There’s one thing poetic about humanity’s try to detect different civilizations someplace within the Milky Way’s expanse. There’s additionally one thing futile about it. However we’re not going to cease. There’s little doubt about that.
One group of scientists thinks that we could have already got detected technosignatures from a technological civilization’s Dyson spheres, however the detection is hidden in our huge troves of astronomical information.
A Dyson sphere is a hypothetical engineering challenge that solely extremely superior civilizations may construct. On this sense, “superior” means the type of nearly unimaginable technological prowess that will enable a civilization to construct a construction round a complete star. These Dyson spheres would enable a civilization to harness all of a star’s power.
A civilization may solely construct one thing so large and sophisticated if that they had reached Stage II within the Kardashev Scale. Dyson spheres might be a technosignature, and a crew of researchers from Sweden, India, the U.Okay., and the U.S. developed a approach to seek for Dyson sphere technosignatures they’re calling Venture Hephaistos. (Hephaistos was the Greek god of fireplace and metallurgy.)
They’ve revealed their results within the Month-to-month Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. The analysis is titled “Venture Hephaistos—II. Dyson sphere candidates from Gaia DR3, 2MASS, and WISE.”
The lead writer is Matías Suazo, a Ph.D. pupil within the Division of Physics and Astronomy at Uppsala College in Sweden. That is the second paper presenting Venture Hephaistos. The primary one is here.
“On this examine, we current a complete seek for partial Dyson spheres by analyzing optical and infrared observations from Gaia, 2MASS, and WISE,” the authors write. These are large-scale astronomical surveys designed for various functions.
Every considered one of them generated an unlimited quantity of knowledge from particular person stars. “This second paper examines the Gaia DR3, 2MASS, and WISE photometry of ~5 million sources to construct a list of potential Dyson spheres,” they clarify.
Combing by way of all of that information is an arduous activity. On this work, the crew of researchers developed a particular information pipeline to work its means by way of the mixed information of all three surveys. They level out that they are trying to find partially accomplished spheres, which might emit extra infrared radiation.
“This construction would emit waste heat within the type of mid-infrared radiation that, along with the extent of completion of the construction, would depend upon its efficient temperature,” Suazo and his colleagues write.
The issue is, they are not the one objects to take action. Many pure objects do, too, like circumstellar dust rings and nebulae. Background galaxies may emit extra infrared radiation and create false positives. It is the pipeline’s job to filter them out.
“A specialised pipeline has been developed to determine potential Dyson sphere candidates specializing in detecting sources that show anomalous infrared excesses that can not be attributed to any recognized pure supply of such radiation,” the researchers clarify.
This flowchart exhibits what the pipeline appears to be like like.
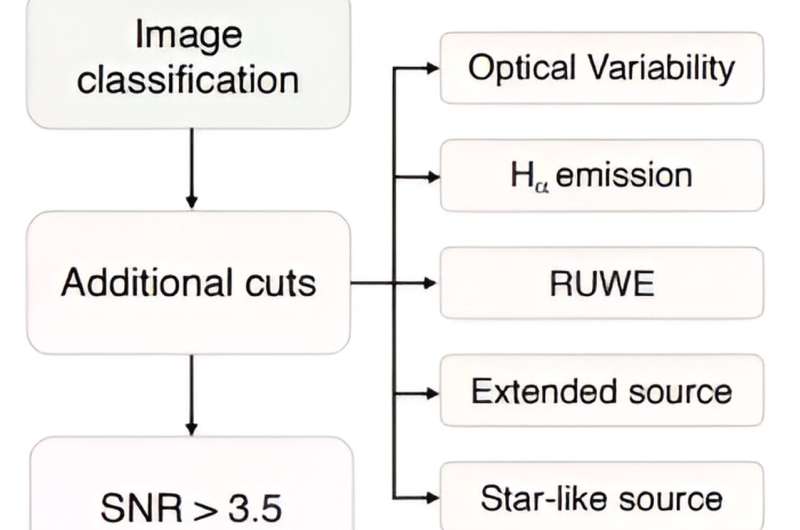
The pipeline is simply step one. The crew topics the listing of candidates to additional scrutiny primarily based on elements like H-alpha emissions, optical variability, and astrometry.
Within the final minimize, 368 sources survived. Of these, 328 had been rejected as blends, 29 had been rejected as irregulars, and 4 had been rejected as nebulars. That left solely seven potential Dyson spheres out of about 5 million preliminary objects, and the researchers are assured that these seven are respectable.
“All sources are clear mid-infrared emitters with no clear contaminators or signatures that point out an apparent mid-infrared origin,” they clarify.
These are the seven strongest candidates, however the researchers know they’re nonetheless simply candidates. There might be different the reason why the seven are emitting extra infrared. “The presence of heat particles disks surrounding our candidates stays a believable clarification for the infrared extra of our sources,” they clarify.
However their candidates appear to be M-type (red dwarf) stars, and particles disks round M-dwarfs are very uncommon. Nonetheless, it will get difficult as a result of some analysis means that particles disks round M-dwarfs type in a different way and current in a different way.
One kind of particles disk referred to as Excessive Particles Disks (EDD) can clarify a few of the luminosity the crew sees round their candidates. “However these sources have by no means been noticed in reference to M dwarfs,” Suazo and his co-authors write.
That leaves the crew with three questions: “Are our candidates unusual younger stars whose flux doesn’t fluctuate with time? Are these stars’ M-dwarf particles disks with an excessive fractional luminosity? Or one thing fully completely different?”
“After analyzing the optical/NIR/MIR photometry of ~5 x 106 sources, we discovered seven obvious M dwarfs exhibiting an infrared extra of unclear nature that’s suitable with our Dyson sphere fashions,” the researchers write of their conclusion.
There are pure explanations for the surplus infrared coming from these seven, “However none of them clearly explains such a phenomenon within the candidates, particularly given that every one are M dwarfs.”
The researchers say that follow-up optical spectroscopy would assist perceive these seven sources higher. A greater understanding of the H-alpha emissions is very useful since they’ll additionally come from younger disks.
“Specifically, analyzing the spectral area round H-alpha can assist us in the end discard or confirm the presence of younger disks,” the researchers write.
“Further analyses are positively essential to unveil the true nature of those sources,” they conclude.
Extra info:
Matías Suazo et al, Venture Hephaistos – II. Dyson sphere candidates from Gaia DR3, 2MASS, and WISE, Month-to-month Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society (2024). DOI: 10.1093/mnras/stae1186
Supplied by
Universe Today
Quotation:
Astronomers are on the hunt for Dyson spheres (2024, Might 10)
retrieved 10 Might 2024
from https://phys.org/information/2024-05-astronomers-dyson-spheres.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any truthful dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for info functions solely.




