Like boulders, rocks, and pebbles scattered throughout a panorama, asteroids are available a variety of sizes. Cataloging asteroids in space is hard as a result of they’re faint they usually do not cease to be photographed as they zip alongside their orbits across the sun.
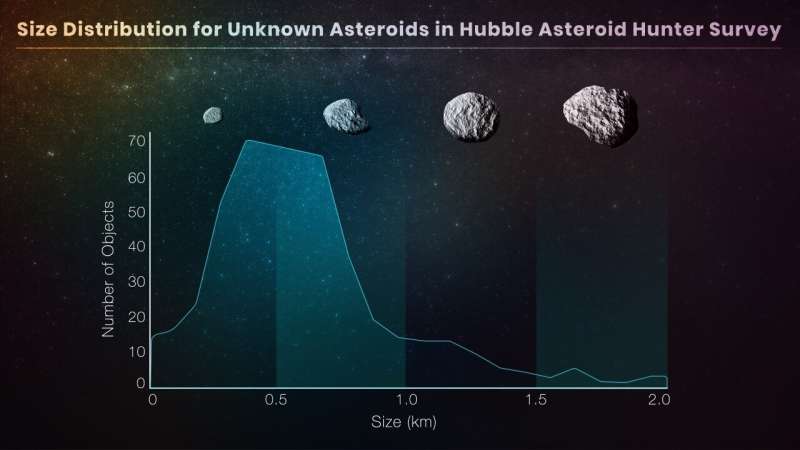
Astronomers just lately used a trove of archived photos taken by NASA’s Hubble House Telescope to visually snag a largely unseen inhabitants of smaller asteroids of their tracks. The treasure hunt required perusing 37,000 Hubble photos spanning 19 years. The payoff was discovering 1,701 asteroid trails, with 1,031 of the asteroids beforehand uncatalogued. About 400 of those uncatalogued asteroids are beneath 1 kilometer in dimension.
Volunteers from around the globe, generally known as “citizen scientists,” contributed to the identification of this asteroid bounty. Skilled scientists mixed the volunteers’ efforts with a machine-learning algorithm to establish the asteroids. It represents a brand new method to discovering asteroids in astronomical archives spanning many years, which can be successfully utilized to different datasets, say the researchers.
“We’re getting deeper into seeing the smaller inhabitants of primary belt asteroids. We have been stunned to see such numerous candidate objects,” mentioned lead creator Pablo García Martín of the Autonomous College of Madrid, Spain. “There was some trace that this inhabitants exists, however now we’re confirming it with a random asteroid inhabitants pattern obtained utilizing the entire Hubble archive. That is essential for offering insights into the evolutionary fashions of our solar system.”
The big, random pattern gives new insights into the formation and evolution of the asteroid belt. Discovering a number of small asteroids favors the concept that they’re fragments of bigger asteroids which have collided and damaged aside, like smashed pottery. This can be a grinding-down course of spanning billions of years.
An alternate concept for the existence of smaller fragments is that they shaped that method billions of years in the past. However there isn’t any conceivable mechanism that may preserve them from snowballing as much as bigger sizes as they agglomerated dust from the planet-forming circumstellar disk round our sun. “Collisions would have a sure signature that we will use to check the present primary belt inhabitants,” mentioned co-author Bruno Merín of the European House Astronomy Centre, in Madrid, Spain .
Novice astronomers educate AI to seek out asteroids
Due to Hubble’s quick orbit across the Earth, it may possibly seize wandering asteroids by means of their telltale trails within the Hubble exposures. As considered from an Earth-based telescope, an asteroid leaves a streak throughout the image. Asteroids “photobomb” Hubble exposures by showing as unmistakable, curved trails in Hubble pictures.
As Hubble strikes across the Earth, it adjustments its perspective whereas observing an asteroid, which additionally strikes alongside its personal orbit. By realizing the place of Hubble throughout the commentary and measuring the curvature of the streaks, scientists can decide the distances to the asteroids and estimate the shapes of their orbits.
The asteroids snagged principally dwell in the principle belt, which lies between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter. Their brightness is measured by Hubble’s delicate cameras. And evaluating their brightness to their distance permits for a dimension estimate. The faintest asteroids within the survey are roughly one forty-millionth the brightness of the faintest star that the human eye can see.
“Asteroid positions change with time, and due to this fact, you can not discover them simply by coming into coordinates as a result of, at totally different occasions, they won’t be there,” mentioned Merín. “As astronomers we do not have time to go searching by means of all of the asteroid photos. So we received the thought to collaborate with over 10,000 citizen-science volunteers to peruse the large Hubble archives.”
In 2019 a global group of astronomers launched the Hubble Asteroid Hunter, a citizen-science undertaking to establish asteroids in archival Hubble information. The initiative was developed by researchers and engineers on the European Science and Know-how Centre (ESTEC) and the European House Astronomy Centre’s science information middle (ESDC), in collaboration with the Zooniverse platform, the world’s largest and hottest citizen-science platform, and Google.
A total of 11,482 citizen-science volunteers, who offered almost 2 million identifications, have been then given a coaching set for an automatic algorithm to establish asteroids primarily based on synthetic intelligence. This pioneering method could also be successfully utilized to different datasets.
The undertaking will subsequent discover the streaks of beforehand unknown asteroids to characterize their orbits and examine their properties, comparable to rotation durations. As a result of most of those asteroid streaks have been captured by Hubble a few years in the past, it’s not doable to observe them up now to find out their orbits.
The findings are revealed within the journal Astronomy & Astrophysics.
Extra info:
Pablo García-Martín et al, Hubble Asteroid Hunter, Astronomy & Astrophysics (2024). DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361/202346771
Quotation:
Hubble goes trying to find small primary belt asteroids (2024, April 18)
retrieved 18 April 2024
from https://phys.org/information/2024-04-hubble-small-main-belt-asteroids.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any truthful dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for info functions solely.




