A Curtin-led analysis workforce has discovered asteroid impacts on the moon tens of millions of years in the past coincided exactly with a few of the largest meteorite impacts on Earth, such because the one which worn out the dinosaurs.
The research additionally discovered that main affect occasions on Earth weren’t stand-alone occasions, however had been accompanied by a collection of smaller impacts, shedding new gentle on asteroid dynamics within the inside solar system, together with the chance of doubtless devastating Earth-bound asteroids.
The worldwide analysis workforce studied microscopic glass beads aged as much as 2 billion years outdated that had been present in lunar soil introduced again to Earth in December 2020 as a part of the Chinese language Nationwide House Company’s Chang’e-5 Lunar mission. The warmth and strain of meteorite impacts created the glass beads and so their age distribution ought to mimic the impacts, revealing a timeline of bombardments.
Lead writer Professor Alexander Nemchin, from Curtin College’s House Science and Expertise Middle (SSTC) within the College of Earth and Planetary Sciences, stated the findings suggest that the timing and frequency of asteroid impacts on the moon might have been mirrored on Earth, telling us extra concerning the historical past of evolution of our personal planet.
“We mixed a variety of microscopic analytical methods, numerical modeling, and geological surveys to find out how these microscopic glass beads from the moon had been fashioned and when,” Professor Nemchin stated.
“We discovered that a few of the age teams of the lunar glass beads coincide exactly with the ages of a few of the largest terrestrial affect crater occasions, together with the Chicxulub affect crater chargeable for the dinosaur extinction occasion.
“The research additionally discovered that giant affect occasions on Earth such because the Chicxulub crater 66 million years in the past may have been accompanied by quite a few smaller impacts. If that is appropriate, it means that the age-frequency distributions of impacts on the moon would possibly present invaluable details about the impacts on the Earth or inside solar system.”
Co-author Affiliate Professor Katarina Miljkovic, additionally from Curtin’s SSTC, stated future comparative research may give additional perception into the geological historical past of the moon.
“The following step could be to check the information gleaned from these Chang’e-5 samples with different lunar soils and crater ages to have the ability to uncover different important moon-wide affect occasions which could in flip reveal new proof about what impacts might have affected life on Earth,” Affiliate Professor Miljkovic stated.
-
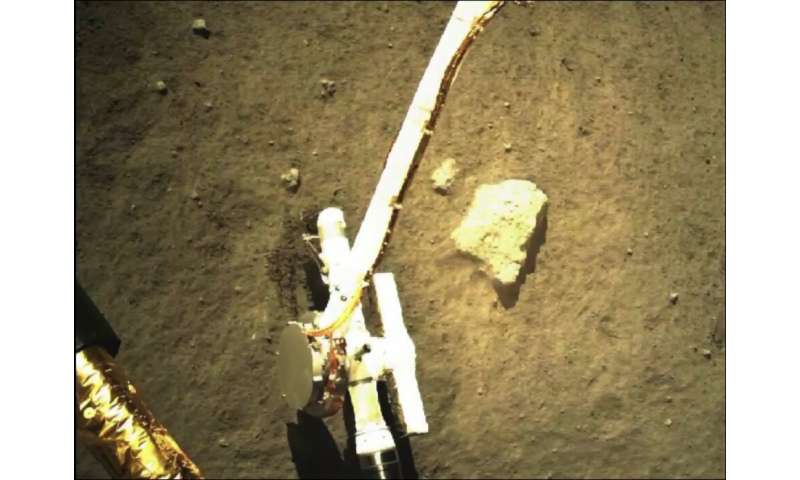

Chang’e-5 Lunar probe gathering. Credit score: CNSA Lunar Exploration and House Engineering Middle
-
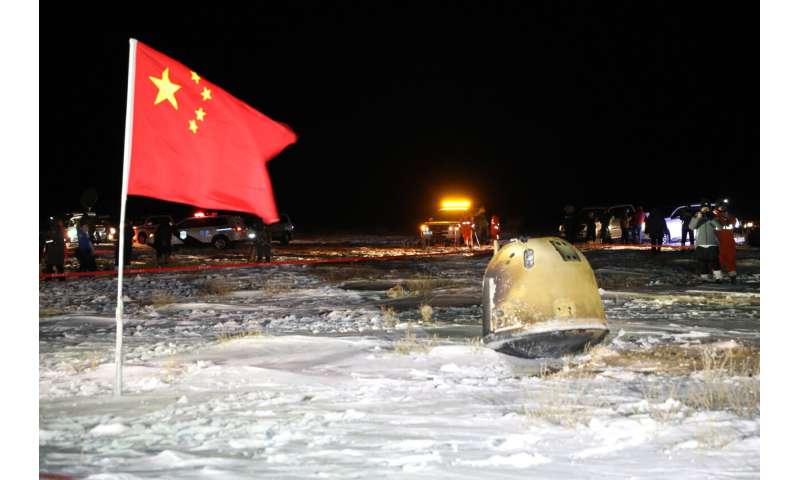

Chang’e-5 return capsule. Credit score: CNSA Lunar Exploration and House Engineering Middle
-
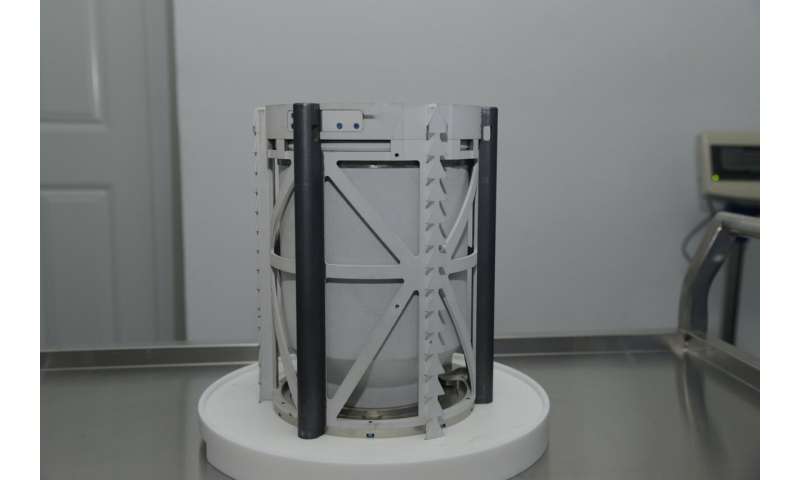

Chang’e-5 lunar samples capsule. Credit score: CNSA Lunar Exploration and House Engineering Middle
-
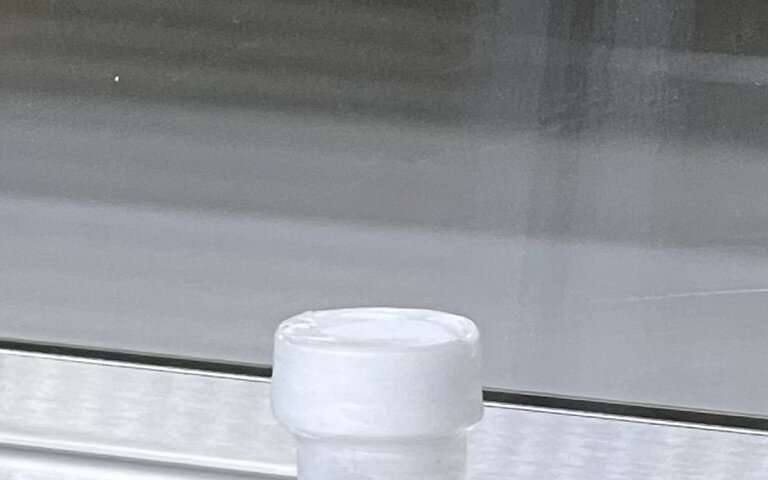

Chang’e-5 lunar soil from CE5C0400. Credit score: Beijing SHRIMP Middle, Institute of Geology, CAGS
The international collaboration was supported by the Australian Analysis Council and concerned researchers from Australia, China, U.S., UK and Sweden together with co-authors Dr. Marc Norman from the Australian Nationwide College, Dr. Tao Lengthy from the Beijing SHRIMP Middle on the Chinese language Academy of Geological Sciences and Ph.D. scholar Yuqi Qian from the China College of Geosciences.
Titled “Constraining the formation and transport of lunar affect glasses utilizing the ages and chemical compositions of Chang’e-5 glass beads,” the analysis was printed in Science Advances.
Tao Lengthy, Constraining the formation and transport of lunar affect glasses utilizing the ages and chemical compositions of Chang’e-5 glass beads, Science Advances (2022). DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.abq2542. www.science.org/doi/10.1126/sciadv.abq2542
Quotation:
Lunar glass reveals moon asteroid impacts mirrored on Earth (2022, September 28)
retrieved 28 September 2022
from https://phys.org/information/2022-09-lunar-glass-moon-asteroid-impacts.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any truthful dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for data functions solely.




