The universe is increasing, however how briskly precisely? The reply seems to rely on whether or not you estimate the cosmic enlargement charge—known as the Hubble’s fixed, or H0—primarily based on the echo of the Large Bang (the cosmic microwave background, or CMB) otherwise you measure H0 straight primarily based on immediately’s stars and galaxies. This downside, often known as the Hubble pressure, has puzzled astrophysicists and cosmologists world wide.
A examine carried out by the Stellar Normal Candles and Distances analysis group, led by Richard Anderson at EPFL’s Institute of Physics, provides a brand new piece to the puzzle. Their analysis, revealed in Astronomy & Astrophysics, has achieved probably the most correct calibration of Cepheid stars—a sort of variable star whose luminosity fluctuates over an outlined interval—for distance measurements up to now primarily based on information collected by the European House Company’s (ESA’s) Gaia mission. This new calibration additional amplifies the Hubble pressure.
The Hubble fixed (H0) is called after the astrophysicist who—along with Georges Lemaître—found the phenomenon within the late Nineteen Twenties. It is measured in kilometers per second per megaparsec (km/s/Mpc), the place 1 Mpc is round 3.26 million mild years.
The perfect direct measurement of H0 makes use of a “cosmic distance ladder,” whose first rung is ready by absolutely the calibration of the brightness of Cepheids, now recalibrated by the EPFL examine. In flip, Cepheids calibrate the subsequent rung of the ladder, the place supernovae—highly effective explosions of stars on the finish of their lives—hint the enlargement of space itself.
This distance ladder, measured by the Supernovae, H0, for the Equation of State of darkish power (SH0ES) workforce led by Adam Riess, winner of the 2011 Nobel Prize in Physics, places H0 at 73.0 ± 1.0 km/s/Mpc.
First radiation after the Large Bang
H0 will also be decided by deciphering the CMB—which is the ever-present microwave radiation left over from the Large Bang greater than 13 billion years in the past. Nonetheless, this “early universe” measurement technique has to imagine probably the most detailed bodily understanding of how the universe evolves, rendering it mannequin dependent. The ESA’s Planck satellite has offered probably the most full information on the CMB, and in response to this technique, H0 is 67.4 ± 0.5 km/s/Mpc.
The Hubble pressure refers to this discrepancy of 5.6 km/s/Mpc, relying on whether or not the CMB (early universe) technique or the gap ladder (late universe) technique is used. The implication, offered that the measurements carried out in each strategies are appropriate, is that there’s something improper within the understanding of the fundamental bodily legal guidelines that govern the universe. Naturally, this main difficulty underscores how important it’s for astrophysicists’ strategies to be dependable.
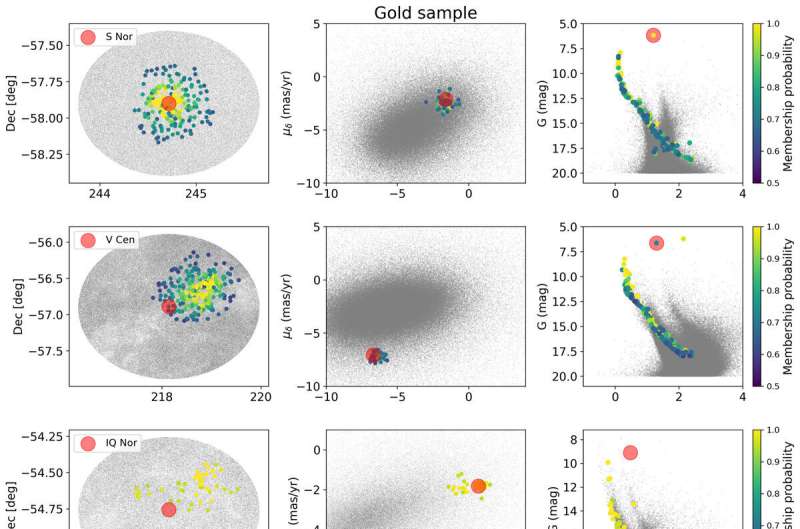
The brand new EPFL examine is so vital as a result of it strengthens the primary rung of the gap ladder by enhancing the calibration of Cepheids as distance tracers. Certainly, the brand new calibration permits us to measure astronomical distances to inside ± 0.9%, and this lends sturdy help to the late universe measurement. Moreover, the outcomes obtained at EPFL, in collaboration with the SH0ES workforce, helped to refine the H0 measurement, leading to improved precision and an elevated significance of the Hubble pressure.
“Our examine confirms the 73 km/s/Mpc enlargement charge, however extra importantly, it additionally gives probably the most exact, dependable calibrations of Cepheids as instruments to measure distances up to now,” says Anderson.
“We developed a way that looked for Cepheids belonging to star clusters made up of a number of lots of of stars by testing whether or not stars are shifting collectively by the Milky Way. Because of this trick, we might make the most of one of the best information of Gaia’s parallax measurements whereas benefiting from the acquire in precision offered by the various cluster member stars. This has allowed us to push the accuracy of Gaia parallaxes to their restrict and gives the firmest foundation on which the gap ladder will be rested.”
Rethinking fundamental ideas
Why does a distinction of only a few km/s/Mpc matter, given the huge scale of the universe? “This discrepancy has an enormous significance,” says Anderson.
“Suppose you wished to construct a tunnel by digging into two reverse sides of a mountain. In the event you’ve understood the kind of rock accurately and in case your calculations are appropriate, then the 2 holes you are digging will meet within the middle. But when they do not, meaning you’ve got made a mistake—both your calculations are improper otherwise you’re improper about the kind of rock.
“That is what is going on on with the Hubble fixed. The extra affirmation we get that our calculations are correct, the extra we are able to conclude that the discrepancy means our understanding of the universe is mistaken, that the universe is not fairly as we thought.”
The discrepancy has many different implications. It calls into query the very fundamentals, like the precise nature of darkish power, the time-space continuum, and gravity. “It means we’ve to rethink the fundamental ideas that type the muse of our total understanding of physics,” says Anderson.
His analysis group’s examine makes an vital contribution in different areas, too. “As a result of our measurements are so exact, they offer us perception into the geometry of the Milky Way,” says Mauricio Cruz Reyes, a Ph.D. scholar in Anderson’s analysis group and lead writer of the examine. “The extremely correct calibration we developed will allow us to higher decide the Milky Way’s measurement and form as a flat-disk galaxy and its distance from different galaxies, for instance. Our work additionally confirmed the reliability of the Gaia information by evaluating them with these taken from different telescopes.”
Extra info:
Mauricio Cruz Reyes et al, A 0.9% calibration of the Galactic Cepheid luminosity scale primarily based on Gaia DR3 information of open clusters and Cepheids, Astronomy & Astrophysics (2023). DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361/202244775
Supplied by
Ecole Polytechnique Federale de Lausanne
Quotation:
A brand new measurement might change our understanding of the universe (2023, April 4)
retrieved 4 April 2023
from https://phys.org/information/2023-04-universe.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any truthful dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for info functions solely.




