The climactic finish of a seven-year voyage comes Sunday when a NASA capsule is because of land within the Utah desert, carrying to Earth the biggest asteroid samples ever collected.
Scientists have excessive hopes for the pattern, saying it can present a greater understanding of the formation of our solar system and the way Earth grew to become liveable.
The Osiris-Rex probe’s remaining, fiery descent by means of Earth’s environment might be perilous, however the US space company is hoping for a soft landing, round 9:00am native (15H00 GMT), in a navy check vary in northwestern Utah.
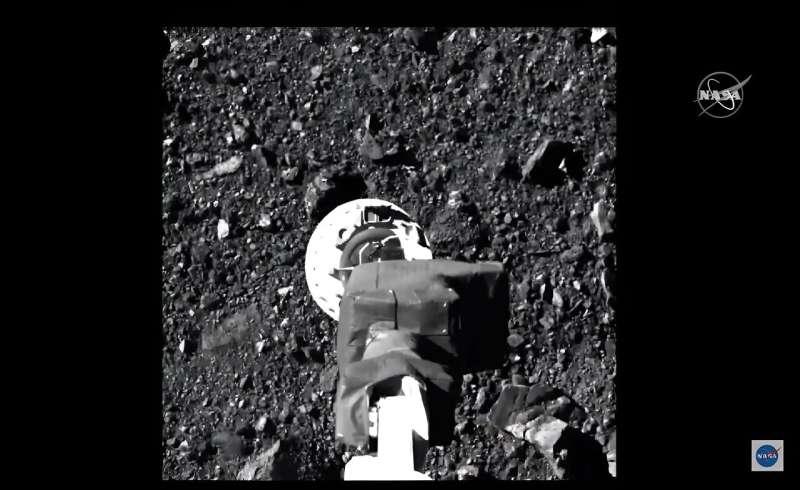
4 years after its 2016 launch, the probe landed on the asteroid Bennu and picked up roughly 9 ounces (250 grams) of dust from its rocky floor.
Even that small quantity, NASA says, ought to “assist us higher perceive the sorts of asteroids that would threaten Earth” and solid gentle “on the earliest historical past of our solar system,” NASA Administrator Invoice Nelson stated.
“This pattern return is actually historic,” NASA scientist Amy Simon informed AFP. “That is going to be the largest pattern we have introduced again because the Apollo moon rocks” had been returned to Earth.
However the capsule’s return would require “a harmful maneuver,” she acknowledged.
Osiris-Rex is ready to launch the capsule—from an altitude of greater than 67,000 miles (108,000 kilometers)—some 4 hours earlier than it lands.
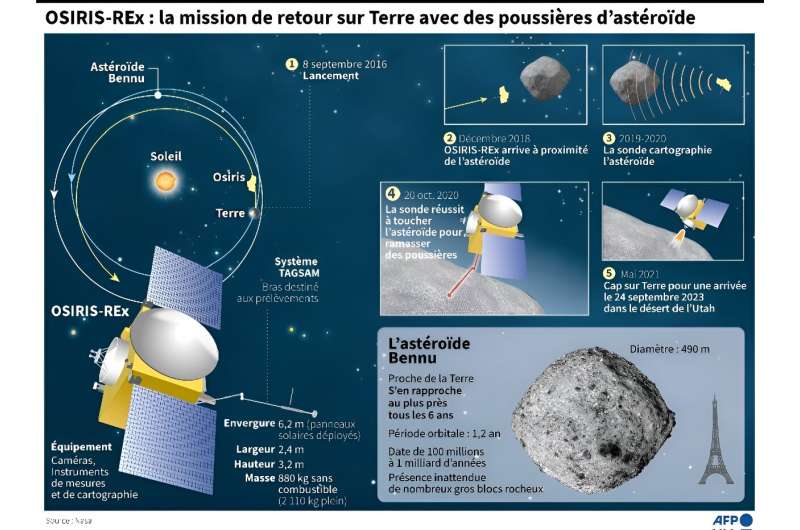
The fiery passage by means of the environment will come solely within the final 13 minutes, because the capsule hurtles downward at a velocity of greater than 27,000 miles per hour, with temperatures of as much as 5,000 Fahrenheit (2,760 Celsius).
Its fast descent, monitored by military sensors, might be slowed by two successive parachutes. Ought to they fail to deploy accurately, a “onerous touchdown” would observe.
If it seems that the goal zone (37 by 9 miles) may be missed, NASA controllers may determine on the final second to not launch the capsule.
The probe would then maintain its cargo and make one other orbit of the sun. Scientists must wait till 2025 earlier than attempting a brand new touchdown.
If it succeeds, nevertheless, Osiris-Rex would head towards a date with one other asteroid.
Japanese samples
As soon as the tire-sized capsule touches down in Utah, a workforce in protecting masks and gloves will place it in a web to be airlifted by helicopter to a brief “clear room” close by.
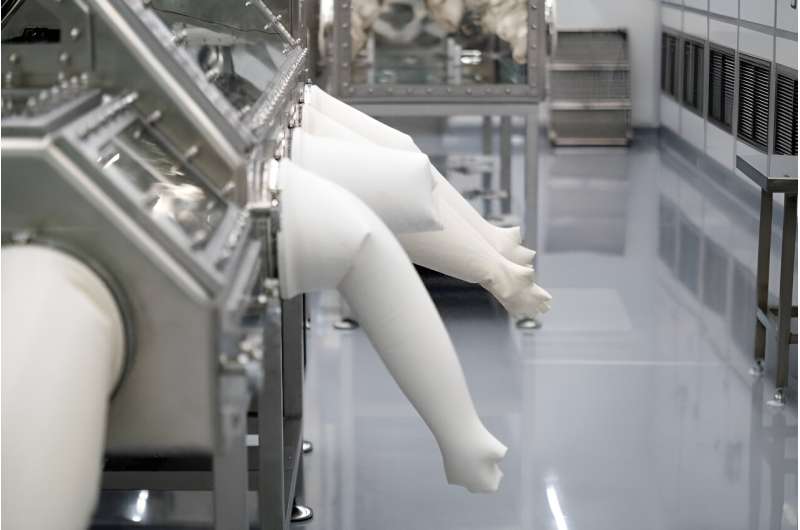

NASA needs this accomplished as rapidly and thoroughly as attainable to keep away from any contamination of the pattern with desert sands, skewing check outcomes.
On Monday, assuming all goes properly, the pattern might be flown by aircraft to NASA’s Johnson House Heart in Houston, Texas. There, the field might be opened in one other “clear room”—the start of a days-long course of.
NASA plans to announce its first outcomes at a information convention October 11.
Many of the pattern might be conserved for research by future generations. Roughly one-fourth of it will likely be instantly utilized in experiments, and a small quantity might be despatched to Japan and Canada, companions within the mission.
Japan had earlier given NASA a couple of grains from the asteroid Ryugu, after bringing 0.2 ounce of dust to Earth in 2020 through the Hayabusa-2 mission. Ten years earlier than, it had introduced again a microscopic amount from one other asteroid.
However the pattern from Bennu is far bigger, permitting for considerably extra testing, Simon stated.

Earth’s origin story
Asteroids are composed of the unique supplies of the solar system, relationship to some 4.5 billion years in the past, and have remained comparatively intact.
They “can provide us clues about how the solar system shaped and developed,” stated Osiris-Rex program government Melissa Morris.
“It is our personal origin story.”
By putting Earth’s floor, “we do imagine asteroids and comets delivered organic material, probably water, that helped life flourish right here on Earth,” Simon stated.
Scientists imagine Bennu, which is 1,640 toes in diameter, is wealthy in carbon—a constructing block of life on Earth—and accommodates water molecules locked in minerals.
Bennu had shocked scientists in 2020 when the probe, through the few seconds of contact with the asteroid’s floor, had sunk into the soil, revealing an unexpectedly low density, kind of like a kids’s pool full of plastic balls.
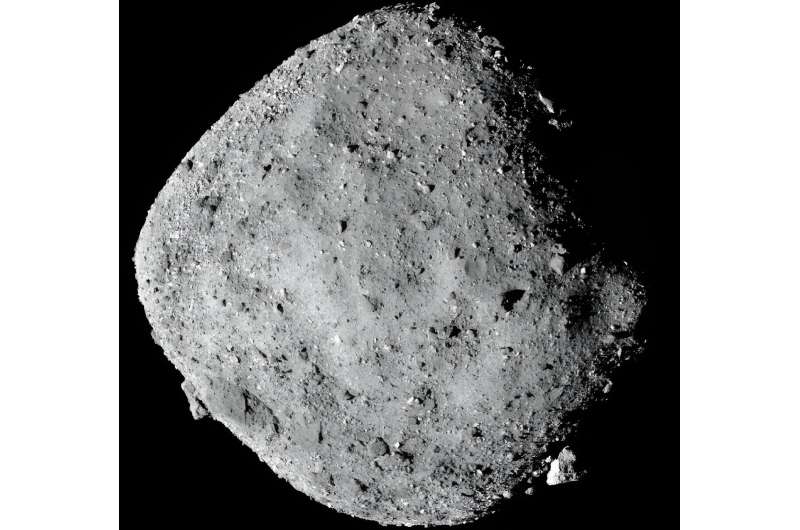

Understanding its composition may come in useful within the—distant—future.
For there’s a slight, however non-zero, likelihood (one in 2,700) that Bennu may collide catastrophically with Earth, although not till 2182.
However NASA final 12 months succeeded in deviating the course of an asteroid by crashing a probe into it in a check, and it’d in some unspecified time in the future must repeat that train—however with a lot larger stakes.
© 2023 AFP
Quotation:
NASA readies for dramatic return of asteroid pattern to Earth (2023, September 24)
retrieved 24 September 2023
from https://phys.org/information/2023-09-nasa-readies-asteroid-sample-earth.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any truthful dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for info functions solely.




