ESA’s Mars Specific has revealed that Mars churns up surprisingly Earth-like cloud patterns which are harking back to these in our planet’s tropical areas.
Earth and Mars have vastly completely different atmospheres. The dry, chilly environment of Mars consists nearly totally of carbon dioxide whereas Earth’s is wealthy in nitrogen and oxygen. Its atmospheric density is lower than one fiftieth of Earth’s environment—equal to the density discovered at about 35 km above Earth’s floor.
Regardless of being wildly completely different, their cloud patterns have been discovered to be surprisingly Earth-like, pointing to comparable formation processes.
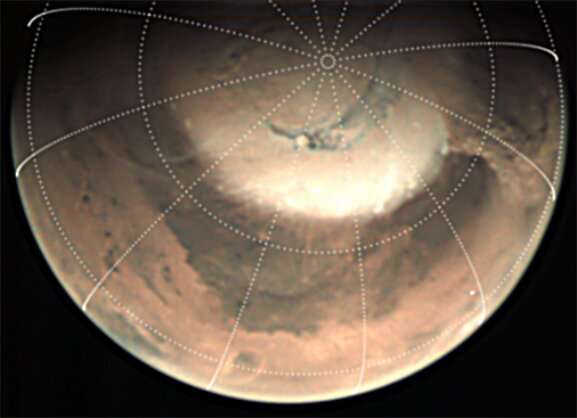
A brand new research dives deeper into two dust storms that occurred close to the Martian North Pole in 2019. The storms have been monitored throughout springtime on the North Pole, a time when native storms generally brew across the receding ice cap.
Two cameras on board Mars Specific—the Visible Monitoring Digicam (VMC) and the Excessive Decision Stereo Digicam (HRSC)—along with the MARCI digicam on board NASA’s Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter, imaged the storms from orbit.
The sequence of VMC pictures exhibits that the storms seem to develop and disappear in repeated cycles over a interval of days, exhibiting widespread options and shapes. Spiral shapes are notably seen within the wider views of the HRSC pictures. The spirals are between 1,000 and a pair of,000 km in size, and their origin is similar as that of the extratropical cyclones noticed in Earth’s mid-latitudes and polar latitudes.
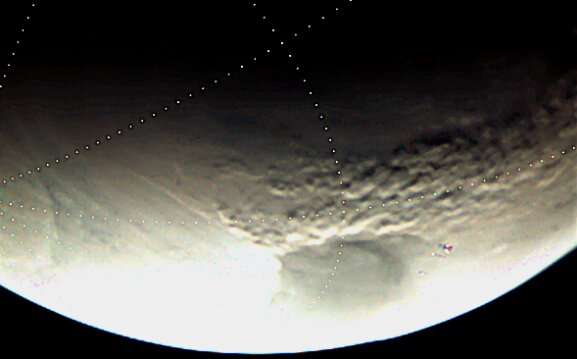
The photographs reveal a selected phenomenon on Mars. They present that the Martian dust storms are made up of recurrently spaced smaller cloud cells, organized like grains or pebbles. The feel can be seen in clouds in Earth’s environment.
The acquainted textures are shaped by convection, whereby sizzling air rises as a result of it’s much less dense than the cooler air round it. The kind of convection noticed right here is named closed-cell convection, when air rises within the heart of small cloud pockets, or cells. The gaps of sky across the cloud cells are the pathways for cooler air to sink under the recent rising air.
On Earth, the rising air accommodates water which condenses to kind clouds. The dust clouds imaged by Mars Specific present the identical course of, however on Mars the rising air columns include dust fairly than water. The sun heats dust-laden air inflicting it to rise and kind dusty cells. The cells are surrounded by areas of sinking air which have much less dust. This offers rise to the granular sample additionally seen within the picture of clouds on Earth.
By monitoring the motion of cells within the sequence of pictures, the wind speed might be measured. Wind blows over the cloud options at speeds of as much as 140 km/h, inflicting the form of the cells to elongate within the path of the wind. Regardless of the chaotic and dynamic atmospheres of Mars and Earth, nature creates these orderly patterns.
“When considering of a Mars-like environment on Earth, one may simply consider a dry desert or polar area. It’s fairly surprising then, that by monitoring the chaotic motion of dust storms, that parallels might be drawn with the processes that happen in Earth’s moist, sizzling, and decidedly very un-Mars-like tropical areas,” feedback Colin Wilson, ESA’s Mars Specific challenge scientist.
One key perception made doable with the VMC pictures is the measurement of the altitude of dust clouds. The size of the shadows they solid are measured and mixed with data of the sun’s place to measure the peak of the clouds above the Martian floor. Outcomes revealed that dust can attain roughly 6–11 km above the bottom and the cells have typical horizontal sizes of 20–40 km.

“Regardless of the unpredictable habits of dust storms on Mars and the sturdy wind gusts that accompany them, we now have seen that inside their complexity, organized buildings comparable to fronts and mobile convection patterns can emerge,” explains Agustín Sánchez-Levaga from the Universidad del País Vasco UPV/EHU (Spain), who leads the VMC science staff and is lead writer of a paper presenting the brand new evaluation.
Such organized mobile convection will not be distinctive to Earth and Mars; observations of the Venusian environment by Venus Specific arguably present comparable patterns. “Our work on Mars dry convection is an extra instance of the worth of comparative research of comparable phenomena occurring in planetary atmospheres with the intention to higher perceive the mechanisms underlying them below completely different situations and environments,” provides Agustín.
In addition to studying extra about how planetary atmospheres “work,” understanding dust storms is related for future missions to Mars. In excessive circumstances, dust storms can block a lot of the sunshine from the sun from reaching the solar cells of rovers on the floor of the purple planet. In 2018, a planetary-scale dust storm not solely blocked daylight reaching the floor, but additionally lined the solar panels of NASA’s Alternative rover with dust. Each of those components led to the rover dropping electrical energy, ending the mission.
Monitoring the evolution of dust storms is essential for serving to defend future solar-powered missions—and finally crewed missions to the planet—towards such highly effective phenomena.
“Mobile patterns and dry convection in textured dust storms on the fringe of Mars North Polar Cap,” by A. Sánchez-Lavega et al, is printed within the November 15, 2022 challenge of the journal Icarus.
Extra data:
A. Sánchez-Lavega et al, Mobile patterns and dry convection in textured dust storms on the fringe of Mars North Polar Cap, Icarus (2022). DOI: 10.1016/j.icarus.2022.115183
Supplied by
European Space Agency
Quotation:
Martian dust storms churn up Earth-like clouds (2022, November 16)
retrieved 16 November 2022
from https://phys.org/information/2022-11-martian-storms-churn-earth-like-clouds.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any honest dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for data functions solely.




