Astronomers analyzing 13 years of knowledge from NASA’s Fermi Gamma-ray House Telescope have discovered an surprising and as but unexplained characteristic outdoors of our galaxy.
“It’s a utterly serendipitous discovery,” mentioned Alexander Kashlinsky, a cosmologist on the College of Maryland and NASA’s Goddard House Flight Middle in Greenbelt, who offered the analysis on the 243rd meeting of the American Astronomical Society in New Orleans. “We discovered a a lot stronger sign, and in a special a part of the sky, than the one we had been on the lookout for.”
Intriguingly, the gamma-ray sign is present in the same path and with an almost similar magnitude as one other unexplained characteristic, one produced by a few of the most energetic cosmic particles ever detected.
A paper describing the findings is printed in The Astrophysical Journal Letters.
The staff was looking for a gamma-ray characteristic associated to the CMB (cosmic microwave background), the oldest mild within the universe. Scientists say the CMB originated when the new, increasing universe had cooled sufficient to kind the primary atoms, an occasion that launched a burst of sunshine that, for the primary time, may permeate the cosmos. Stretched by the next enlargement of space over the previous 13 billion years, this mild was first detected within the type of faint microwaves everywhere in the sky in 1965.
Within the Seventies, astronomers realized that the CMB had a so-called dipole construction, which was later measured at excessive precision by NASA’s COBE (Cosmic Background Explorer) mission. The CMB is about 0.12% hotter, with extra microwaves than common, towards the constellation Leo, and colder by the identical quantity, with fewer microwaves than common, in the other way.
With a view to research the tiny temperature variations inside the CMB, this sign should be eliminated. Astronomers typically regard the sample because of the movement of our personal solar system relative to the CMB at about 230 miles (370 kilometers) per second.
This movement will give rise to a dipole sign within the mild coming from any astrophysical supply, however to this point the CMB is the one one which has been exactly measured. By on the lookout for the sample in different types of mild, astronomers may affirm or problem the concept that the dipole is due totally to our solar system’s movement.
“Such a measurement is essential as a result of a disagreement with the dimensions and path of the CMB dipole may present us with a glimpse into bodily processes working within the very early universe, doubtlessly again to when it was lower than a trillionth of a second outdated,” mentioned co-author Fernando Atrio-Barandela, a professor of theoretical physics on the College of Salamanca in Spain.
The staff reasoned that by including collectively a few years of knowledge from Fermi’s LAT (Giant Space Telescope), which scans the whole sky many occasions a day, a associated dipole emission sample may very well be detected in gamma rays. Because of the results of relativity, the gamma-ray dipole needs to be amplified by as a lot as 5 occasions over the presently detected CMB’s.
The scientists mixed 13 years of Fermi LAT observations of gamma rays above about 3 billion electron volts (GeV); for comparability, seen mild has energies between about 2 and three electron volts. They eliminated all resolved and recognized sources and stripped out the central aircraft of our Milky Way galaxy with a purpose to analyze the extragalactic gamma-ray background.
“We discovered a gamma-ray dipole, however its peak is situated within the southern sky, removed from the CMB’s, and its magnitude is 10 occasions larger than what we’d anticipate from our movement,” mentioned co-author Chris Shrader, an astrophysicist on the Catholic College of America in Washington and Goddard. “Whereas it’s not what we had been on the lookout for, we suspect it might be associated to the same characteristic reported for the highest-energy cosmic rays.”
Cosmic rays are accelerated charged particles—largely protons and atomic nuclei. The rarest and most energetic particles, known as UHECRs (ultrahigh-energy cosmic rays), carry greater than a billion occasions the power of three GeV gamma rays, and their origins stay one of many largest mysteries in astrophysics.
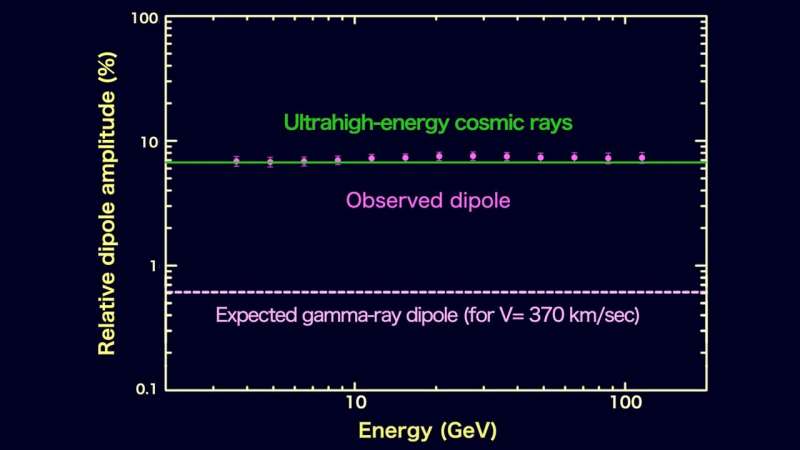
Since 2017, the Pierre Auger Observatory in Argentina has reported a dipole within the arrival path of UHECRs. Being electrically charged, cosmic rays are diverted by the galaxy’s magnetic subject by totally different quantities relying on their energies, however the UHECR dipole peaks in a sky location just like what Kashlinsky’s staff finds in gamma rays. And each have strikingly comparable magnitudes—about 7% extra gamma rays or particles than common coming from one path and correspondingly smaller quantities arriving from the other way.
The scientists assume it is seemingly the 2 phenomena are linked—that as but unidentified sources are producing each the gamma rays and the ultrahigh-energy particles. To unravel this cosmic conundrum, astronomers should both find these mysterious sources or suggest different explanations for each options.
Extra info:
A. Kashlinsky et al, Probing the Dipole of the Diffuse Gamma-Ray Background, The Astrophysical Journal Letters (2024). DOI: 10.3847/2041-8213/acfedd
Supplied by
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Quotation:
Fermi Gamma-ray House Telescope detects shock gamma-ray characteristic past our galaxy (2024, January 11)
retrieved 11 January 2024
from https://phys.org/information/2024-01-fermi-gamma-ray-space-telescope.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any truthful dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for info functions solely.




