How distant is doomed Betelgeuse?
Betelgeuse, the intense pink star within the constellation Orion the Hunter, is in the long run stage of its stellar life. Sometime, it’ll explode as a supernova. In late 2019 and early 2020, Betelgeuse abruptly and unexpectedly dimmed. Some joked it’d quickly explode! It didn’t, however nonetheless … what if it did? When Betelgeuse goes supernova, will it have an effect on earthly life? How distant is Betelgeuse?
The excellent news is that if Betelgeuse explodes, it’s shut sufficient to placed on a spectacular gentle present however far sufficient to not trigger us on Earth any hurt. To reply the space query first, Betelgeuse is roughly 724 light-years away. However getting that reply, even for a comparatively close by star, is surprisingly troublesome.
New measurement methods
It’s solely within the final 30 years that astronomers have obtained extra correct measurements for the space to Betelgeuse and different close by stars. New applied sciences clarify this advance. It started in 1989, when the European House Company (ESA) launched a space telescope known as Hipparcos, named after the well-known Greek astronomer Hipparchus. Over a number of years of observations, the Hipparcos space telescope offered parallax and distance information for greater than 100,000 comparatively close by stars.
These measurements turned the premise for a lot of the estimated distances to stars that you simply see immediately.
The unique Hipparcos information gave a parallax of seven.63 milliarcseconds for Betelgeuse; that’s about one-millionth the width of the full moon. Computations based mostly on that parallax yielded a distance of about 430 light-years.
Measurement errors
However Betelgeuse is what’s often called a variable star. Which means its brightness fluctuates with time. That mentioned, the excitement over Betelgeuse’s dimming was as a result of it was the largest dip in brightness ever noticed. And therein started the issue in estimating Betelgeuse’s distance.
Subsequent research discovered an error within the strategies used for decreasing the Hipparcos information for variable stars. An effort to right these errors gave a parallax of 5.07 milliarcseconds. That modified Betelgeuse’s estimated distance from 430 light-years to about 643 light-years, plus or minus 46 light-years.
However wait, there’s extra. In 2017, astronomers published new calculations that additional refined Betelgeuse’s parallax to 4.51 milliarcseconds. This new evaluation of knowledge from Hipparcos additionally included observations from a number of ground-based radio telescopes. That positioned Betelgeuse at a distance of about 724 light-years, or, extra precisely, between 613 and 881 light-years, when information uncertainties are included.
Why Gaia can’t measure the space of Betelgeuse
You would possibly know that the European House Company’s Gaia astrometry mission has the purpose of constructing a three-dimensional map of our Milky Way galaxy. With Gaia’s 3rd data release in June 2022, ESA mentioned it now had estimates for almost 2 billion stars within the galaxy.
But Betelgeuse isn’t a kind of stars, and astronomers can’t use Gaia to discover a extra exact distance for Betelgeuse. The reason being that Betelgeuse is simply too vibrant for the spacecraft’s sensors.
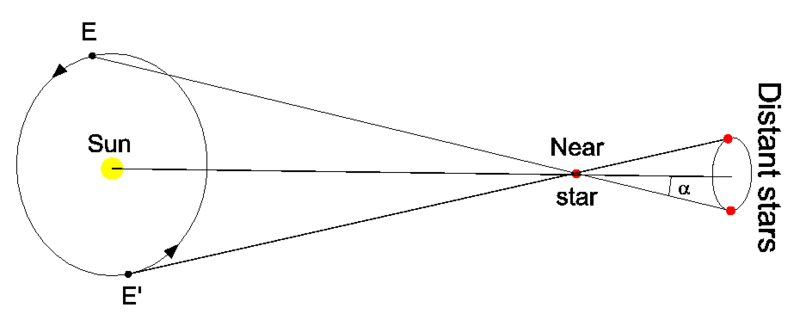
Extra about parallax
Have you ever ever seen a close-by object from two completely different places and observed how its place modified with respect to distant landmarks? That’s the impact known as parallax. Astronomers receive measurements of a close-by star’s place within the sky relative to distant background stars six months aside. Throughout that point, Earth has traveled to the alternative aspect of its orbit. Thus, two places are about 186 million miles (300 million km) aside, or the diameter of Earth’s orbit. The distinction within the close by star’s relative place on the two places permits astronomers to derive a parallax angle and calculate a distance to the close by star.
Historical Greek astronomers understood the idea of parallax, however they lacked the expertise to make very wonderful angular measurements on the sky. Because of this, all measurements of stellar parallax failed till German astronomer Friedrich Bessel succeeded in 1838. He used a telescope, and although his two observing places had been on reverse sides of Earth’s orbit, he was barely in a position to make out a tiny angular displacement. However it was sufficient to find out a distance of 11 light-years to the close by star 61 Cygni.
Limits of utilizing parallax
From Bessel’s time till Hipparcos’ launch in 1989, astronomers compiled only some thousand parallaxes. The method was troublesome for quite a few components. The extraordinarily small angles concerned, imperfections within the devices, and the murkiness of Earth’s personal environment all hinder measurements. The environment distorts observations from the Earth, even from very clear and darkish places corresponding to deserts and mountaintops.
Hipparcos, in acquiring observations from space beginning in 1989, pushed previous the constraints imposed by Earth’s environment to get positional information of stars at unprecedented accuracy for that point. Astronomers are persevering with to refine these measurements with new improvements in devices and information evaluation, utilizing ground- and space-based observatories.
Backside line: Measuring the space to Betelgeuse is especially troublesome as a result of it’s a variable star. Advanced calculations based mostly on information from the Hipparcos space telescope and ground-based radio telescopes point out it’s about 724 light-years away.
Wish to maintain observe of how vibrant or dim Betelgeuse is on any given day? Comply with the Betelgeuse Status account on Mastodon.




