The massive spiral galaxy subsequent door
Though several dozen minor galaxies lie nearer to our Milky Way, the Andromeda galaxy is the closest massive spiral galaxy to ours. Excluding the Large and Small Magellanic Clouds, seen from Earth’s Southern Hemisphere, the Andromeda galaxy is the brightest exterior galaxy seen in our night time sky. And, at 2.5 million light-years, it’s essentially the most distant factor we people can see with the unaided eye.
Observe: The massive spiral Triangulum galaxy is barely extra distant at 2.7 million light-years. Just like the Andromeda galaxy, it’s a member of our Local Group of galaxies. And it’s generally mentioned to be seen to the attention additionally. Nevertheless it’s turned face-on to us, and so has a low surface brightness. Not like the Andromeda galaxy, it’s very laborious to see.
Astronomers generally name the Andromeda galaxy by the title Messier 31, or M31. It was the thirty first on a well-known listing of fuzzy sky objects compiled by the French astronomer Charles Messier (1730-1817). His catalog listed “objects to keep away from” when comet-hunting. These days, beginner astronomers search out these objects with their telescopes and binoculars. They’re a few of most stunning deep-sky objects identified.
Most Messier objects are star clusters or fuel clouds in our Milky Way galaxy. However the Andromeda galaxy is a complete separate galaxy, even greater than our Milky Way. In a dark sky, you possibly can see that it’s huge on the sky as effectively, a smudge of distant gentle bigger than a full moon.
Some photos of M31 from our EarthSky neighborhood


When to search for it
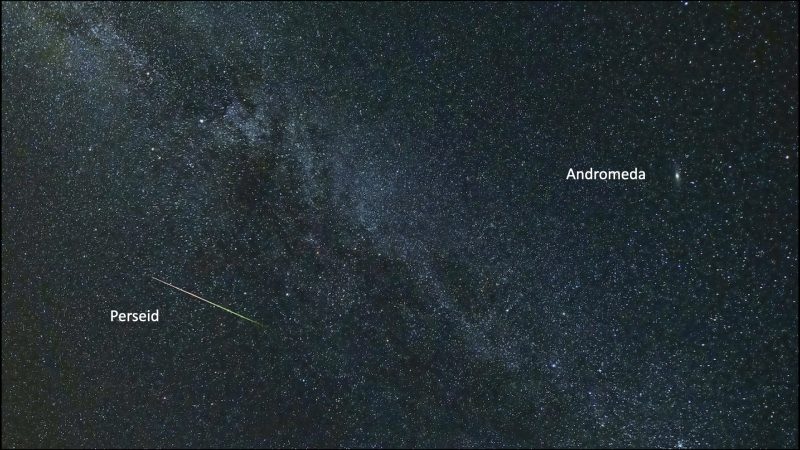
From mid-northern latitudes, you possibly can see Andromeda – M31 – for at the least a part of each night time, all yr lengthy. However most individuals see the galaxy first round August or September, when it’s excessive sufficient within the sky to be seen from night till dawn.
In early September, start in search of the galaxy in mid-evening, about halfway between your native dusk and midnight.
In late September and early October, the Andromeda galaxy shines in your japanese sky at dusk, swings excessive overhead in the course of the night time, and stands relatively excessive within the west on the onset of morning daybreak.
Winter evenings are additionally good for viewing the Andromeda galaxy.
If you’re far from city lights, and also you’re stargazing throughout a moonless night time through the late summer time, or on any autumn or winter night, it’s potential that you just’ll merely discover the galaxy there in your night time sky. However if you happen to don’t handle to simply see it, you possibly can star-hop to search out the galaxy in one in all two methods. The simplest approach is to make use of the constellation Cassiopeia the Queen. You may as well use the Great Square of Pegasus.
Use Cassiopeia to search out the Andromeda galaxy
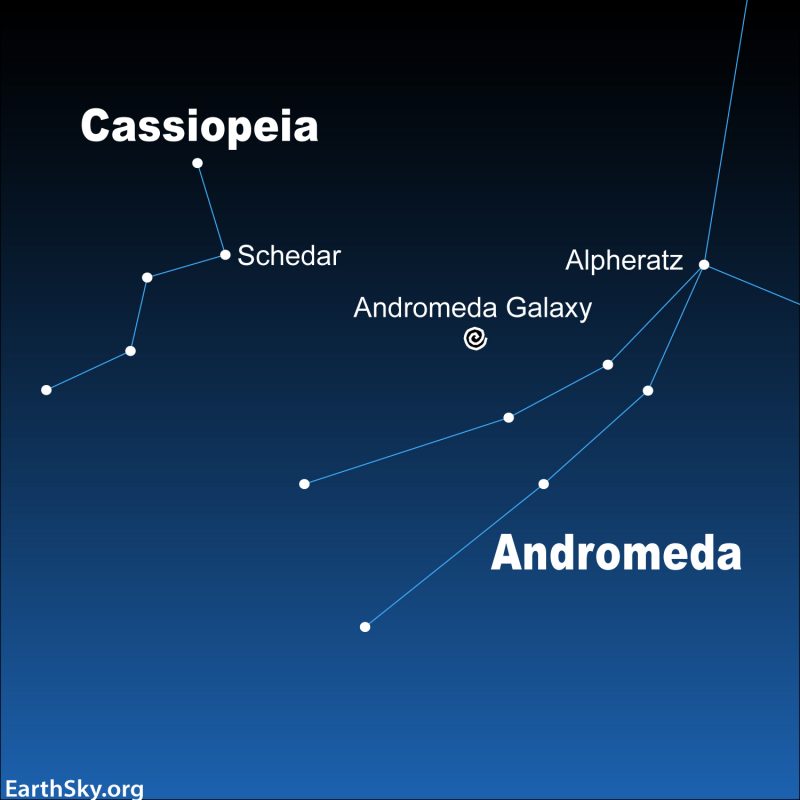
The constellation Cassiopeia is straightforward to search out. Look usually northward on the sky’s dome for a sample of stars formed just like the letter M or W. In the event you can acknowledge the North Star, Polaris – and if you understand how to search out the Large Dipper – bear in mind that the Large Dipper and Cassiopeia transfer round Polaris just like the fingers of a clock, all the time reverse one another.
When you’ve discovered Cassiopeia, search for its star Schedar. Within the illustration above, see how Schedar factors to the Andromeda galaxy?
Or use the Nice Sq. to search out M31
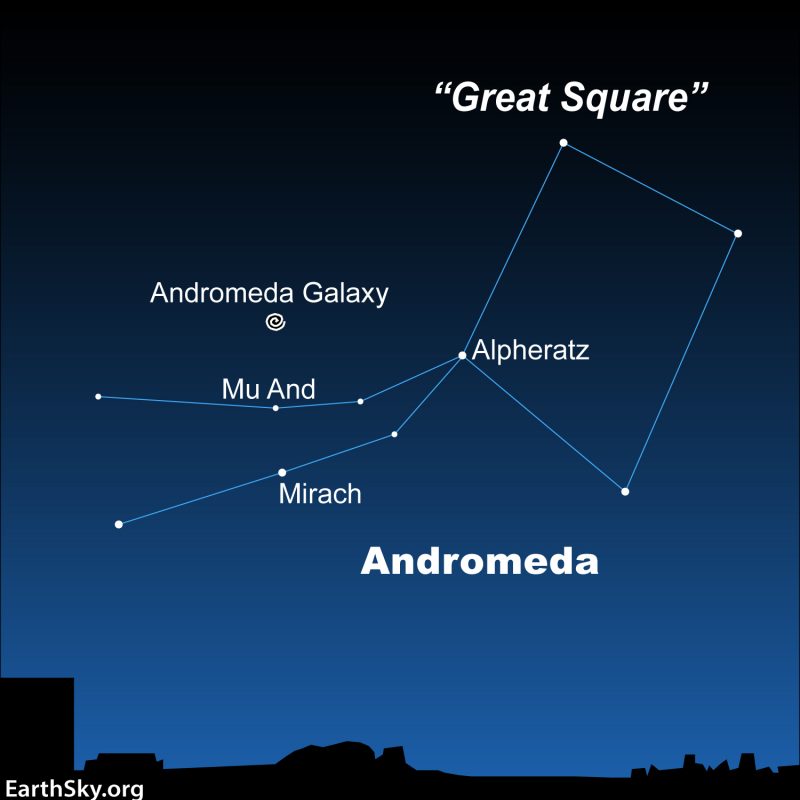
You may as well star-hop to the Andromeda galaxy, utilizing the Nice Sq. of Pegasus. It’s an extended route. However, in some ways, it’s extra stunning.
You’ll be hopping to the Andromeda galaxy from the Nice Sq. of Pegasus. In autumn, the Nice Sq. of Pegasus appears like an important huge baseball diamond within the japanese sky. Envision the underside star of the Sq.’s 4 stars as residence plate, then draw an imaginary line from the “1st base” star although the “third base” star to find two streamers of stars flying away from the Nice Sq.. These stars belong to the constellation Andromeda the Princess.
On every streamer, go two stars north (left) of the third base star, finding the celebrities Mirach and Mu Andromedae. Draw a line from Mirach by means of Mu Andromedae, going twice the Mirach/Mu Andromedae distance. You’ve simply landed on the Andromeda galaxy, which appears like a smudge of sunshine to the unaided eye.
In the event you can’t see the Andromeda galaxy with the attention alone, by all means use binoculars.
Historical past of our data of the Andromeda galaxy
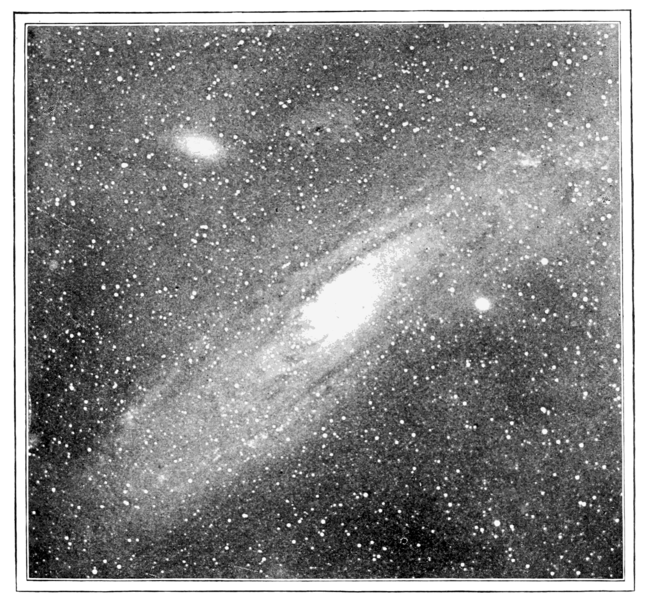

At one time, the Andromeda galaxy was known as the Nice Andromeda Nebula. Astronomers thought this patch of sunshine was composed of glowing gases, or was maybe a solar system within the means of formation.
It wasn’t till the twentieth century that astronomers have been capable of resolve the Andromeda spiral nebula into particular person stars. This discovery result in an issue about whether or not the Andromeda spiral nebula and different spiral nebulae lie inside or outdoors the Milky Way.
Within the Twenties Edwin Hubble lastly put the matter to relaxation, when he used Cepheid variable stars throughout the Andromeda galaxy to find out that it’s certainly an “island universe” residing past the bounds of our Milky Way galaxy.
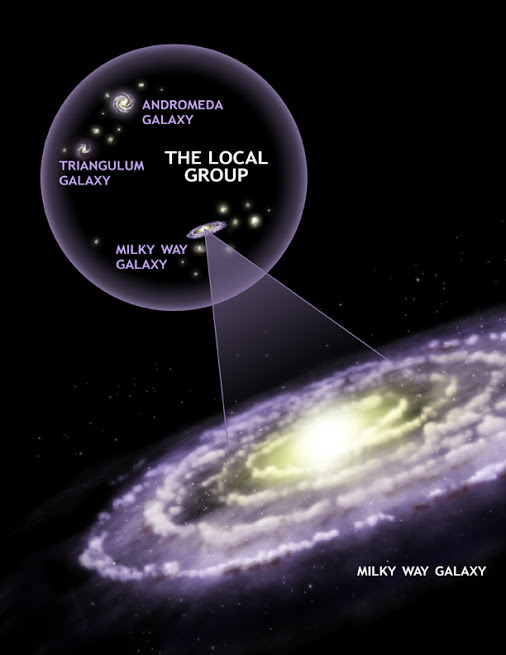
Andromeda and Milky Way in context
The Andromeda and Milky Way galaxies reign as the 2 most huge and dominant galaxies throughout the Local Group of galaxies. The Andromeda galaxy is the biggest galaxy of the Native Group, which, along with the Milky Way, additionally comprises the Triangulum galaxy and about 30 different smaller galaxies.
Each the Milky Way and the Andromeda galaxies lay declare to a couple of dozen satellite galaxies. Each are some 100,000 light-years throughout, containing sufficient mass to make billions of stars.
Astronomers have found that our Native Group is on the outskirts of an enormous cluster of a number of thousand galaxies, which astronomers name the Virgo Cluster.
We additionally know of an irregular supercluster of galaxies, which comprises the Virgo Cluster, which in flip comprises our Native Group, which in flip comprises our Milky Way galaxy and the close by Andromeda galaxy. No less than 100 galaxy teams and clusters are positioned inside this Virgo Supercluster. Its diameter is regarded as about 110 million light-years.
And the Virgo Supercluster is regarded as one in all thousands and thousands of superclusters within the observable universe.
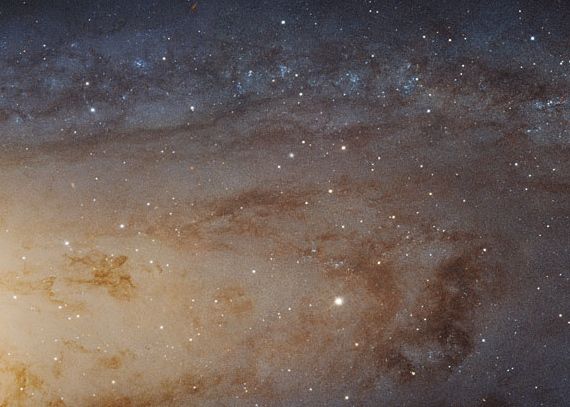

Will the Andromeda galaxy collide with the Milky Way?
One in all our readers wrote:
I’ve heard that the Andromeda galaxy will sometime collide with our galaxy! Is that also a particular chance?
A particular chance describes a lot of what we all know – or assume we all know – concerning the universe. As for the Andromeda galaxy and its future collision with our Milky Way: the primary try to measure the radial velocity of this galaxy (its movement ahead or again, alongside our line of sight) was made in 1912. After that, astronomers believed for some many years that the galaxy was approaching at practically 200 miles per second (321 km/s), however later astronomers disagreed.
Then in Could 2012, NASA astronomers announced they will now predict the time of this collision of titanic galaxies with certainty. Bear in mind, although, that the Andromeda galaxy is 2.2 million light-years away, with a single light-year being nearly 6 trillion miles (10 trillion kilometers). So though it does seem that this galaxy is approaching our Milky Way galaxy … it’s nothing to lose sleep over. When will they collide? In response to NASA astronomers in 2012, it’ll be 4 billion years from now.
Nevertheless, in March 2022, the peer-reviewed Astrophysical Journal printed new analysis revealing that the collision between our galaxies is already underway. Or at the least our galactic halos – which include fuel, dust and stray stars – could already be touching.
Read more: Andromeda galaxy and the Milky Way are merging
When galaxies collide …
What occurs when galaxies collide? They don’t precisely crash into one another. As a result of there’s a lot extra space than stars even in a galaxy, colliding galaxies move by means of one another, like ghosts.
However, colliding galaxies do work together through gravity, which can trigger them to vary form and even merge into a bigger galaxy. Try this cool video: Night sky as Milky Way and Andromeda galaxies merge.

The Andromeda galaxy (M31) is positioned on the coordinates RA: 0h 42.7m; Dec: 41o 16′ north.
Backside line: At 2.5 million light-years, the good Andromeda galaxy (Messier 31) charges as essentially the most distant object you possibly can see with the unaided eye.
Enjoying EarthSky? Sign up for our free daily newsletter today!




