Astronomers investigating probably the most urgent mysteries of the cosmos—the speed at which the universe is increasing—are readying themselves to review this puzzle in a brand new means utilizing NASA’s Nancy Grace Roman Area Telescope. As soon as it launches by Could 2027, astronomers will mine Roman’s broad swaths of photos for gravitationally lensed supernovae, which can be utilized to measure the enlargement price of the universe.
There are a number of unbiased methods astronomers can measure the current enlargement price of the universe, referred to as the Hubble fixed. Completely different strategies have yielded totally different values, known as the Hubble pressure.
A lot of Roman’s cosmological investigations will probably be into elusive darkish power, which impacts how the universe is increasing over time. One major device for these investigations is a reasonably conventional technique, which compares the intrinsic brightness of objects like Kind Ia supernovae to their perceived brightness to find out distances.
Alternatively, astronomers might use Roman to look at gravitationally lensed supernovae. This technique of exploring the Hubble fixed is exclusive from conventional strategies as a result of it is based mostly on geometric strategies and never brightness.
“Roman is the perfect device to let the research of gravitationally lensed supernovae take off,” stated Lou Strolger of the Area Telescope Science Institute (STScI) in Baltimore, co-lead of the workforce getting ready for Roman’s research of those objects. “They’re uncommon, and really arduous to seek out. Now we have needed to get fortunate in detecting a number of of them early sufficient. Roman’s intensive area of view and repeated imaging in excessive decision will assist these possibilities.”
Utilizing numerous observatories like NASA’s Hubble Area Telescope and James Webb Area Telescope, astronomers have found simply eight gravitationally lensed supernovae within the universe. Nonetheless, solely two of these eight have been viable candidates to measure the Hubble fixed because of the kind of supernovae they’re and the period of their time-delayed imaging.
Gravitational lensing happens when the sunshine from an object, like a stellar explosion, on its technique to Earth passes by way of a galaxy or galaxy cluster and will get deflected by the immense gravitational area. The sunshine splits alongside totally different paths and varieties a number of photos of the supernova within the sky as we see it.
Relying on the variations between the paths, the supernova photos seem delayed by hours to months and even years. Exactly measuring this distinction in arrival instances between the a number of photos results in a mixture of distances that constrain the Hubble fixed.
“Probing these distances in a essentially totally different means than extra widespread strategies, with the identical observatory on this case, will help make clear why numerous measurement strategies have yielded totally different outcomes,” added Justin Pierel of STScI, Strolger’s co-lead on this system.
Discovering the needle within the haystack
Roman’s intensive surveys will be capable to map the universe a lot quicker than Hubble can, with the telescope “seeing” greater than 100 instances the world of Hubble in a single picture.
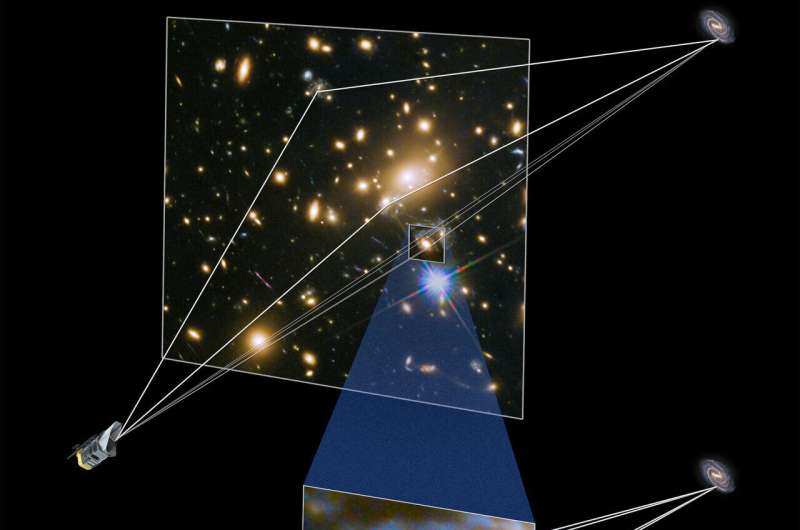
“Somewhat than gathering a number of footage of timber, this new telescope will permit us to see the whole forest in a single snapshot,” Pierel defined.
Particularly, the Excessive Latitude Time Area Survey will observe the identical space of the sky repeatedly, which is able to permit astronomers to review targets that change over time. This implies there will probably be a rare quantity of information—over 5 billion pixels every time—to sift by way of as a way to discover these very uncommon occasions.
“As a result of these are uncommon, leveraging the complete potential of gravitationally lensed supernovae depends upon a excessive degree of preparation,” stated Pierel. “We wish to make all of the instruments for locating these supernovae prepared upfront so we do not waste any time sifting by way of terabytes of information when it arrives.”
The undertaking will probably be carried out by a workforce of researchers from numerous NASA facilities and universities nationwide.
The preparation will happen in a number of phases. The workforce will create knowledge discount pipelines designed to detect gravitationally lensed supernovae in Roman imaging mechanically. To coach these pipelines, the researchers will even create simulated imaging: 50,000 simulated lenses are wanted, and there are solely 10,000 precise lenses at present recognized.
The info discount pipelines created by Strolger and Pierel’s workforce will complement pipelines being created to review darkish power with Kind Ia supernovae.
“Roman is actually the primary alternative to create a gold-standard pattern of gravitationally lensed supernovae,” concluded Strolger. “All our preparations now will produce all of the elements wanted to make sure we will successfully leverage the big potential for cosmology.”
Supplied by
Space Telescope Science Institute
Quotation:
NASA’s Roman telescope to make use of uncommon occasions to calculate enlargement price of universe (2024, February 7)
retrieved 7 February 2024
from https://phys.org/information/2024-02-nasa-roman-telescope-rare-events.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any truthful dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for info functions solely.




