Our Milky Way galaxy is an awe-inspiring function of the night time sky, viewable with the bare eye as a hazy band of stars stretching from horizon to horizon.
For the primary time, the IceCube Neutrino Observatory in Antarctica has produced a picture of the Milky Way utilizing neutrinos—tiny, ghost-like astronomical messengers.
In analysis revealed June 29 within the journal Science, the IceCube Collaboration—a world group of greater than 350 scientists—presents proof of high-energy neutrino emission coming from the Milky Way.
We’ve not but found out precisely the place in our galaxy these particles are coming from. However immediately’s end result brings us nearer to discovering among the galaxy’s most excessive environments.
Neutrino astronomy
Neutrinos supply a singular view of the cosmos as they will journey straight from locations no different radiation or particles can escape from. This makes them very fascinating to astronomers, as a result of neutrinos supply a window into the intense cosmic environments that create one other sort of particle referred to as cosmic rays.
Cosmic rays are high-energy particles that permeate our universe, however their origins are troublesome to pin down. Cosmic rays are electrically charged, which suggests their path by space is scrambled by magnetic fields, and by the point one arrives at Earth there isn’t a method to inform the place it got here from.
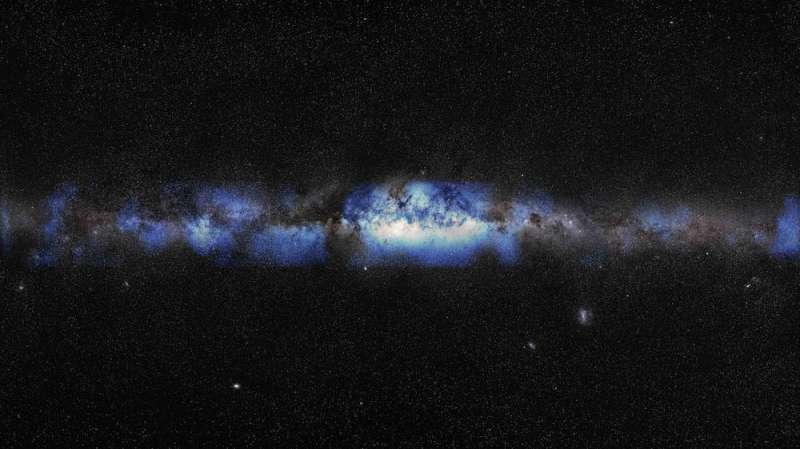

Nevertheless, the environments that speed up cosmic rays to extraordinary energies additionally produce neutrinos—and neutrinos haven’t any electric charge, in order that they journey in good straight traces. So if we will detect the trail of neutrinos arriving at Earth, this may level again to the place the neutrinos had been created.
However detecting these neutrinos just isn’t really easy.
The best way to hunt neutrinos
The IceCube Neutrino Observatory just isn’t removed from the South Pole. It makes use of greater than 5,000 light sensors arrayed all through a cubic kilometer of pristine Antarctic ice to seek for indicators of high-energy neutrinos from our galaxy and past.
Huge numbers of neutrinos are streaming by Earth on a regular basis, however solely a tiny fraction of them stumble upon something on their means by.
Every neutrino interplay makes a tiny flash of sunshine—and people tiny flashes are what the IceCube sensors look out for. The route and vitality of the neutrino may be decided from the quantity and sample of sunshine detected.
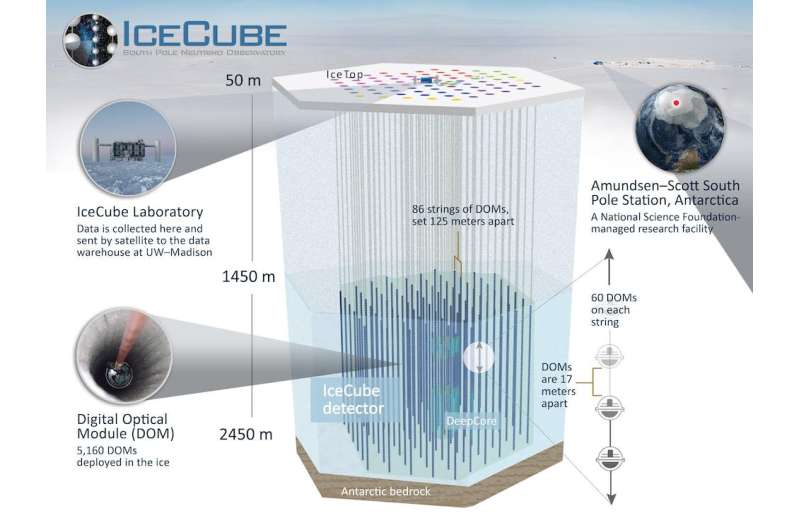
IceCube has beforehand detected high-energy neutrinos coming from outdoors the Milky Way. Nevertheless, it has been more difficult to isolate the lower-energy neutrinos coming from inside our galaxy.
It’s because some flashes IceCube detected may be traced to cosmic rays hitting Earth’s environment, which create neutrinos and different particles referred to as muons. To filter out these flashes, IceCube researchers have developed methods to tell apart particles created within the environment and people from additional afield by the form of the sunshine patterns they create within the ice.
Filtering out the undesirable detections has made IceCube extra delicate to astrophysical neutrinos. The ultimate breakthrough that allowed the creation of a neutrino picture of the Milky Way got here from machine-learning strategies that enhance the identification of cascades of sunshine produced by neutrinos, in addition to the willpower of the neutrino’s route and vitality.
Closing in on cosmic rays
The brand new neutrino lens on our galaxy will assist reveal the place probably the most highly effective accelerators of galactic cosmic rays are positioned. We hope to find out how energetic these particles can get, and the inside workings of those high-energy galactic engines.
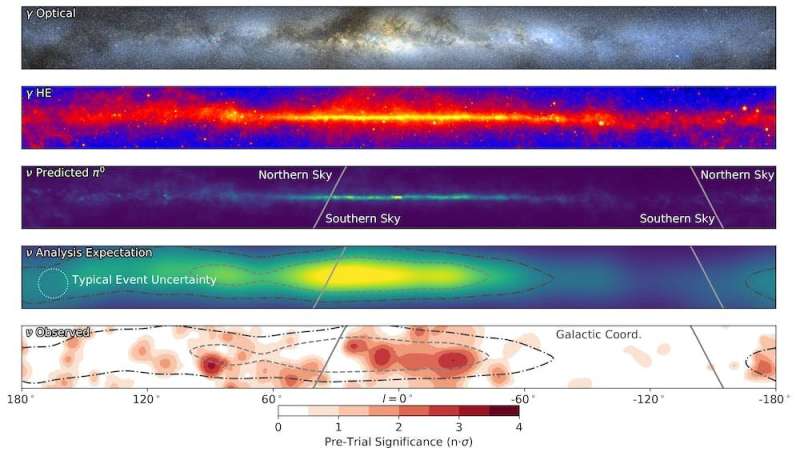
Nevertheless, we’re but to pinpoint these accelerators throughout the Milky Way. The brand new IceCube evaluation discovered proof for neutrinos coming from broad areas of the galaxy, however was not capable of discern particular person sources.
Our workforce, on the College of Canterbury in New Zealand and the College of Adelaide in Australia, has a plan to understand that subsequent step.
We’re making fashions to foretell the neutrino sign near probably particle accelerators so we will goal our searches for neutrinos.

Undergraduate scholar Rhia Hewett and Ph.D. scholar Ryan Burley are inspecting pairs of accelerator candidates and molecular dust clouds. They plan to estimate the flux of neutrinos produced by cosmic rays interacting within the clouds, after the neutrinos journey from the accelerators.
They’ll use their outcomes to allow a targeted search of IceCube information for the sources of neutrino emissions. We imagine this may present the important thing to utilizing IceCube to unlock the secrets and techniques of probably the most energetic processes within the Milky Way.
Extra data:
et al, Remark of high-energy neutrinos from the Galactic airplane, Science (2023). DOI: 10.1126/science.adc9818
Offered by
The Conversation
This text is republished from The Conversation underneath a Inventive Commons license. Learn the original article.![]()
Quotation:
A neutrino portrait of our galaxy reveals high-energy particles from throughout the Milky Way (2023, July 1)
retrieved 1 July 2023
from https://phys.org/information/2023-06-neutrino-portrait-galaxy-reveals-high-energy.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any honest dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for data functions solely.




