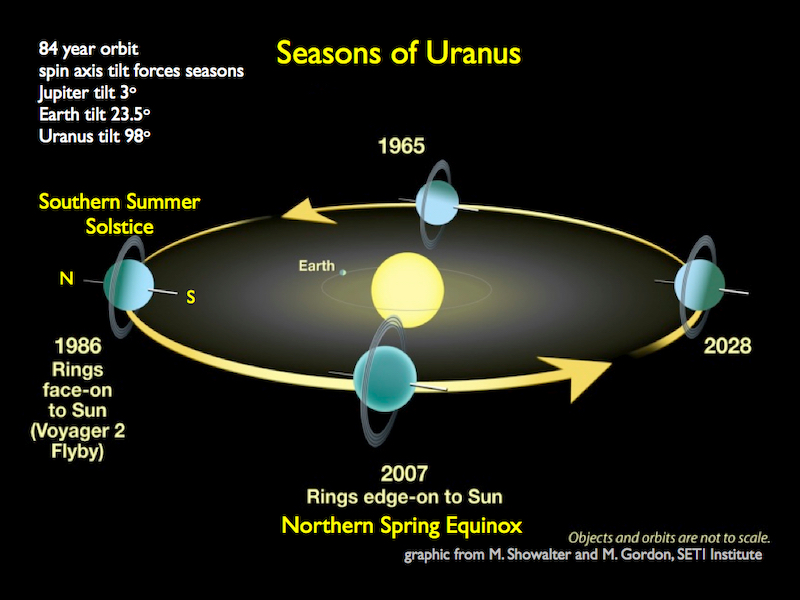
Unusual seasons of Uranus
Uranus has weird seasons, no less than from our earthly perspective. As we discover distant exoplanets – or take into consideration moons or rocky asteroids on this solar system – who is aware of what vary of variations we’ll discover? However for the second we do know this. Uranus has uncommon seasons, in distinction to Earth and the opposite main identified planets. It’s as a result of Uranus’ spin axis lies practically sideways with respect to the airplane of its orbit across the sun. In comparison with Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn and Neptune – all of which spin elegantly, practically upright, as they orbit our native star – Uranus appears nearly as if it’s rolling across the sun, like a rolling ball.
Earth’s axis is tilted 23.5 degrees from perpendicular with respect to the airplane of our orbit across the sun. Uranus’s axis is tilted at 98 levels! So Uranus is tilted practically sideways to the airplane of the solar system, the only flat sheet of space wherein practically all of the planets and moons orbit.
And, talking of its orbit, Uranus orbits 1.8 billion miles (2.9 billion km) from the sun. Subsequently, Uranus takes a very long time to orbit the sun as soon as. Its “yr” is 84 Earth-years lengthy. That makes every of its 4 seasons 21 years lengthy. That’s another excuse we on Earth consider Uranus’ seasons as unusual.
Like Earth, Uranus has an almost round orbit, so it at all times stays at roughly the identical distance from the sun. Not like Mars – whose orbit is extra elliptical than that of Earth or Uranus – Uranus’ distance from the sun isn’t a think about its seasonal change.
As a substitute, as on Earth, the planet’s tilt is what offers Uranus its 4 seasons.
The 2024 lunar calendars are here! Best Christmas gifts in the universe! Check ’em out here.
Excessive tilt means excessive seasons
So take into consideration how Uranus’ tilt impacts its seasons, in distinction to earthly seasons. Right here’s one distinction. Earth’s tilt means our north and south polar areas have a midnight sun in summer time and a protracted polar night in winter. Since Earth’s axis tilt is comparatively small, these darkish and vibrant instances at Earth’s poles have an effect on a comparatively small a part of our planet.
However the tilt of Uranus’ spin axis – 98 levels – is big. In consequence, in summer time, one pole of Uranus plus a big part of that pole’s hemisphere faces the sun repeatedly for 21 years. In the meantime, the opposite half of Uranus – the winter half – is in darkness for 21 years. That’s a protracted polar night time, and a protracted midnight sun!
Spring and fall on Uranus are equally weird. Across the equinoxes on Uranus, daylight strikes the equatorial area of the planet. Throughout these seasons, the size of a day on Uranus performs an vital function in its local weather. Uranus spins on its axis about each 17 hours, 14 minutes. So its day-night cycle lasts that lengthy.
So, for a lot of the planet’s spring and fall, a big proportion of the planet has day and night time about each 17 hours. It’s fairly a distinction to the summer time and winter seasons when half the planet is both in darkness or daylight.

What we see from Earth and spacecraft
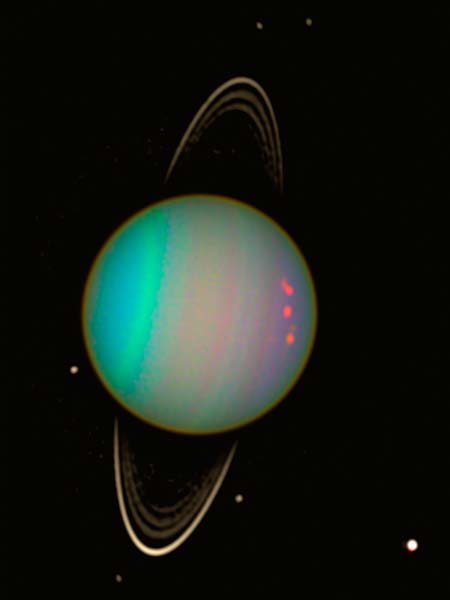
The acute seasonal modifications trigger dramatic shifts in Uranus’ cloud patterns. Earth- and space-based observatories have noticed this variation over a long time of Uranus-watching. The Voyager 2 spacecraft is the one craft from Earth that has ever flown previous Uranus. That was in 1986. Voyager 2 encountered this world throughout its southern hemisphere summer time. The spacecraft noticed Uranus as blue and featureless.
Within the years since Voyager 2’s flyby of Uranus, astronomical observing applied sciences have develop into extra highly effective. As Uranus moved in its 84-year orbit across the sun, we’ve seen the seasons on Uranus change.
Because the Voyager 2 observations, Uranus has emerged from the grip of its decades-long winter/summer time season. Its southern hemisphere autumn equinox occurred in 2007; that’s when the sun was shining above Uranus’ equator. Daylight reached some latitudes for the primary time in years. Mild and heat within the environment triggered gigantic storms comparable in dimension to North America (however with temperatures of -300 Fahrenheit/-184 Celsius), seen as vibrant spots within the planet’s environment.
Following seasonal modifications from Earth
Round that point, Earth- and space-based telescopes revealed extra clouds within the environment of Uranus. Bands encircling the planet modified in dimension and brightness as daylight struck elements of the planet for the primary time in a long time. Plus, a dark spot appeared – and extra vibrant spots – which observers have been capable of observe for years.
What extra will we see within the a long time and years forward as Uranus strikes towards the lengthy winter/summer time portion of its orbit as soon as extra?
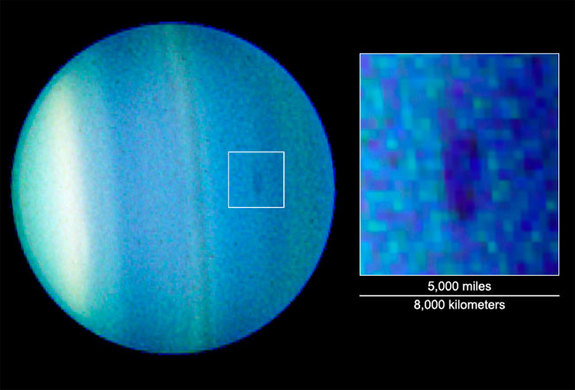

Backside line: The rotation axis of Uranus has a really massive tilt that causes excessive seasonal modifications. This ends in elevated exercise in its environment throughout the planet’s spring and fall seasons.
Read more: Uranus at opposition on November 13, 2023
Read more: Uranus discovered by accident in 1781




