Simulated flyover view of Hydraotes Chaos, a area of chaotic terrain on Mars. The information for the simulation is from the European House Company’s Mars Express orbiter. Researchers discovered an historical mud lake on this area. May this mud lake on Mars maintain traces of historical microbial life? Video through ESA/ DLR/ FU Berlin.
If there was ever life on Mars billions of years in the past, we should be capable of discover traces of it. And historical lakes or different water-related sediments are good locations to look. On October 18, 2023, researchers on the Planetary Science Institute announced that they found proof for an historical mud lake on Mars that might be superb to protect such microscopic biosignatures, in the event that they ever existed. A mud lake is a lake with accumulating muddy sediments on the underside. The mud lake on Mars is close to the northern lowlands in a area of complicated shaped from historical flood channels and aquifers.
The researchers, led by Alexis Rodriguez on the Planetary Science Institute, published their peer reviewed paper in Scientific Reviews (Nature) on October 18.
An historical mud lake on Mars in Hydraotes Chaos
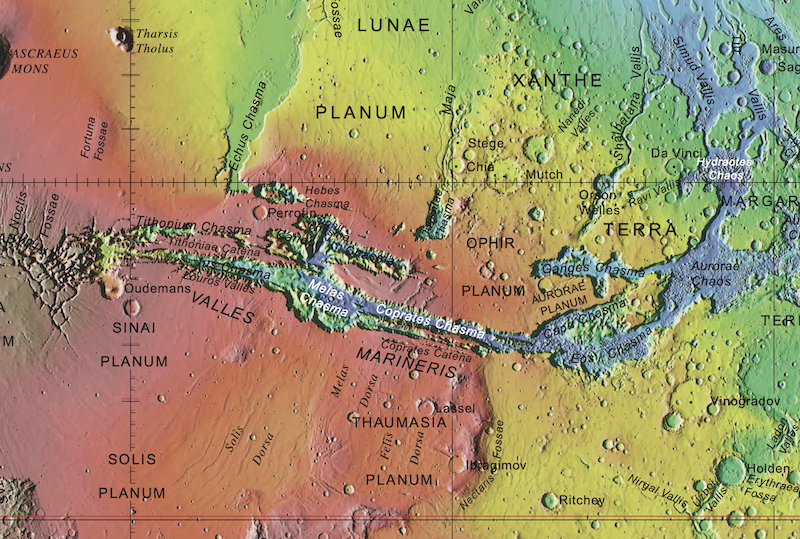
The mud lake is in a area known as Hydraotes Chaos, which is simply above the equator close to the east finish of the huge canyon Valles Marineris. This space is what scientists name chaotic terrain or chaos terrain, the place aquifers as soon as existed beneath the floor. In reality, the mud lake’s supply of water was the aquifers on this space. The drier floor collapsed above the aquifers on this area, creating the jumbled “chaotic” terrain we see right this moment.
Drainage – the pure elimination of extra water – from the aquifers additionally shaped the sedimentary plains inside Hydraotes Chaos. These sediments, as soon as wealthy in water, may have preserved traces of historical Martian microorganisms, simply as they do on Earth. That subsurface surroundings may even have endured lengthy after all of the water dried up on the floor and have become inhospitable.
The 2024 lunar calendars are here! Best Christmas gifts in the universe! Check ’em out here.
Rodriguez said:
Our analysis focuses on a sedimentary unit inside Hydraotes Chaos, which we interpret to be the remnants of a mud lake shaped by discharges from gas-charged mudstone stratigraphy relationship again to just about 4 billion years in the past, a time when the floor of Mars was seemingly liveable. These sediments may harbor proof of life from that or subsequent intervals. You will need to keep in mind that the subsurface of Mars might need included habitability lasting the length of life’s historical past on Earth.
A fancy panorama
As well as, historical flood channels, 1000’s of miles lengthy, lower throughout the Martian floor and finish within the northern lowlands. Scientists have lengthy postulated {that a} former ocean as soon as crammed these lowlands. The channels induced intensive erosion and launched subsurface sediments from the aquifers. That materials now covers a lot of the northern lowlands. This complexity of the panorama could make it troublesome to check the traditional aquifers. As Rodriguez defined:
Venturing into the northern plains for sampling may show precarious, as distinguishing between supplies sourced from the aquifers and people eroded and transported throughout channel formation may develop into an intricate process. The plains, located inside Hydraotes Chaos, supply a singular glimpse into historical aquifer supplies. These plains, which we expect shaped from mud extruding right into a basin immediately above their supply aquifer, present a extra focused exploration alternative. In contrast to huge flood channels with their complicated erosion patterns, this discovering simplifies the examination of Martian aquifers, lowering the chance of overland sedimentary acquisition, and opens a brand new window into Mars’ geological previous.
There are additionally mud volcanoes on this area. These small volcanoes as soon as launched moist sediments containing salts to the floor, as a substitute of scorching magma.
Big water-filled caverns
Along with the aquifers – that are water-rich porous rock – there have been additionally large water-filled chambers on this chaotic terrain. Co-author Bryan Travis on the Planetary Science Institute mentioned:
Our numerical fashions reveal an interesting story. The lake’s supply aquifer seemingly originated from phase segregation inside the mudstone, forming huge water-filled chambers, a number of kilometers extensive and tons of of meters deep. This course of was seemingly triggered by intrusive igneous exercise. Furthermore, the noticed segmented subsidence throughout the chaotic terrain suggests an interconnected community of chambers, depicting steady water-filled large caverns, some reaching kilometers in widths and lengths, approach bigger than any recognized Earth counterparts.
Mud lake on Mars may protect historical biomolecules
The ensuing mud lake would have been an excellent place to protect any biomolecules (organic molecules) related to life. Rodriguez mentioned:
Initially, biomolecules may have been dispersed all through the amount of huge groundwater-filled cavities. Because the water was launched to the floor and ponded, the water went away, forsaking lags of sediments and doubtlessly excessive concentrations of biomolecules.
Because the paper said:
The meltwater, originating from various thermally affected mudstone depths, may have doubtlessly harbored various biosignatures, which may have develop into concentrated inside the lake’s sedimentary residue.
A mission to Hydraotes Chaos?
The sediments left behind on the floor, from the unique aquifers, are nonetheless there right this moment. They’d, to make sure, be a great goal for sampling by a future Mars mission. And in reality, NASA is contemplating doing simply that, as co-author Mary Beth Wilhelm at NASA Ames Analysis Middle famous:
NASA Ames is contemplating the plains as a potential touchdown web site for a mission to seek for proof of biomarkers, particularly lipids. These biomolecules are extraordinarily resistant and will have endured billions of years on Mars.
The paper added:
Thus, we suggest that Hydraotes Chaos deserves precedence consideration in future missions aiming to detect Martian biosignatures.
Co-author Jeffrey Kargel on the Planetary Science Institute added:
As well as, the examine area consists of widespread mud volcanoes and potential diapirs, offering extra home windows into subsurface, doubtlessly liveable rocks. A small rover may, inside quick distances, pattern the mud lake sediments and these supplies, dramatically growing the chances of biosignature detection.
Backside line: Researchers on the Planetary Science Institute mentioned that an historical mud lake on Mars can be an excellent place to seek for proof of extinct microbial life.
Via Planetary Science Institute




