Earth’s protecting ambiance has sheltered life for billions of years, making a haven the place evolution produced advanced lifeforms like us. The ozone layer performs a crucial function in shielding the biosphere from lethal UV radiation. It blocks 99% of the sun’s highly effective UV output. Earth’s magnetosphere additionally shelters us.
However the sun is comparatively tame. How efficient are the ozone and the magnetosphere at defending us from highly effective supernova explosions?
Each million years—a small fraction of Earth’s 4.5 billion-year lifetime—an enormous star explodes inside 100 parsecs (326 light-years) of Earth. We all know this as a result of our solar system sits inside an enormous bubble in space referred to as the Native Bubble.
It is a cavernous area of space the place hydrogen density is way decrease than outdoors the bubble. A sequence of supernovae explosions within the earlier 10 to twenty million years carved out the bubble.
Supernovae are harmful, and the nearer a planet is to 1, the extra lethal its results. Scientists have speculated on the consequences that supernova explosions have had on Earth, questioning if they’ve triggered mass extinctions or not less than partial extinctions.
A supernova’s gamma-ray burst and cosmic rays can deplete Earth’s ozone and permit ionizing UV radiation to achieve the planet’s floor. The results may also create extra aerosol particles within the ambiance, rising cloud protection and inflicting international cooling.
A new research article revealed in Communications Earth & Setting examines supernova explosions and their impact on Earth. It’s titled “Earth’s ambiance protects the biosphere from close by supernovae.” The lead writer is Theodoros Christoudias from the Local weather and Environment Analysis Middle, Cyprus Institute, Nicosia, Cyprus.
The Native Bubble is not the one proof of close by core-collapse supernovae (SNe) in the previous couple of million years. Ocean sediments additionally include 60Fe, a radioactive isotope of iron with a half-life of two.6 million years.
SNe expel 60Fe into space once they explode, indicating {that a} close by supernova exploded about 2 million years in the past. There’s additionally 60Fe in sediments that point out one other SN explosion about 8 million years in the past.
Researchers have correlated an SN explosion with the Late Devonian extinction about 370 million years in the past. In a single paper, researchers discovered plant spores burned by UV mild, a sign that one thing highly effective depleted Earth’s ozone layer. In actual fact, Earth’s biodiversity declined for about 300,000 years previous to the Late Devonian extinction, suggesting that a number of SNe may’ve performed a job.
Earth’s ozone layer is in fixed flux. As UV vitality reaches it, it breaks ozone molecules (O3) aside. That dissipates the UV vitality, and the oxygen atoms mix into O3 once more. The cycle repeats.
That is a simplified model of the atmospheric chemistry concerned, however it serves for example the cycle. A close-by supernova may overwhelm the cycle, depleting the ozone column density and permitting extra lethal UV to achieve Earth’s floor.
However within the new paper, Christoudias and his fellow authors recommend that Earth’s ozone layer is far more resilient than thought and gives ample safety towards SNe inside 100 parsecs. Whereas earlier researchers have modeled Earth’s ambiance and its response to a close-by SN, the authors say that they’ve improved on that work.
They modeled Earth’s ambiance with an Earth Programs Mannequin with Atmospheric Chemistry (EMAC) mannequin to check the influence of close by SNe explosions on Earth’s ambiance. Utilizing EMAC, the authors say they’ve modeled “the advanced atmospheric circulation dynamics, chemistry, and course of feedbacks” of Earth’s ambiance.
These are wanted to “simulate stratospheric ozone loss in response to elevated ionization, resulting in ion-induced nucleation and particle development to CCN” (cloud condensation nuclei).
“We assume a consultant close by SN with GCR (galactic cosmic ray) ionization charges within the ambiance which can be 100 occasions current ranges,” they write. That correlates with a supernova explosion about 100 parsecs or 326 light-years away.
“The utmost ozone depletion over the poles is lower than the present-day anthropogenic ozone gap over Antarctica, which quantities to an ozone column lack of 60–70%,” the authors clarify. “Then again, there is a rise of ozone within the troposphere, however it’s properly inside the ranges ensuing from current anthropogenic air pollution.”
However let’s lower to the chase. We wish to know if Earth’s biosphere is secure or not.
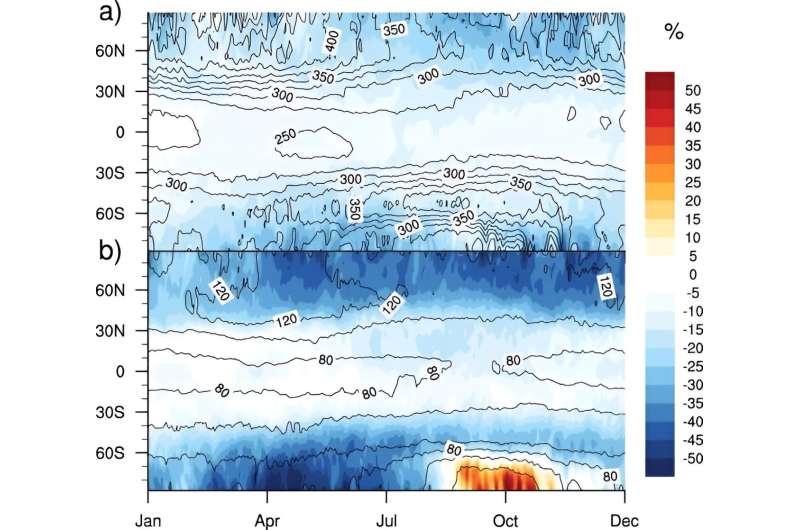
The utmost imply stratospheric ozone depletion from 100 occasions extra ionizing radiation than regular, consultant of a close-by SN, is about 10% globally. That is about the identical lower as our anthropogenic air pollution causes. It would not have an effect on the biosphere very a lot.
“Though important, it’s unlikely that such ozone adjustments would have a significant influence on the biosphere, particularly as a result of a lot of the ozone loss is discovered to happen at excessive latitudes,” the authors clarify.
However that is for contemporary Earth. Throughout the pre-Cambrian, earlier than life exploded in a multiplication of types, the ambiance had solely about 2% oxygen. How would an SN have an effect on that? “We simulated a 2% oxygen ambiance since this is able to probably signify circumstances the place the rising biosphere on land would nonetheless be notably delicate to ozone depletion,” the authors write.
“Ozone loss is about 10%–25% at mid-latitudes and an order of magnitude decrease within the tropics,” the authors write. At minimal ozone ranges on the poles, ionizing radiation from an SN may truly find yourself rising the ozone column. “We conclude that these adjustments of atmospheric ozone are unlikely to have had a significant influence on the rising biosphere on land through the Cambrian,” they conclude.
What about international cooling?
International cooling would enhance, however to not a harmful extent. Over the Pacific and Southern oceans, CCN may enhance by as much as 100%, which appears like quite a bit. “These adjustments, whereas climatically related, are akin to the distinction between the pristine pre-industrial ambiance and the polluted present-day ambiance.” They’re saying that it might cool the ambiance by about the identical quantity as we’re heating it now.
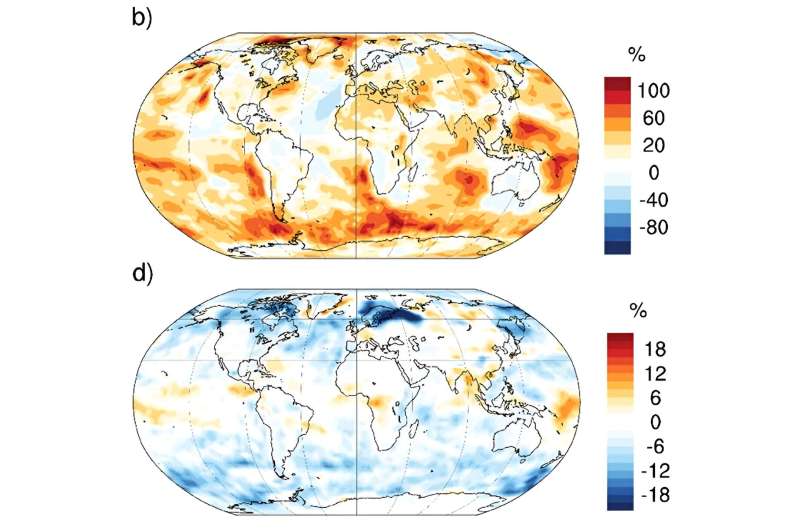
The researchers level out that their research considerations the whole biosphere, not people. “Our research doesn’t think about the direct well being dangers to people and animals ensuing from publicity to elevated ionizing radiation,” they write.
Relying on particular person circumstances, people might be uncovered to harmful ranges of radiation over time. However general, the biosphere would hum alongside regardless of a 100-fold enhance in UV radiation. Our ambiance and magnetosphere can deal with it.
“Total, we discover that close by SNe are unlikely to have prompted mass extinctions on Earth,” the authors write. “We conclude that our planet’s atmosphere and geomagnetic area successfully protect the biosphere from the consequences of close by SNe, which has allowed life to evolve on land over the past lots of of million years.”
This research reveals that Earth’s biosphere won’t undergo enormously so long as supernova explosions hold their distance.
Extra info:
Theodoros Christoudias et al, Earth’s ambiance protects the biosphere from close by supernovae, Communications Earth & Setting (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s43247-024-01490-9
Supplied by
Universe Today
Quotation:
Earth’s ambiance is our greatest protection towards close by supernovae, research suggests (2024, June 19)
retrieved 19 June 2024
from https://phys.org/information/2024-06-earth-atmosphere-defense-nearby-supernovae.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any honest dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for info functions solely.




