Astronauts’ brains want a break after lengthy missions
On June 8, 2023, scientists on the College of Florida announced outcomes of a brand new examine that mentioned astronauts have to take a three-year break after lengthy spaceflights to permit their brains time to recuperate.
The researchers learn mind scans of 30 astronauts. They studied earlier than and after spaceflight scans of those that had been in space for simply two weeks to those that had been in space greater than six months. What they discovered was that astronauts who had been in space longer than 6 months confirmed important enlargement of the mind’s ventricles. And, these astronauts with mind modifications wanted at the least three years again on Earth for the ventricles to totally recuperate.
The scientists published their findings on June 8, 2023, within the peer-reviewed journal Scientific Studies.
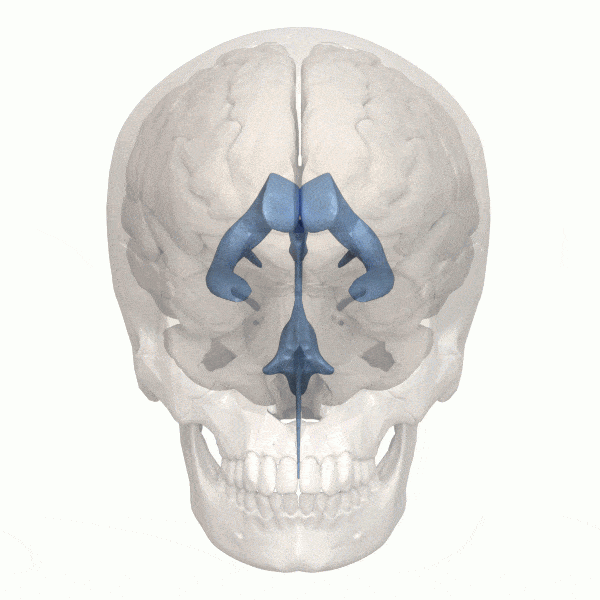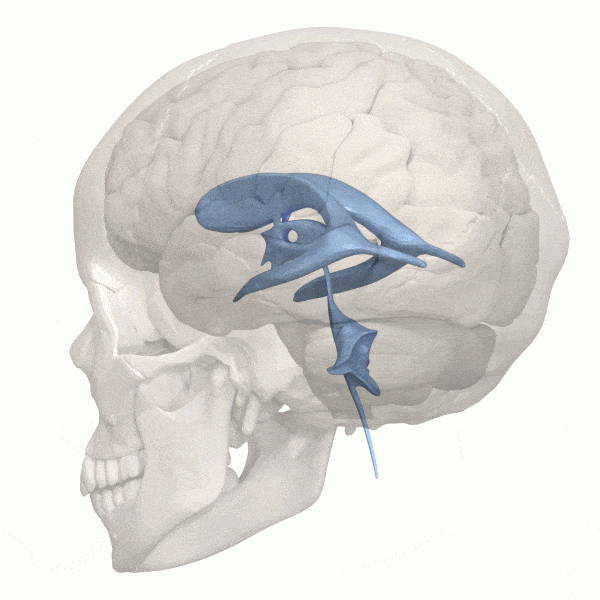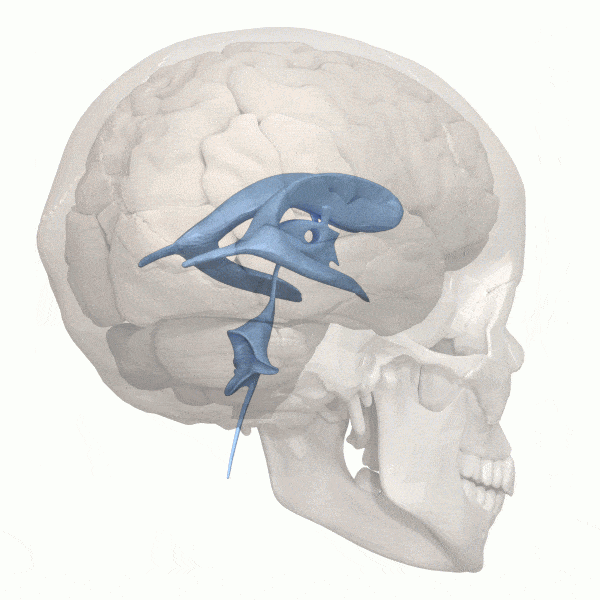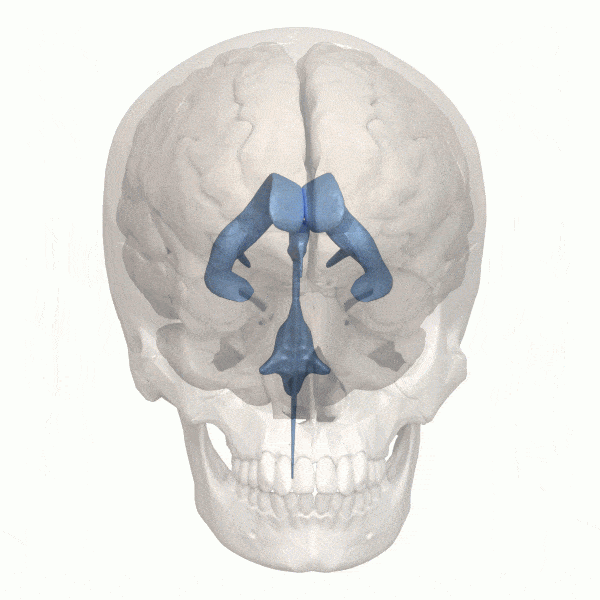
What are the mind’s ventricles?
The ventricular system within the human mind accommodates 4 giant open cavities deep inside your mind – ventricles – that maintain cerebrospinal fluid. This cerebrospinal fluid cushions the mind, offering safety. The ventricles additionally perform as a system that gives nourishment and waste removing from the mind.
When an astronaut is in a zero-gravity setting for an prolonged time frame, the fluid of their our bodies isn’t naturally pulled down towards the bottom. Due to this fact, fluid can shift upward into the mind. This pushes the mind increased throughout the cranium, inflicting the ventricles to enlarge.
Rachael Seidler, an writer of the examine from the College of Florida, mentioned:
We discovered that the extra time individuals spent in space, the bigger their ventricles grew to become. Many astronauts journey to space multiple time, and our examine reveals it takes about three years between flights for the ventricles to totally recuperate.
The researchers discovered that the enlargement of the mind’s ventricles was the longest-lived impact on the mind from spaceflight. Nonetheless, they’re unsure but how this mind change impacts astronauts. Seidler mentioned:
We don’t but know for positive what the long-term penalties of that is on the well being and behavioral well being of space vacationers, so permitting the mind time to recuperate looks like a good suggestion.
Finding out astronauts’ brains
Right here’s how the 30 astronauts the researchers studied broke down by way of mission size:
- 8 astronauts had been on two-week missions
- 18 had been on six-month missions
- 4 had been in space for about one yr
Total, the examine supplied excellent news for individuals who lengthy to both go to space or finally reside there. A two-week journey to space didn’t have an effect on mind ventricles. So in case you had been hoping to take a fast journey into space from the quickly rising trade of space tourism, your ventricles ought to be wonderful. As well as, these planning to go to Mars or take longer missions shouldn’t have to fret about ever-growing ventricles. The researchers discovered that for astronauts in space greater than six months, the ventricular enlargement impact tapered off. Seidler defined:
The most important leap comes if you go from two weeks to 6 months in space. There isn’t any measurable change within the ventricles’ quantity after solely two weeks.
We had been completely happy to see that the modifications don’t improve exponentially, contemplating we are going to finally have individuals in space for longer intervals.
Backside line: A brand new examine discovered that astronaut’s brains want a three-year break after lengthy missions. Missions of as much as six months broaden the ventricles in astronauts’ brains, a system that protects, nourishes and exports waste.
Source: Impacts of spaceflight experience on human brain structure




