When the rover Perseverance landed on Mars, it was outfitted with the primary working microphone on the planet’s floor. Scientists have used it to make the first-ever audio recording of an extraterrestrial whirlwind.
The research was printed in Nature Communications by planetary scientist Naomi Murdoch and a workforce of researchers on the Nationwide Greater French Institute of Aeronautics and House and NASA. Roger Wiens, professor of Earth, atmospheric and planetary sciences in Purdue College’s Faculty of Science, leads the instrument workforce that made the invention. He’s the principal investigator of Perseverance’s SuperCam, a set of instruments that comprise the rover’s “head” that features superior remote-sensing devices with a variety of spectrometers, cameras and the microphone.
“We will be taught much more utilizing sound than we are able to with a few of the different instruments,” Wiens stated. “They take readings at common intervals. The microphone lets us pattern, not fairly on the speed of sound, however almost 100,000 instances a second. It helps us get a stronger sense of what Mars is like.”
The microphone will not be on constantly; it information for about three minutes each couple of days. Getting the whirlwind recording, Wiens stated, was fortunate, although not essentially surprising. Within the Jezero Crater, the place Perseverance landed, the workforce has noticed proof of almost 100 dust devils—tiny tornadoes of dust and grit—for the reason that rover’s touchdown. That is the primary time the microphone was on when one handed over the rover.
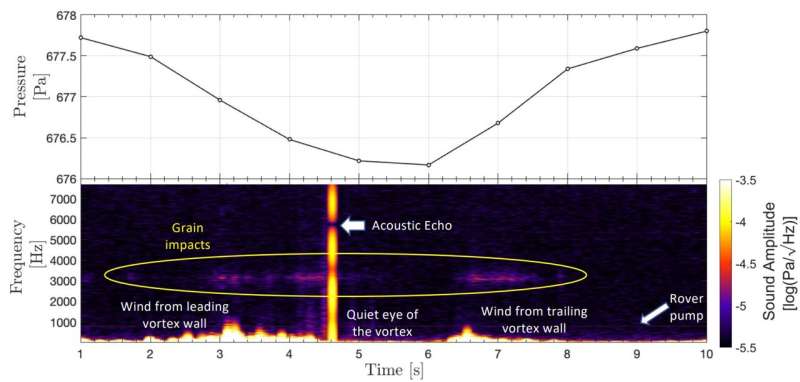
The sound recording of the dust satan, taken along with air stress readings and time-lapse pictures, assist scientists perceive the Martian environment and climate.
“We might watch the stress drop, take heed to the wind, then have a bit of little bit of silence that’s the eye of the tiny storm, after which hear the wind once more and watch the stress rise,” Wiens stated. All of it occurred in a couple of seconds.
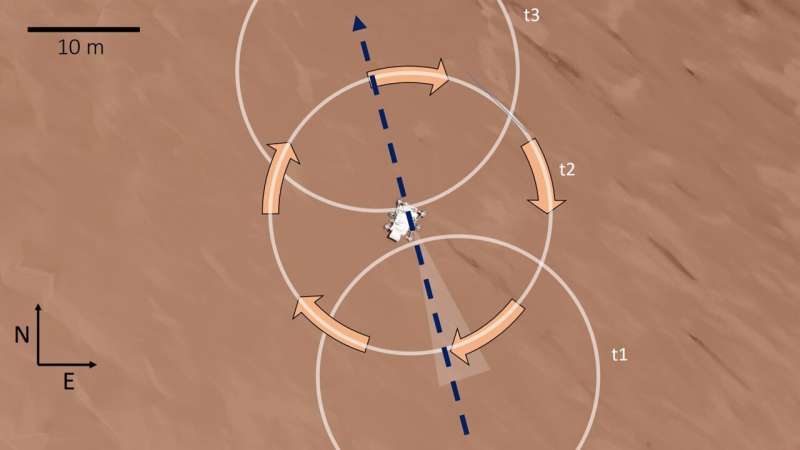
“The wind is quick—about 25 miles per hour, however about what you’d see in a dust satan on Earth. The distinction is that the air stress on Mars is a lot decrease that the winds, whereas simply as quick, push with about 1% of the stress the identical pace of wind would have again on Earth. It is not a strong wind, however clearly sufficient to loft particles of grit into the air to make a dust satan.”
The knowledge signifies that future astronauts won’t have to fret about gale-force winds blowing down antennas or habitats—so future Mark Watneys will not be left behind—however the wind might have some advantages. The breezes blowing grit off the solar panels of different rovers—particularly Alternative and Spirit—could also be what helped them final a lot longer.
“These rover groups would see a gradual decline in energy over quite a few days to weeks, then a soar. That was when wind cleared off the solar panels,” Wiens stated.
The shortage of such wind and dust devils within the Elysium Planitia the place the InSight mission landed might assist clarify why that mission is winding down.
“Similar to Earth, there’s totally different climate in numerous areas on Mars,” Wiens stated. “Utilizing all of our devices and instruments, particularly the microphone, helps us get a concrete sense of what it might be prefer to be on Mars.”
Extra info:
Naomi Murdoch et al, The sound of a Martian dust satan, Nature Communications (2022). DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-35100-z. www.nature.com/articles/s41467-022-35100-z
Supplied by
Purdue University
Quotation:
Scientists get first-ever sound recording of dust devils on Mars (2022, December 13)
retrieved 13 December 2022
from https://phys.org/information/2022-12-scientists-first-ever-devils-mars.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any truthful dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for info functions solely.




