If life ever existed on Mars, the Perseverance rover’s verification of lake sediments on the base of the Jezero crater reinforces the hope that traces may be discovered within the crater.
In new analysis printed within the journal Science Advances, a crew led by UCLA and The College of Oslo reveals that sooner or later, the crater full of water, depositing layers of sediments on the crater floor. The lake subsequently shrank and sediments carried by the river that fed it shaped an unlimited delta. Because the lake dissipated over time, the sediments within the crater had been eroded, forming the geologic options seen on the floor at this time.
The intervals of deposition and erosion passed off over eons of environmental modifications, the radar signifies, confirming that inferences concerning the Jezero crater’s geologic historical past based mostly on Mars pictures obtained from space are correct.
“From orbit we will see a bunch of various deposits, however we will not inform for certain if what we’re seeing is their unique state, or if we’re seeing the conclusion of a protracted geological story,” mentioned David Paige, a UCLA professor of Earth, planetary and space sciences and first creator of the paper. “To inform how this stuff shaped, we have to see under the floor.”
The rover, which is concerning the measurement of a automobile and carries seven scientific instruments, has been exploring the 30-mile-wide crater, finding out its geology and environment and amassing samples since 2021. Perseverance’s soil and rock samples can be introduced again to Earth by a future expedition and studied for proof of previous life.
Between Could and December 2022, Perseverance drove from the crater flooring onto the delta, an enormous expanse of three billion-year-old sediments that, from orbit, resembles the river deltas on Earth.
Because the rover drove onto the delta, Perseverance’s Radar Imager for Mars’ Subsurface Experiment, or RIMFAX, instrument fired radar waves downward at 10-centimeter intervals and measured pulses mirrored from depths of about 20 meters under the floor. With the radar, scientists can see all the way down to the bottom of the sediments to disclose the highest floor of the buried crater flooring.
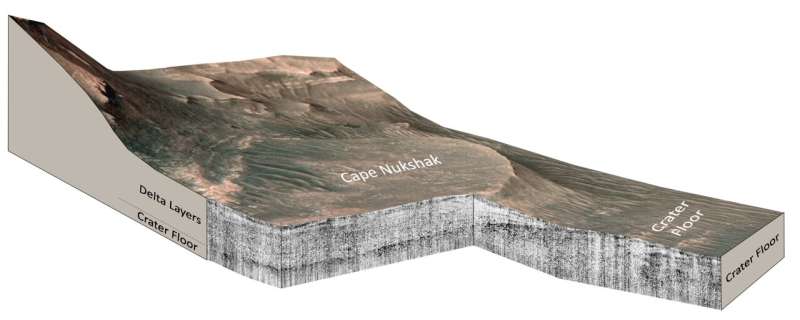
Years of analysis with ground-penetrating radar and testing of RIMFAX on Earth have taught scientists easy methods to learn the construction and composition of subsurface layers from their radar reflections. The ensuing subsurface picture reveals rock layers that may be interpreted like a freeway street reduce.
“Some geologists say that the flexibility of radar to see underneath the floor is type of like dishonest,” mentioned Paige, who’s RIMFAX’s deputy principal investigator.
RIMFAX imaging revealed two distinct intervals of sediment deposition sandwiched between two intervals of abrasion. UCLA and the College of Oslo report that the crater flooring under the delta just isn’t uniformly flat, suggesting {that a} interval of abrasion occurred previous to the deposition of lake sediments.
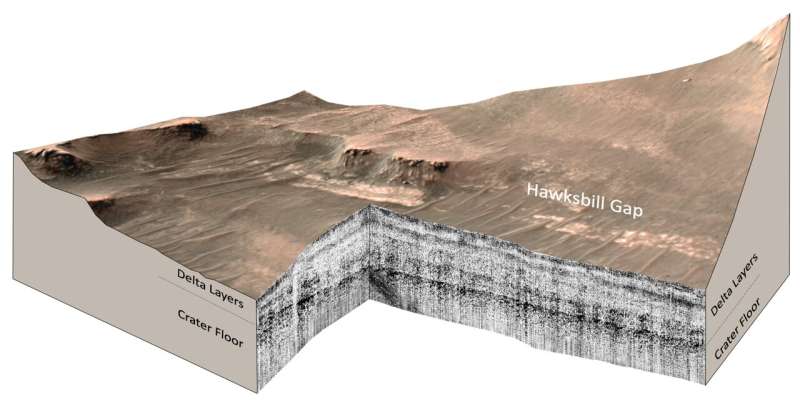
The radar pictures present that the sediments are common and horizontal—identical to sediments deposited in lakes on Earth. The existence of lake sediments had been suspected in previous studies, however has been confirmed by this analysis.
A second interval of deposition occurred when fluctuations within the lake degree allowed the river to deposit a broad delta that when prolonged far out into the lake, however has now eroded again nearer to the river’s mouth.
“The modifications we see preserved within the rock record are pushed by large-scale modifications within the Martian setting,” Paige mentioned. “It is cool that we will see a lot proof of change in such a small geographic space, which permits us lengthen our findings to the size of your complete crater.”
Extra info:
David Paige et al, Floor penetrating radar observations of the contact between the western delta and the crater flooring of Jezero Crater, Mars, Science Advances (2024). DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adi8339. www.science.org/doi/10.1126/sciadv.adi8339
Supplied by
University of California, Los Angeles
Quotation:
Affirmation of historical lake on Mars gives hope that Perseverance rover’s soil and rock samples maintain traces of life (2024, January 26)
retrieved 26 January 2024
from https://phys.org/information/2024-01-ancient-lake-mars-perseverance-rover.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any truthful dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for info functions solely.




