After beginning science operations in February, Japan-led XRISM (X-ray Imaging and Spectroscopy Mission) studied the monster black hole on the middle of galaxy NGC 4151.
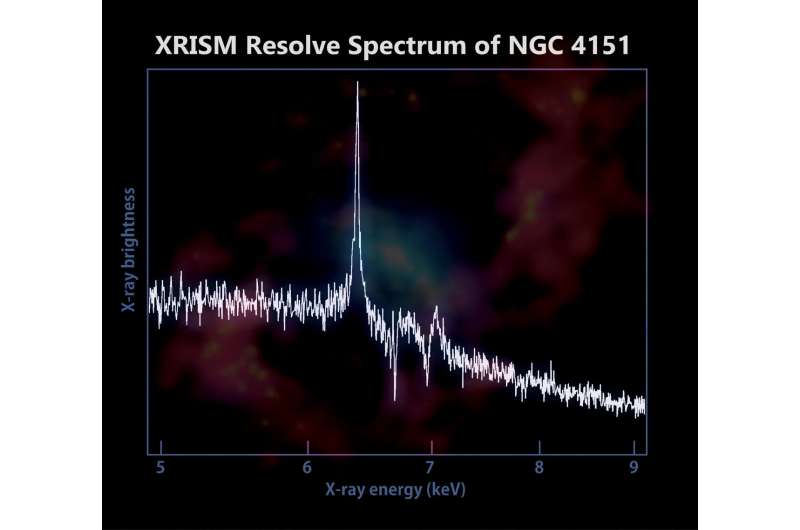
“XRISM’s Resolve instrument captured an in depth spectrum of the world across the black hole,” stated Brian Williams, NASA’s undertaking scientist for the mission on the company’s Goddard House Flight Middle in Greenbelt, Maryland. “The peaks and dips are like chemical fingerprints that may inform us what parts are current and reveal clues concerning the destiny of matter because it nears the black hole.”
XRISM (pronounced “crism”) is led by JAXA (Japan Aerospace Exploration Company) in collaboration with NASA, together with contributions from ESA (European House Company). It launched on Sept. 6, 2023. NASA and JAXA developed Resolve, the mission’s microcalorimeter spectrometer.
NGC 4151 is a spiral galaxy round 43 million light-years away within the northern constellation Canes Venatici. The supermassive black hole at its middle holds greater than 20 million instances the sun’s mass.
The galaxy can be lively, which implies its middle is unusually shiny and variable. Fuel and dust swirling towards the black hole kind an accretion disk round it and warmth up via gravitational and frictional forces, creating variability. Among the matter getting ready to the black hole kinds twin jets of particles that blast out from either side of the disk at practically the pace of sunshine. A puffy donut-shaped cloud of fabric referred to as a torus surrounds the accretion disk.
In actual fact, NGC 4151 is among the closest-known lively galaxies. Different missions, together with NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory and Hubble House Telescope, have studied it to study extra concerning the interplay between black holes and their environment, which may inform scientists how supermassive black holes in galactic facilities develop over cosmic time.
The galaxy is uncommonly shiny in X-rays, which made it a super early goal for XRISM.
Resolve’s spectrum of NGC 4151 reveals a pointy peak at energies just below 6.5 keV (kiloelectron volts)—an emission line of iron. Astronomers suppose that a lot of the facility of lively galaxies comes from X-rays originating in sizzling, flaring areas near the black hole. X-rays bouncing off cooler fuel within the disk causes iron there to fluoresce, producing a selected X-ray peak. This enables astronomers to color a greater image of each the disk and erupting areas a lot nearer to the black hole.
The spectrum additionally exhibits a number of dips round 7 keV. Iron positioned within the torus induced these dips as properly, though via absorption of X-rays, quite than emission, as a result of the fabric there may be a lot cooler than within the disk. All this radiation is a few 2,500 instances extra energetic than the sunshine we will see with our eyes.
Iron is only one ingredient XRISM can detect. The telescope can even spot sulfur, calcium, argon, and others, relying on the supply. Every tells astrophysicists one thing completely different concerning the cosmic phenomena scattered throughout the X-ray sky.
XRISM is a collaborative mission between JAXA and NASA, with participation by ESA. NASA’s contribution consists of science participation from CSA (Canadian House Company).
Supplied by
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Quotation:
NASA and JAXA XRISM spot iron fingerprints in close by lively galaxy (2024, Could 8)
retrieved 8 Could 2024
from https://phys.org/information/2024-05-nasa-jaxa-xrism-iron-fingerprints.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any honest dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for data functions solely.




