All over the world this summer season, skilled and beginner astronomers alike will likely be fastened on one small constellation deep within the night time sky. However it’s not the seven stars of Corona Borealis, the “Northern Crown,” which have sparked such fascination.
It is a darkish spot amongst them the place an impending nova occasion—so brilliant it will likely be seen on Earth with the naked eye—is poised to happen.
“It is a once-in-a-lifetime occasion that may create numerous new astronomers on the market, giving younger individuals a cosmic occasion they’ll observe for themselves, ask their very own questions, and accumulate their very own information,” stated Dr. Rebekah Hounsell, an assistant analysis scientist specializing in nova occasions at NASA’s Goddard Area Flight Heart in Greenbelt, Maryland. “It will gasoline the subsequent era of scientists.”
T Coronae Borealis, dubbed the “Blaze Star” and identified to astronomers merely as “T CrB,” is a binary system nestled within the Northern Crown some 3,000 light-years from Earth. The system is comprised of a white dwarf—an Earth-sized remnant of a useless star with a mass corresponding to that of our sun—and an historical pink large slowly being stripped of hydrogen by the relentless gravitational pull of its hungry neighbor.
The hydrogen from the pink large accretes on the floor of the white dwarf, inflicting a buildup of strain and warmth. Finally, it triggers a thermonuclear explosion large enough to blast away that accreted materials. For T CrB, that occasion seems to reoccur, on common, each 80 years.
Do not confuse a nova with a supernova, a remaining, titanic explosion that destroys some dying stars, Hounsell stated. In a nova occasion, the dwarf star stays intact, sending the accrued materials hurtling into space in a blinding flash. The cycle sometimes repeats itself over time, a course of which might keep it up for tens or a whole bunch of 1000’s of years.
“There are a couple of recurrent novae with very brief cycles, however sometimes, we do not typically see a repeated outburst in a human lifetime, and infrequently one so comparatively near our personal system,” Hounsell stated. “It is extremely thrilling to have this front-row seat.”
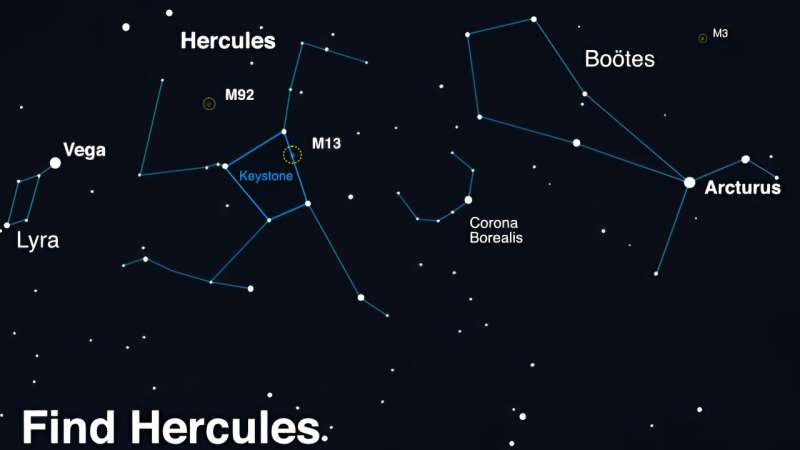
Discovering T Coronae Borealis
The primary recorded sighting of the T CrB nova was greater than 800 years in the past, in autumn 1217, when a person named Burchard, abbot of Ursberg, Germany, famous his observance of “a faint star that for a time shone with nice gentle.”
The T CrB nova was final seen from Earth in 1946. Its conduct over the previous decade seems strikingly just like noticed conduct in an analogous timeframe main as much as the 1946 eruption. If the sample continues, some researchers say, the nova occasion might happen by September 2024.
What ought to stargazers search for? The Northern Crown is a horseshoe-shaped curve of stars west of the Hercules constellation, ideally noticed on clear nights. It may be recognized by finding the 2 brightest stars within the Northern Hemisphere—Arcturus and Vega—and monitoring a straight line from one to the opposite, which is able to lead skywatchers to Hercules and the Corona Borealis.
The outburst will likely be temporary. As soon as it erupts, it will likely be seen to the bare eye for rather less than every week—however Hounsell is assured it will likely be fairly a sight to see.
A coordinated scientific method
Dr. Elizabeth Hays, chief of the Astroparticle Physics Laboratory at NASA Goddard, agreed. She stated a part of the enjoyable in getting ready to watch the occasion is seeing the keenness amongst beginner stargazers, whose ardour for excessive space phenomena has helped maintain a protracted and mutually rewarding partnership with NASA.
“Citizen scientists and space lovers are at all times on the lookout for these robust, brilliant alerts that determine nova occasions and different phenomena,” Hays stated. “Utilizing social media and e-mail, they will ship out instantaneous alerts, and the flag goes up. We’re relying on that international group interplay once more with T CrB.”
Hays is the venture scientist for NASA’s Fermi Gamma-ray Area Telescope, which has made gamma-ray observations from low Earth orbit since 2008. Fermi is poised to watch T CrB when the nova eruption is detected, together with different space-based missions together with NASA’s James Webb Area Telescope, Neil Gehrels Swift Observatory, IXPE (Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer), NuSTAR (Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array), NICER (Neutron star Inside Composition Explorer), and the European Area Company’s INTEGRAL (Excessive Universe Surveyor).
Quite a few ground-based radio telescopes and optical imagers, together with the Nationwide Radio Astronomy Observatory’s Very Massive Array in New Mexico, additionally will participate. Collectively, the varied telescopes and devices will seize information throughout the seen and non-visible gentle spectrum.
“We’ll observe the nova occasion at its peak and thru its decline, because the seen power of the outburst fades,” Hounsell stated. “However it’s equally vital to acquire information throughout the early rise to eruption—so the information collected by these avid citizen scientists looking out now for the nova will contribute dramatically to our findings.”
For astrophysics researchers, that guarantees a uncommon alternative to shed new gentle on the construction and dynamics of recurring stellar explosions like this one.
“Sometimes, nova occasions are so faint and much away that it is onerous to obviously determine the place the erupting power is concentrated,” Hays stated. “This one will likely be actually shut, with numerous eyes on it, finding out the varied wavelengths and hopefully giving us information to begin unlocking the construction and particular processes concerned. We will not wait to get the complete image of what is going on on.”
A few of these eyes will likely be very new. Gamma-ray imagers did not exist the final time T CrB erupted in 1946, and IXPE’s polarization functionality—which identifies the group and alignment of electromagnetic waves to find out the construction and inner processes of high-energy phenomena—can be a brand-new instrument in X-ray astronomy. Combining their information might provide unprecedented perception into the lifecycles of binary programs and the waning however highly effective stellar processes that gasoline them.
Is there an opportunity September will come and go with out the anticipated nova outburst from T CrB? Consultants agree there aren’t any ensures—however hope abides.
“Recurrent novae are unpredictable and contrarian,” stated Dr. Koji Mukai, a fellow astrophysics researcher at NASA Goddard.
“Whenever you assume there cannot presumably be a purpose they observe a sure set sample, they do—and as quickly as you begin to depend on them repeating the identical sample, they deviate from it utterly. We’ll see how T CrB behaves.”
Quotation:
NASA, international astronomers await uncommon nova explosion (2024, June 7)
retrieved 7 June 2024
from https://phys.org/information/2024-06-nasa-global-astronomers-await-rare.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any truthful dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for info functions solely.




