The race is on to find really liveable Earth-like worlds. Whereas we’re beginning to observe the atmospheres of huge doubtlessly liveable planets comparable to Hycean worlds with the telescopes we presently have, probably the most vital breakthroughs will seemingly include the event of superior specialised telescopes. These new designs will seemingly use a starshade to cover the glare of a star and permit us to instantly observe its exoplanets. However will that be sufficient to check distant terrestrial planets?
For the reason that Nineteen Thirties, astronomers have used varied methods to take away glare from a vivid object to disclose fainter objects. For instance, to disclose the solar corona much like what occurs throughout a solar eclipse, astronomers have used a coronagraph that exactly blocks the limb of the sun inside a telescope. The concept was prolonged to have a look at massive planets round stars, the place a small filter hides the starlight from view in order that close by planets could be seen. Nevertheless, these filters had been typically positioned throughout the telescope itself, which limits the precision of the filter.
A starshade would take away the filter from the telescope and place it a big distance from the telescope itself. For a space telescope, this implies having two spacecraft, one for the telescope and one for the shade. By inserting the 2 1000’s of kilometers aside, astronomers would be capable of see planets orbiting extraordinarily near their star. This shall be significantly helpful for Earth-like worlds orbiting red dwarf stars of their habitable zone, that are by far the commonest doubtlessly liveable worlds.
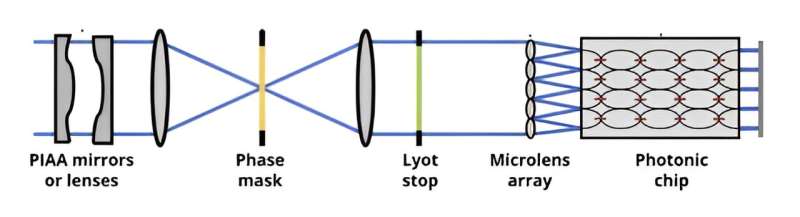
One drawback with that is that crimson dwarfs are a lot fainter than sun-like stars, and the starlight mirrored off their planets is much more faint. So even with a sophisticated starshade to dam the starlight, the planets should be too faint to look at. However a brand new paper on the arXiv preprint server argues that this drawback could possibly be solved because of a sophisticated sort of optics often known as photonics.
Whereas conventional optics can seize faint gentle, photonics works on the size of particular person photons. One in every of its widespread makes use of right this moment is in fiber optic communication, so for those who occur to have fiber web, thank photonics. In astronomy, photonics has been used for issues comparable to high-resolution spectroscopy and the detectors of some radio telescopes.
On this paper, the authors describe ways in which coronagraphs comparable to starshades could possibly be utilized in reference to photonic detectors, making a hybrid system able to observing a lot fainter planets. For instance, gentle on the fringe of a starshade could possibly be centered by microlenses right into a bundle of fiber cables, which might then be routed to particular person photodetectors. The authors word that with cautious design a telescope might detect an optical distinction of greater than 10 billion.
Starshade observatories such because the proposed Liveable Exoplanet Observatory (HabEx) are nonetheless a good distance off. It can seemingly be the 2040s earlier than such a telescope could possibly be launched. So there’s loads of time for astronomical photonics to be developed and improved. However this examine reveals it might revolutionize the way in which we see the universe.
Extra info:
Niyati Desai et al, Built-in photonic-based coronagraphic techniques for future space telescopes, arXiv (2023). DOI: 10.48550/arxiv.2309.04925
Journal info:
arXiv
Offered by
Universe Today
Quotation:
An bold new expertise could be wanted to see different Earths (2023, September 19)
retrieved 20 September 2023
from https://phys.org/information/2023-09-ambitious-technology-earths.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any truthful dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for info functions solely.




