We all know that Mars had rivers and lakes within the distant previous. However what about oceans? There’s certainly tentative proof for an ancient ocean within the northern hemisphere. Nevertheless, scientists have been debating that proof for many years. However now, researchers in China and the U.S. say they’ve discovered new clues in marine sedimentary rocks in Utopia Planitia that will show the existence of that ocean. China’s Zhurong rover found the sedimentary formations. The researchers announced the tantalizing findings in Science China Press on Could 21, 2023.
Professor Long Xiao from the College of Earth Sciences at China College of Geosciences led the analysis group. The group published its accepted peer-reviewed paper in Nationwide Science Evaluate on Could 18, 2023. The paper continues to be present process ultimate enhancing, however is out there as a PDF.
New proof for historic ocean on Mars
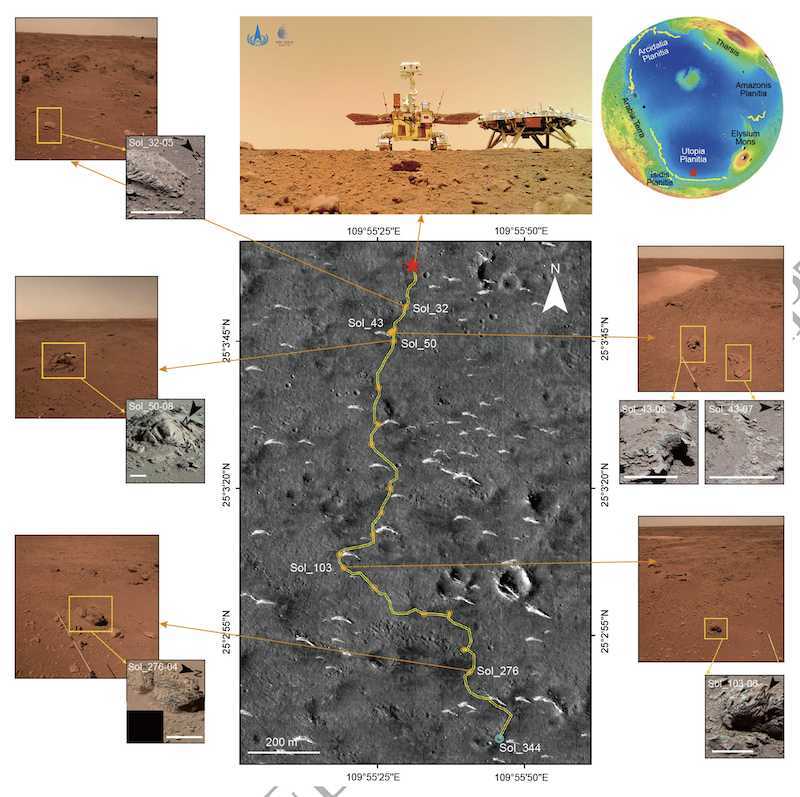
China’s Zhurong rover has been exploring its touchdown website on the southern fringe of Utopia Planitia, within the northern hemisphere of Mars. That is inside the northern lowlands that some scientists say was doubtless as soon as an ocean flooring. The rover’s latest findings now bolster that risk. The rover has been finding out the rocks within the space with its multispectral digital camera (MSCam), and the science group says that Zhurong has discovered marine sedimentary rocks. Whereas most different knowledge supporting the ocean speculation has come from orbiting spacecraft, this new knowledge is in situ (on website).
It’s the Vasitas Borealis Formation (VBF) that the mission scientists interpret to be marine sedimentary rocks. Because the paper explains:
A long time of analysis utilizing remotely-sensed knowledge have extracted proof for the presence of an ocean within the northern lowlands of Mars within the Hesperian, however these claims have remained controversial because of the lack of in situ evaluation of the related geologic unit, the Vastitas Borealis Formation (VBF). The Tianwen-1/Zhurong rover was focused to land inside the VBF close to its southern margin and has traversed virtually 1.2 miles (2 km) southward towards the interpreted shoreline. We report right here on the primary in situ evaluation of the VBF that reveals sedimentary constructions and options in floor rocks that counsel that the VBF was deposited in a marine atmosphere, offering direct assist for the existence of an historic (Hesperian) ocean on Mars.
Multispectral pictures present clues
Zhurong has been steadily transferring south, towards what’s considered an historic shoreline. The rover has taken 106 panoramic pictures up to now throughout its travels. Mission scientists have been finding out the multispectral pictures for clues concerning the rocks’ composition and origin. They discovered bedding constructions which might be completely different from the standard volcanic rock deposits on Mars.
As well as, they had been completely different from rock formations created by blowing sand.
A shallow sea atmosphere
Certainly, the photographs revealed bidirectional circulation, an indication of attainable low-energy tidal currents. They’re much like formations created in shallow marine environments on Earth. The mission group named this area the Zhurong Member. The rocks function small-scale cross-bedding, lens-shaped flaser bedding and small channel constructions.
The paper says:
Bidirectional present orientations are characteristically shaped by common reverse instructions of tidal currents in terrestrial shallow marine environments, and uncommonly in fluvial environments. Though aeolian deposits on Mars additionally comprise some small-scale cross-laminations, the shortage of bigger constructions indicative of aeolian environments helps the interpretation that these are of shallow marine origin.
The photographs additionally confirmed that the layers within the cross-bedding overlap and tilt in two reverse instructions. The thickness of the strata, in addition to the scale of sand grains additionally differs. That is proof for a bidirectional water circulation sample. On Earth, that is frequent in littoral-shallow sea environments.
Historical shorelines of an ocean on Mars and a wild river
Final 12 months, researchers at Penn State and Caltech said they found definitive traces of an outdated shoreline in Mars’ northern hemisphere.
And simply final week, scientists announced that the Perseverance rover has discovered proof for a rollicking river. It was the deepest and fastest-flowing river but noticed – now all dried up in fact – by any rover or lander.
The brand new findings from the Zhurong rover would appear to assist this, and add one other essential piece to the puzzle. That ocean would have been huge, masking a lot of the northern hemisphere of Mars. The subsequent query, in fact, is whether or not it supported any sort of life. Will probably be attention-grabbing to see what else Zhurong finds in its travels, in addition to any future missions to this now-dry ocean wonderland.
Backside line: Scientists in China say that the Zhurong rover has discovered new proof for an historic ocean on Mars, sedimentary rocks shaped in a shallow marine atmosphere. They developed new topographical maps, utilizing NASA knowledge. They estimated the traditional Martian shoreline to be 3.5 billion years outdated and it covers a whole lot of hundreds of sq. kilometers.
Source: Evidence for marine sedimentary rocks in Utopia Planitia: zhurong rover observations
Via Science China Press/ Eurekalert!




