable way forward for humanity.
Backside line: What’s a secure distance from a supernova? To outlive a supernova, latest knowledge signifies Earth must be at the very least 160 light-years away from the exploding star.
Read more: Supernova X-rays zap planets’ atmospheres, 160 light-years away




