Watch the video above to study extra about probably the most distant galaxy found up to now.
NASA printed this original article on Could 30, 2024. Edits by EarthSky.
Most distant galaxy but recognized
During the last two years, astronomers have been utilizing NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope (additionally known as Webb or JWST) to discover what they name the Cosmic Daybreak. It’s the primary few hundred million years after the Big Bang, when the primary stars and galaxies had been born. Trying far out into space and much again in time with Webb, astronomers are utilizing these galaxies to acquire very important insights into the methods wherein the gasoline, stars and black holes had been altering when the universe was very younger. On Could 30, 20224, these astronomers introduced probably the most distant galaxy recognized up to now.
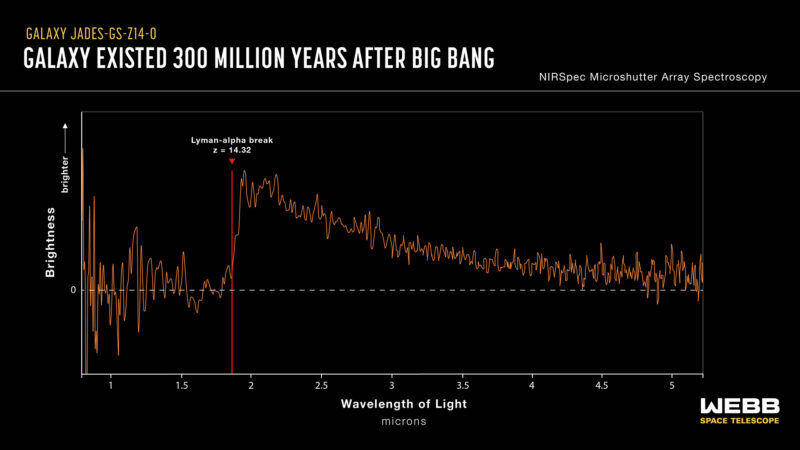
These astronomers from across the globe used Webb to look at galaxies as a part of the JWST Superior Deep Extragalactic Survey (JADES) program. Utilizing Webb’s Close to-Infrared Spectrograph (NIRSpec), they obtained a spectrum of a record-breaking galaxy noticed solely 290 million years after the Large Bang. This corresponds to a redshift of about 14.
Redshift is a measurement of how a lot the enlargement of the universe stretches a galaxy’s gentle. NASA invited Stefano Carniani from Scuola Normale Superiore in Pisa, Italy, and Kevin Hainline from the College of Arizona in Tucson, Arizona, to inform us extra about how Webb discovered this supply and what its distinctive properties inform us about galaxy formation.
Maintain studying to study what they stated.
Discovering the excessive redshift galaxy
Carniani and Hainline stated:
Engineers designed the devices on Webb to search out and perceive the earliest galaxies. And within the first 12 months of observations as a part of the JWST Superior Deep Extragalactic Survey (JADES), we discovered many lots of of candidate galaxies from the primary 650 million years after the Large Bang.
In early 2023, we found a galaxy in our knowledge that had robust proof of being above a redshift of 14, which was very thrilling. However there have been some properties of the supply that made us cautious. The supply was surprisingly vibrant, which we wouldn’t count on for such a distant galaxy. And it was very shut to a different galaxy such that the 2 gave the impression to be a part of one bigger object.
We noticed the supply once more in October 2023 as a part of the JADES Origins Field. New imaging knowledge obtained with Webb’s narrower Close to-Infrared Digital camera (NIRCam) filters pointed much more towards the high-redshift speculation. We knew we would have liked a spectrum, as no matter we’d study can be of immense scientific significance, both as a brand new milestone in Webb’s investigation of the early universe or as a confounding oddball of a middle-aged galaxy.
New most distant galaxy file
Carniani and Hainline continued:
In January 2024, NIRSpec noticed this galaxy, JADES-GS-z14-0, for nearly 10 hours. And when astronomers first processed the spectrum, there was unambiguous proof that the galaxy was certainly at a redshift of 14.32. This shattered the earlier most-distant galaxy file (z = 13.2 of JADES-GS-z13-0).
Seeing this spectrum was extremely thrilling for the entire crew, given the thriller surrounding the supply. This discovery was not only a new distance file for our crew; an important facet of JADES-GS-z14-0 was that at this distance, we all know that this galaxy should be intrinsically very luminous. From the photographs, the supply is greater than 1,600 light-years throughout. In order that proves the sunshine we see comes largely from younger stars and never from emission close to a rising supermassive black hole. This a lot starlight implies the galaxy is a number of lots of of hundreds of thousands of occasions the mass of the sun!
This raises the query: How can nature make such a vibrant, large and enormous galaxy in lower than 300 million years?
Most distant galaxy is surprisingly vibrant
Carniani and Hainline additionally stated:
The info reveal different necessary points of this astonishing galaxy. We see the colour of the galaxy will not be as blue because it might be, indicating among the gentle is reddened by dust, even at these very early occasions.
JADES researcher Jake Helton of Steward Observatory and the College of Arizona additionally recognized that JADES-GS-z14-0 was detected at longer wavelengths with Webb’s Mid-Infrared Instrument (MIRI). And that’s a outstanding achievement contemplating its distance. The MIRI commentary covers wavelengths of sunshine emitted within the visible-light vary, that are redshifted out of attain for Webb’s near-infrared devices.
Jake’s evaluation signifies the brightness of the supply implied by the MIRI commentary is above what can be extrapolated from the measurements by the opposite Webb devices. And so it signifies the presence of robust ionized gasoline emission within the galaxy within the type of vibrant emission lines from hydrogen and oxygen. The presence of oxygen so early within the lifetime of this galaxy is a shock. It suggests a number of generations of very large stars had already lived their lives earlier than we noticed the galaxy.
Distant, luminous galaxy will likely be certainly one of many
Carniani and Hainline famous:
All these observations, collectively, inform us that JADES-GS-z14-0 will not be just like the forms of galaxies which were predicted by theoretical fashions and laptop simulations to exist within the very early universe. Given the noticed brightness of the supply, we are able to forecast the way it would possibly develop over cosmic time. And up to now we now have not discovered any appropriate analogs from the lots of of different galaxies we’ve noticed at excessive redshift in our survey.
Given the comparatively small area of the sky that we searched to search out JADES-GS-z14-0, its discovery has profound implications for the anticipated variety of vibrant galaxies we see within the early universe, as mentioned in one other concurrent JADES research (Robertson et al., recently accepted). It’s doubtless that astronomers will discover many such luminous galaxies, probably at even earlier occasions, over the subsequent decade with Webb. We’re thrilled to see the extraordinary variety of galaxies that existed at Cosmic Daybreak!

This publish highlights knowledge from Webb science in progress, which has not but been by way of the peer-review course of.
Backside line: Astronomers utilizing the Webb space telescope have found probably the most distant galaxy but recognized. It existed 290 million years after the Large Bang.
Source: A shining cosmic dawn: spectroscopic confirmation of two luminous galaxies at z ~ 14




