Mars is among the most explored elements of the solar system, but there are all the time extra discoveries to unveil on Earth’s planetary neighbor. On Earth we’re capable of take direct measurements to know our planet’s meteorological actions, however on Mars scientists should use proof within the panorama to discern this data as an alternative.
One such characteristic of the pink planet’s landscape are barchan dunes in deserts, crescent-shaped sand dunes fashioned by wind patterns predominantly in a single route in areas with a restricted provide of sand. Such aeolian-derived dunes are considerably impacted by the atmospheric circulation on the planet’s floor, with new research printed in Geophysical Analysis Letters discovering that localized topography at scales <100km (comparable to deep impression craters from rocky or icy meteorites) can deflect winds and trigger modifications in barchan dune formation.
Dr. Lior Rubanenko, Assistant Professor on the Technion—Israel Institute of Expertise, and colleagues used machine studying to characterize Mars’ wind patterns based mostly upon the morphology of greater than 700,000 barchan dunes. This information was obtained from photographs taken by a specialised digicam on the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter, a spacecraft that has been orbiting the planet since 2006 to gather data on its geology and local weather.
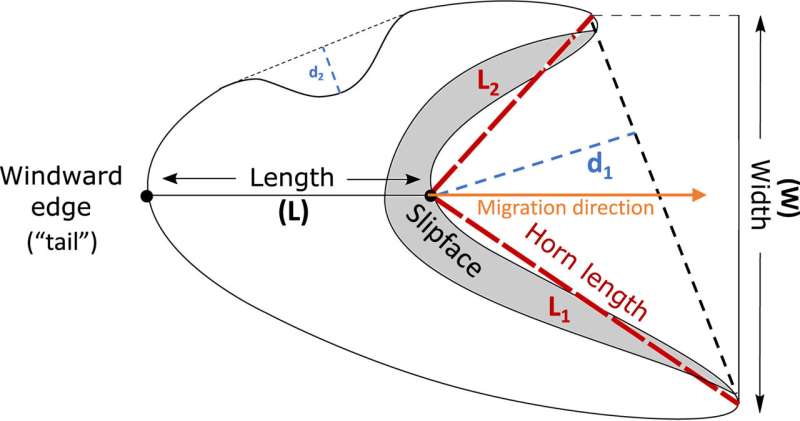
The machine studying element was skilled to stipulate the form of dunes robotically to map dune fields. From these photographs the scientists recognized the orientation of the steep facet (slipface) of the dunes and their ideas (known as horns) protruding from edges. The place the horns are asymmetrical with one being longer than the opposite, this means the interplay of a number of wind instructions.
The analysis crew discovered a definite sample arising in dune migration ensuing from summer season atmospheric circulation patterns, these being northwards directed at mid-latitudes and cyclonic (counterclockwise motion a couple of heart of low strain) close to the north pole. The latter can also be damaged right into a smaller element experiencing the alternative anticyclonic wind route, which the authors particularly attribute to the consequences of winds shifting throughout the polar ice cap.
At latitudes above 45°N, Dr. Rubanenko and colleagues found dune migration patterns are dominantly easterly, matching the cyclonic polar vortex circulation, whereas at latitudes under this all the way down to -45°N they’re southerly-directed. Native wind regimes most keenly have an effect on areas the place topographic options are 10–50km in measurement horizontally, however has little impression when landmarks exceed 100km-scales, these as an alternative being impacted by the bigger planetary wind techniques.
One limitation of the machine studying venture nonetheless is that it doesn’t absolutely take into account the complexities of fixing wind regimes between day and evening and throughout seasons, however as an alternative focuses on longer-term patterns. It additionally struggles in areas with important topographic modifications, such because the bigger impression craters of Valles Marineris, Hellas and Argyre, the place dunes are dispersed throughout a bigger space.
These craters act as sand traps, supplying ample materials for the formation of dune fields, which kind nearer to the middle of the crater basin the deeper they’re. Migration inside craters could possibly be attributable to stronger winds blowing down the slopes.

Whereas extra refinement of the machine studying know-how is required, preliminary analysis right here does monitor with actual information when examined and matches floor proof for the route of wind-blown dust and sand throughout dust storms.
As on Earth, planetary-scale circulation patterns present a common development shifting from the poles to the equator of Mars with disruption within the mid-latitudes. Understanding the atmospheric circulation patterns on Mars is vital for supporting manned missions to the planet and the prospect of future habitability.
Extra data:
L. Rubanenko et al, World Floor Winds and Aeolian Sediment Pathways on Mars From the Morphology of Barchan Dunes, Geophysical Analysis Letters (2023). DOI: 10.1029/2022GL102610
© 2023 Science X Community
Quotation:
Sand dunes reveal atmospheric wind patterns on Mars (2023, September 25)
retrieved 25 September 2023
from https://phys.org/information/2023-09-sand-dunes-reveal-atmospheric-patterns.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any honest dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for data functions solely.




