NASA published this original article on April 25, 2023. Edits by EarthSky.
Asteroid Phaethon simply acquired a little bit weirder
We’ve identified for some time that asteroid 3200 Phaethon acts like a comet. It brightens and types a tail when it’s close to the sun. And it’s the supply of the annual Geminid meteor shower, regardless that comets are answerable for most meteor showers. Scientists blamed Phaethon’s comet-like habits on dust escaping from the asteroid because it’s scorched by the sun. Nonetheless, a brand new examine utilizing two NASA solar observatories reveals that Phaethon’s tail just isn’t dusty in any respect. The truth is, it’s manufactured from sodium fuel.
Qicheng Zhang, a California Institute of Know-how Ph.D. pupil, is the lead creator of a paper published within the peer-reviewed Planetary Science Journal reporting the outcomes. Zhang mentioned:
Our evaluation exhibits that Phaethon’s comet-like exercise can’t be defined by any type of dust.
The distinction between comets and asteroids
Asteroids, that are largely rocky, don’t normally kind tails after they strategy the sun. Nonetheless, comets are a mixture of ice and rock and usually kind tails because the sun vaporizes their ice. The vaporization blasts materials off their surfaces and leaves a path of particles alongside their orbits. When Earth passes by a particles path, these cometary bits expend in our ambiance and produce a meteor shower.
Asteroid Phaethon produces the Geminid meteor bathe
After astronomers found 3200 Phaethon in 1983, they realized that the asteroid’s orbit matched that of the Geminid meteor shower. This indicated Phaethon was the supply of the annual meteor bathe, regardless that Phaethon was an asteroid and never a comet.
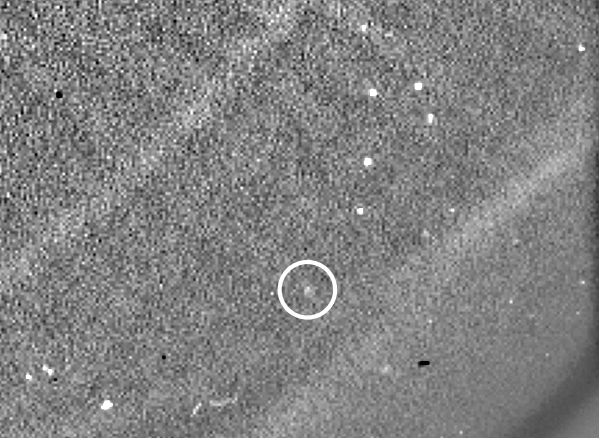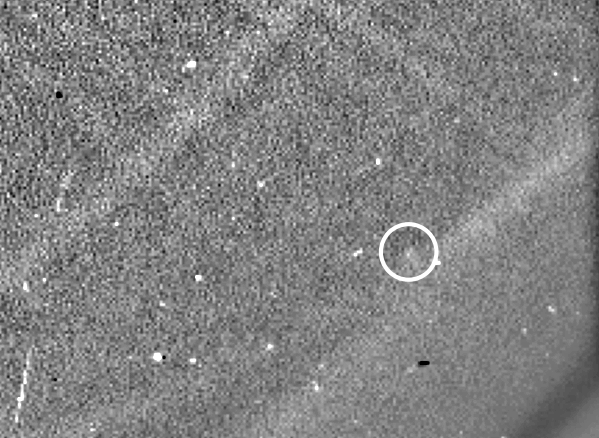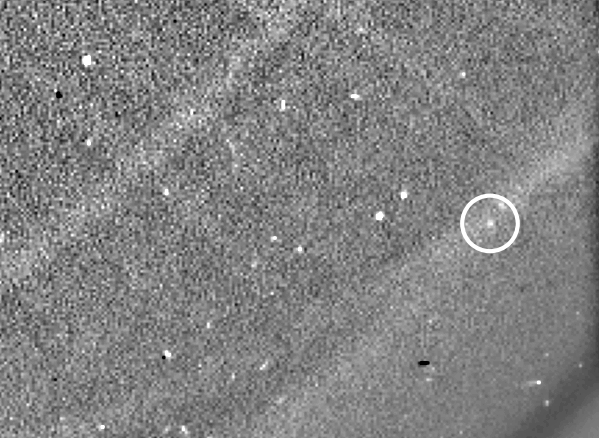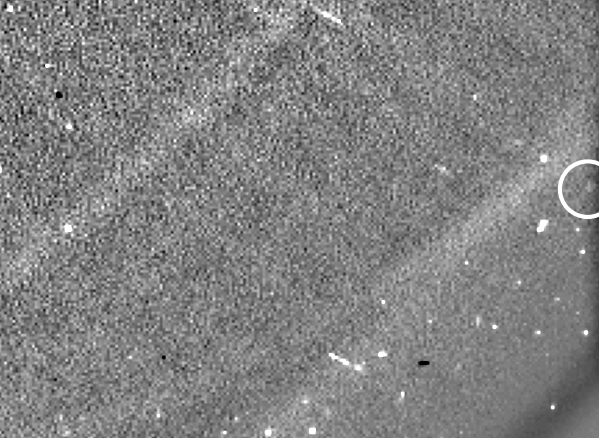
The tail was noticed at perihelion in 2009
In 2009, NASA’s Photo voltaic Terrestrial Relations Observatory (STEREO) noticed a brief tail extending from Phaethon. On the time, the asteroid reached its closest level to the sun (or “perihelion”) alongside its 524-day orbit. Common telescopes hadn’t seen the tail earlier than as a result of it solely types when Phaethon is just too near the sun to look at. Nonetheless, solar observatories can observe it then. STEREO additionally noticed Phaethon’s tail develop on later solar approaches in 2012 and 2016. The tail’s look supported the concept dust was escaping the asteroid’s floor when heated by the sun.
Then, in 2018, one other solar mission imaged a part of the Geminid particles path and located a shock. Observations from NASA’s Parker Solar Probe confirmed that the path contained way more materials than Phaethon may probably shed throughout its shut approaches to the sun.
Zhang’s workforce puzzled whether or not one thing else, aside from dust, was behind Phaethon’s comet-like habits. Zhang indicated:
Comets usually glow brilliantly by sodium emission when very close to the sun, so we suspected sodium may likewise serve a key position in Phaethon’s brightening.
An earlier study, based mostly on fashions and lab checks, urged that the sun’s intense warmth throughout Phaethon’s shut solar approaches may certainly vaporize sodium throughout the asteroid and drive comet-like exercise.
Colour filters have been in a position to detect sodium and dust
Hoping to seek out out the composition of the tail, Zhang seemed for it once more throughout Phaethon’s newest perihelion in 2022. He used the Photo voltaic and Heliospheric Observatory (SOHO) spacecraft – a joint mission between NASA and the European Area Company (ESA) – which has shade filters that may detect sodium and dust. Zhang’s workforce additionally searched archival photos from STEREO and SOHO, discovering the tail throughout 18 of Phaethon’s shut solar approaches between 1997 and 2022.
In SOHO’s observations, the asteroid’s tail appeared shiny within the filter that detects sodium. However it didn’t seem within the filter that detects dust. As well as, the form of the tail and the way in which it brightened as Phaethon handed the sun matched precisely what scientists would count on if it have been manufactured from sodium, however not if it have been manufactured from dust.
The tail of Phaethon is manufactured from sodium
Staff member Karl Battams of the Naval Analysis Laboratory mentioned:
Not solely do we have now a extremely cool consequence that type of upends 14 years of desirous about a well-scrutinized object, however we additionally did this utilizing information from two heliophysics spacecraft – SOHO and STEREO – that have been under no circumstances supposed to check phenomena like this.
Beneath are two photos of the asteroid Phaethon. Within the orange picture on the left, Phaethon seems as a shiny, blurry object with a faint tail under it. Within the blue picture on the precise, nothing seems.
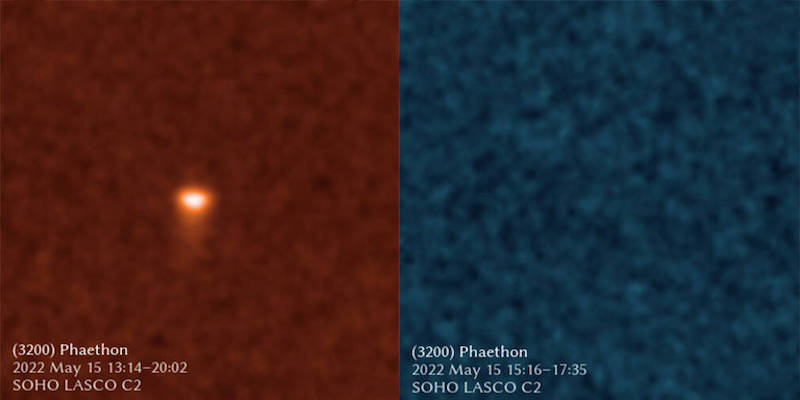

Zhang and his colleagues now ponder whether some comets discovered by SOHO – and by citizen scientists learning SOHO photos as a part of the Sungrazer Project – will not be comets in any respect. Zhang defined:
Lots of these different sunskirting ‘comets’ might also not be ‘comets’ within the standard, icy physique sense, however might as an alternative be rocky asteroids like Phaethon heated up by the sun.
How does Phaethon shed sufficient dust for the Geminids?
Nonetheless, one vital query stays. If Phaethon doesn’t shed a lot dust, how does it provide the particles for the Geminid meteor bathe each December?
Zhang’s workforce suspects that some kind of disruptive occasion occurred a couple of thousand years in the past. Maybe a chunk of the asteroid broke aside underneath the stresses of Phaethon’s rotation. That might trigger Phaethon to eject the billion tons of fabric estimated to make up the Geminid particles stream. However what that occasion was stays a thriller.
Extra solutions might come from an upcoming Japan Aerospace Exploration Company (JAXA) mission known as DESTINY+. That’s brief for Demonstration and Experiment of Area Know-how for Interplanetary voyage Phaethon fLyby and dUst Science. Later this decade, the DESTINY+ spacecraft will fly previous Phaethon. So it’ll picture its rocky floor and examine any dust which may exist round this enigmatic asteroid.
Backside line: The asteroid Phaethon is the father or mother object of the annual Geminid meteor bathe. It types a comet-like tail manufactured from sodium, not dust.




