EarthSky’s Will Triggs created this 1-minute video abstract for you, of the latest discovery of 60 Dyson sphere candidates.
- If any really exist, Dyson spheres, or Dyson swarms, are synthetic megastructures, constructed by extraterrestrial civilization to harness their stars’ power.
- Astronomers have discovered 60 attainable candidates stars, after looking by hundreds of thousands of stars for indicators of Dyson spheres.
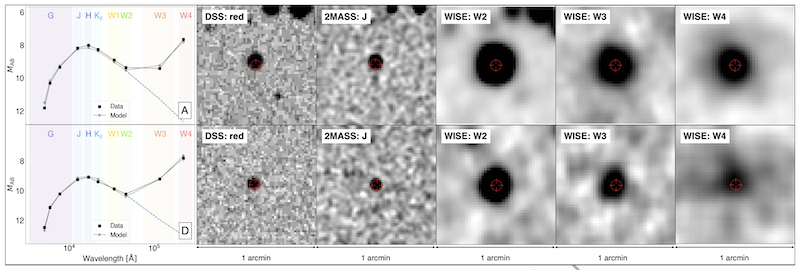
- The 60 candidate stars vary from crimson dwarfs to bigger stars together with sun-like stars, as much as 6,500 light-years away. All present excesses of infrared warmth that, up to now, scientists haven’t defined.
60 new Dyson sphere candidates
In the event that they exist, Dyson spheres are gargantuan synthetic constructions, constructed by extraterrestrial civilizations round round their stars, with the objective of capturing power. First proposed in 1960 by physicist Freeman Dyson, they’re an unimaginable thought experiment. However do such objects actually exist? Two groups of astronomers in Sweden and Italy not too long ago performed a brand new seek for attainable proof of Dyson spheres. The astronomers examined 5 million stars, as much as 6,500 light-years away. And so they discovered 60 attainable candidate stars. The celebs, each red dwarfs (or M dwarfs) and bigger ones together with sun-like stars, are emitting as much as 60 occasions extra infrared warmth than scientists anticipated.
Nevertheless, the outcomes match with what astronomers would anticipate to see from Dyson spheres. The groups discovered the candidates within the newest Gaia DR3 information from the European Gaia satellite in addition to the Two Micron All Sky Survey (2MASS) and Broad-field Infrared Survey Explorer (WISE).
The researchers stated it’s troublesome to elucidate the observations with at the moment identified pure processes. And even when the method is almost certainly a beforehand unknown pure phenomenon, it’s nonetheless a captivating discovery.
Jonathan O’Callaghan, a science journalist primarily based in London, wrote concerning the head-scratching leads to New Scientist on Could 10, 2024.
Dyson spheres are huge constructions that may very well be utilized by aliens to seize the power of a star – and astronomers have discovered alerts from 60 stars within the Milky Way according to such units. https://t.co/Ozyzaqds8B
— New Scientist (@newscientist) May 10, 2024
Two new papers are at the moment accessible within the Month-to-month Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society and arXiv. The first one (Could 6, 2024) focuses on seven red dwarf stars, and the second one (March 27, 2024) covers the opposite 53 stars.
A technosignature hiding in public information
The primary paper stated:
Dyson spheres, megastructures that may very well be constructed by superior civilizations to harness the radiation power of their host stars, symbolize a possible technosignature, that in precept could also be hiding in public information already collected as a part of giant astronomical surveys.
7 Dyson sphere candidates round crimson dwarfs
The celebs studied vary from crimson dwarfs to sun-like stars to ones bigger than our sun. Moreover, many of the stars are additionally older, though just a few look like younger.
Matías Suazo at Uppsala College in Sweden led the staff that found the seven candidates round red dwarf stars. All these candidates are inside 900 light-years of Earth.
Just like the second staff, they discovered an extra of infrared radiation round these stars. In accordance with the researchers, the celebs appeared as much as 60 occasions brighter in infrared than they anticipated. This extra infrared radiation is likely one of the signatures of attainable Dyson spheres. The paper said:
Lastly, the pipeline identifies seven candidates deserving of additional evaluation. All of those objects are M dwarfs, for which astrophysical phenomena can’t simply account for the noticed infrared extra emission.
There are a number of pure explanations for the infrared extra in literature, however none of them clearly explains such a phenomenon within the candidates, particularly given that each one are M dwarfs.
And, as of now, at the very least, troublesome to elucidate with identified pure causes. So, may there be a non-natural rationalization? It’s attainable, and as Suazo said in New Scientist:
Probably the most fascinating rationalization may very well be precise Dyson spheres.
Unexplained spikes in infrared radiation
Because the researchers defined, the spikes in infrared radiation with these seven crimson dwarfs are according to a temperature as much as 400 levels Celsius (750 levels Fahrenheit). They might, theoretically, be according to a partial Dyson sphere, the place a number of large segments or satellites orbit the star as an alternative of 1 closed sphere. That’s a variation of a Dyson sphere that scientists have additionally theorized. The New Scientist article said:
This extra infrared warmth would have been brought on by temperatures of as much as 400 levels Celsius, according to what we’d anticipate from a Dyson sphere. As much as 16% of every star must be obscured to account for the surplus, which means it will extra possible be a variant of the concept referred to as a Dyson swarm – a set of enormous satellites orbiting the star to gather power – if really of synthetic origin.
Co-author Jason Wright at Pennsylvania State College said:
This isn’t like a single strong shell across the star.
53 extra candidates
The seven candidates round red dwarf stars are intriguing, however there’s extra. Particularly, 53 extra candidates, all bigger stars, some like our personal sun. These have been the main focus of the second paper. Gabriella Contardo on the Worldwide Faculty for Superior Research (SISSA) in Italy led this search. These stars are as much as 6,500 light-years away. The paper said:
Stellar infrared excesses can point out varied phenomena of curiosity, from protoplanetary disks to debris disks, or (extra speculatively) technosignatures alongside the strains of Dyson spheres. On this paper, we conduct a big seek for such excesses, designed as a data-driven contextual anomaly detection pipeline. We focus our search on FGK stars near the principle sequence to favor non-young host stars. We search for extra within the mid-infrared, unlocking a big pattern to go looking in whereas favoring excessive infrared extra akin to those produced by excessive particles disks.
Whereas many of the stars are older, just a few look like youthful, because the paper famous:
We obtained a set of 53 candidates that show attention-grabbing mid-infrared extra. A number of of these objects look like younger stars (exhibiting excessive hydrogen alpha emission). A big fraction of our candidates appears to have variability within the optical, and a few within the mid-infrared. This will additionally point out youth, however a correct age estimation utilizing gyrochronology and a variability evaluation is required.
Doable explanations
Scientists don’t know the reason for the surplus infrared warmth on all these stars. The observations match with what astronomers have stated they’d anticipate to see from Dyson spheres or swarms, primarily based on theoretical research. After all, that doesn’t show these actually are alien megastructures … at the very least not but. Scorching, planet-forming particles disks – protoplanetary disks – are one risk. The issue is many of the 60 stars are outdated. Any planet-forming particles disks ought to have cooled and disappeared by now. That’s, in fact, aside from attainable asteroid belts or Oort clouds, like in our personal solar system. However even these are extraordinarily chilly environments.
Likewise, one other concept is every star simply occurs to be in entrance of a extra distant galaxy, as seen from Earth. However how possible is that? We don’t know but.
Extra observations wanted
To make sure, whereas the observations are troublesome to elucidate with identified pure processes, there may nonetheless be another pure mechanism, unknown till now, that may clarify them. Solely additional observations, maybe by the James Webb Space Telescope, will assist scientists determine what’s actually occurring. As Contardo famous:
Each units of candidates are attention-grabbing. You want follow-up observations to verify something.
Wright added:
Both we’ll rule all of them out and say Dyson spheres are fairly uncommon and really arduous to seek out, or they’ll dangle round as candidates and we’ll research the heck out of them.
The primary paper concluded:
We want to stress that though our candidates show properties according to partial Dyson spheres, it’s positively untimely to presume that the mid-infrared offered in these sources originated from them. The mid-infrared information high quality for these objects is usually fairly low, and we require extra information to find out their nature.
The invention of the Dyson sphere
Within the Sixties, physicist and astronomer Freeman J. Dyson proposed the concept of synthetic megastructures constructed by an alien civilization extra superior than our personal. Their goal is to seize as a lot warmth from the host star as attainable, for power functions. Numerous ideas vary from full spheres across the stars to partial spheres or rings. An alternate to an entire sphere enclosing the star could be a partial sphere. These solar panels would orbit and encompass the host star as a Dyson swarm.
Backside line: Two groups of astronomers in Europe say they’ve discovered 60 Dyson sphere candidates. Are they alien megastructures or a beforehand unknown pure phenomenon?
Source: Project Hephaistos – II. Dyson sphere candidates from Gaia DR3, 2MASS and WISE
Source: A Data-Driven Search For Mid-Infrared Excesses Among Five Million Main-Sequence FGK Stars
Read more: A Dyson sphere harvests the energy of stars
Read more: How Gaia could help find Dyson spheres




