Penguins with their flipper-like wings might look comical as they waddle on land. However within the water, these wings and torpedo-shaped our bodies make these seabirds knowledgeable, sleek divers. Scientists said on August 1, 2024, that fossilized penguin bones from New Zealand, dated to 24 million years in the past, at the moment are revealing new particulars on the evolution of penguins’ wings.
These findings have been published within the peer-reviewed Journal of the Royal Society of New Zealand on August 1, 2024.
Penguins are well-adapted for ocean life
There are 18 species of penguins alive right now. These flightless birds stay largely alongside Southern Hemisphere coastlines and oceans. One exception is a species discovered north of the equator on the Galápagos Islands. The biggest penguin species, the emperor penguin that lives in Antarctica, is over 4 ft (1.2 meters) tall. On the different excessive is the diminutive little blue penguin, of Australia and New Zealand, that measures only a foot (30 cm) in size.
Penguins are knowledgeable ocean swimmers that feed on fish, krill and squid. They’ve streamlined our bodies optimized for transferring via water. And so they use their finlike wings to propel ahead, as if flying underwater. The gentoo penguin is the quickest diver. It could actually attain speeds of as much as 22 miles per hour (35 kph) and might dive as deep as 660 ft (200 m). An emperor penguin can dive as a lot as 1,800 ft (548 m) deep. Smaller penguins, just like the little blue penguin, nevertheless, are inclined to forage nearer to the water floor.
A lacking hyperlink in penguin evolution
Trendy-day penguins started their evolutionary journey about 34 million years in the past, through the Oligocene. Pakudyptes hakataramea, the brand new penguin species reported by the researchers, lived 24 million years in the past in New Zealand. It was recognized from fossilized wing bones discovered within the Hakataramea Valley, South Canterbury, New Zealand, in 1987.
Pakudyptes was a small penguin, concerning the dimension of the little blue penguin, the smallest penguin species alive right now.
Tatsuro Ando of the Ashoro Museum of Paleontology in Japan is the paper’s lead creator. He mentioned in a press release that Pakudyptes’s wing bones stuffed a niche within the bone types seen in fossils and presently dwelling (or extant) penguins. He commented:
Particularly, the form of the wing bones [between fossil and extant penguins] differed drastically, and the method by which penguins’ wings got here to have their current kind and performance remained unclear.
The humerus and ulna spotlight how penguins’ wings have advanced.
Surprisingly, whereas the shoulder joints of the wing of Pakudyptes have been very near the situation of the present-day penguin, the elbow joints have been similar to these of older kinds of fossil penguins.
Pakudyptes is the primary fossil penguin ever discovered with this mixture, and it’s the “key” fossil to unlocking the evolution of penguins’ wings.
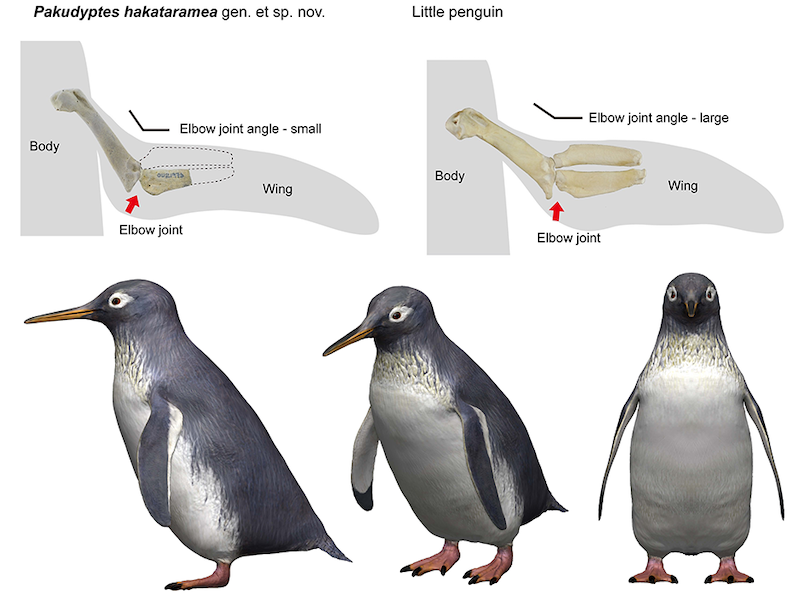
Pakudyptes bone construction signifies it was additionally a diver
Trendy penguins have dense thick bones that assist them keep buoyancy whereas diving. Based on Carolina Loch on the College of Otago, Pakudyptes’s inner bone construction revealed it solely dove to shallow depths. The outer bone layer – the bone cortex – was thick whereas the interior cavity that might have contained bone marrow was open. This bone construction was much like that of the little blue penguin.
The fossilized humerus and ulna additionally confirmed areas the place muscle tissue and ligaments as soon as hooked up to it. That helped reveal how Pakudyptes used its wings to swim underwater.
Loch remarked:
Penguins advanced quickly from the Late Oligocene to Early Miocene, and Pakudyptes is a vital fossil from this era. Its small dimension and distinctive mixture of bones might have contributed to the ecological range of recent penguins.
Backside line: A penguin fossil from 24 million years in the past in New Zealand has shed new gentle on the evolution of penguins’ wings.
Read more: New emperor penguin colonies discovered by satellite




