Due to new subtle strategies and state-of-the-art services, astronomy has entered a brand new period wherein the depth of the sky can lastly be accessed. The substances of our cosmic residence, the Milky Way galaxy—stars, gasoline, magnetic fields—can in the end be mapped in 3D.
The space between stars is soiled. It’s full of small dust grains, most of that are related in dimension with the smoke from a cigarette. The grains will not be spherical and consequently their lengthy axis tends to align with any native galactic magnetic fields. These dust grains additionally emit a polarized glow in the identical frequencies because the cosmic microwave background—the “ashes” of the Huge Bang—thus contaminating our view of the earliest moments within the lifetime of the universe.
In addition they take up among the starlight passing by way of them, very similar to a polaroid filter would, imprinting details about the magnetic fields inside which they stay on the polarization of the rising gentle. Polarization is a property of sunshine rays which signifies a attribute route they’ve, at all times perpendicular to the route gentle propagates in space.
Magnetic fields are tremendously essential for the evolution of our galaxy, regulating the formation of latest stars, shaping galactic buildings, and turning gasoline flows into cosmic accelerators extra highly effective than CERN.
The polarization of starlight is then the important thing: it holds the data on the all-important magnetic fields of the galaxy, and it’s the “dust fabric” that may assist us clear our view of the early universe—if solely we might observe sufficient of it, and research it in depth, in an effort to extract all the data it carries.
That is precisely the scope of the PASIPHAE survey, an international collaboration between the Institute of Astrophysics of FORTH (IA-FORTH) and the College of Crete in Greece, IUCAA in India, the South African Astronomical Observatory, the California Institute of Know-how in america, and the College of Oslo in Norway. PASIPHAE goals to measure the polarization of hundreds of thousands of stars over giant components of the sky. And now, we will catch a primary glimpse of the capabilities of this formidable endeavor.
A group of researchers, led by Dr. Vincent Pelgrims (previous PASIPHAE postdoctoral scholar at IA-FORTH and now a Marie Curie fellow on the Inter-university Institute for Excessive Energies at ULB in Belgium) has demonstrated the ability of the PASIPHAE information and reconstruction approach utilizing observations taken with its precursor instrument, the RoboPol polarimeter working at Skinakas Observatory in Greece over the previous 10 years.
The scientists measured the polarization of greater than 1,500 stars in part of the sky practically 15 instances the world of the full moon, mixed them with distances measured for every star by ESA’s Gaia satellite, and a classy algorithm they’ve developed, and mapped with unprecedented decision the magnetic fields in that route of the sky.
“That is the primary time that such a big quantity of the galactic magnetic field has been reconstructed in three dimensions with such positive decision,” says Dr. Pelgrims. “We discovered a number of dust clouds on this area of the galaxy, and we have been capable of decide for the primary time their distances—out to hundreds of sunshine years—in addition to their polarimetric properties, revealing the magnetic subject that permeates these clouds.”
The group is releasing this primary excessive decision tomographic map of the galactic magnetic subject over a considerable area of the sky, which they current in the present day (April 23) within the journal Astronomy & Astrophysics.
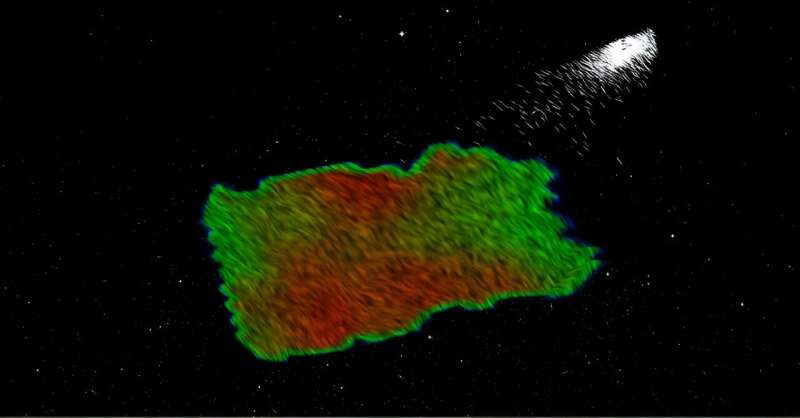
“This represents an incredible achievement towards a three-dimensional mapping of the Milky Way and its magnetic subject,” says Prof. Vasiliki Pavlidou from the College of Crete and affiliate school of IA-FORTH and co-author of the publication. “The construction of the galactic magnetic subject is at present not effectively constrained.
“This hampers progress in a number of analysis fields such because the research of the ultra-high vitality cosmic rays. The potential of such 3D mapping to result in breakthroughs in all domains linked to the galactic magnetic subject is critical.”
“In our paper, we’ve got solely scratched the floor of the chances that lie forward,” says Prof. Konstantinos Tassis, additionally of the College of Crete and affiliate school of IA-FORTH, co-author of the publication and principal investigator of the PASIPHAE undertaking.
“Think about such a map—however for a lot of the sky. This 3D atlas of the magnetic subject of the galaxy will turn out to be a actuality over the subsequent few years with the assistance of the devoted devices WALOPs that can begin mapping the polarization of stars within the sky this 12 months.”
Extra info:
V. Pelgrims et al, The primary degree-scale starlight-polarization-based tomography map of the magnetized interstellar medium, Astronomy & Astrophysics (2024). DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361/202349015
Offered by
Institute of Astrophysics
Quotation:
A primary glimpse at our galaxy’s magnetic subject in 3D (2024, April 23)
retrieved 23 April 2024
from https://phys.org/information/2024-04-glimpse-galaxy-magnetic-field-3d.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any truthful dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for info functions solely.




