A global crew of astronomers together with UCL’s (College Faculty London’s) Professor Mike Barlow has found the primary conclusive proof {that a} neutron star exists on the middle of Supernova 1987A, a star explosion noticed 37 years in the past.
Supernovae are the spectacular finish results of the collapse of stars extra huge than 8–10 instances the mass of the sun. They’re the primary sources of chemical components (reminiscent of carbon, oxygen, silicon, and iron) that make life doable. The collapsed core of those exploding stars can lead to a lot smaller neutron stars, composed of the densest matter within the identified universe, or black holes.
Supernova 1987A, situated within the Massive Magellanic Cloud, a neighboring dwarf galaxy, was the closest, brightest supernova seen within the evening sky in 400 years.
Neutrinos, unimaginably small sub-atomic particles, have been produced within the supernova and detected on Earth (23 February, 1987) the day earlier than the supernova was seen, indicating {that a} neutron star will need to have shaped. Nevertheless, it has not been identified whether or not the neutron star endured or collapsed right into a black hole, because the star has been obscured by dust that shaped after the explosion.
Within the new examine, published within the journal Science, researchers used two devices on the James Webb House Telescope (JWST), MIRI and NIRSpec, to watch the supernova at infrared wavelengths and located proof of heavy argon and sulfur atoms whose outer electrons had been stripped off (i.e. the atoms had been ionized) near the place the star explosion occurred.
The crew modeled varied eventualities and located that these atoms may solely have been ionized by ultra-violet and X-ray radiation from a sizzling cooling neutron star or, alternatively, from the winds of relativistic particles accelerated by a quickly rotating neutron star and interacting with surrounding supernova materials (pulsar wind nebula).
If the previous state of affairs is true, the floor of the neutron star could be about one million levels, having cooled down from 100 billion levels or so for the time being of formation on the core of the collapse greater than 30 years earlier.
Co-author Professor Mike Barlow (UCL Physics & Astronomy) stated, “Our detection with James Webb’s MIRI and NIRSpec spectrometers of sturdy ionized argon and sulfur emission traces from the very middle of the nebula that surrounds Supernova 1987A is direct proof of the presence of a central supply of ionizing radiation. Our information can solely be fitted with a neutron star as the facility supply of that ionizing radiation.
“This radiation will be emitted from the million diploma floor of the new neutron star, in addition to by a pulsar wind nebula that would have been created if the neutron star is quickly spinning and dragging charged particles round it.
“The thriller over whether or not a neutron star is hiding within the dust has lasted for greater than 30 years and it’s thrilling that we have now solved it.
“Supernovae are the primary sources of chemical components that make life doable—so we wish to get our fashions of them proper. There isn’t any different object just like the neutron star in Supernova 1987A, so near us and having shaped so lately. As a result of the fabric surrounding it’s increasing, we are going to see extra of it as time goes on.”
Professor Claes Fransson (Stockholm College, Sweden), the lead creator of the examine, stated, “Due to the excellent spatial decision and wonderful devices on JWST we have now, for the primary time, been capable of probe the middle of the supernova and what was created there.
“We now know that there’s a compact supply of ionizing radiation, probably by a neutron star. Now we have been searching for this from the time of the explosion, however needed to look ahead to JWST to have the ability to confirm the predictions.”
Dr. Patrick Kavanagh (Maynooth College, Eire), one other creator of the examine, stated, “It was so thrilling trying on the JWST observations of SN 1987A for the primary time. As we checked the MIRI and NIRSpec information, the very vivid emission from argon on the middle of SN 1987A jumped out. We knew instantly that this was one thing particular that would lastly reply the query on the character of the compact object.”
Professor Josefin Larsson (Royal Institute of Expertise (KTH), Sweden), a co-author of the examine, stated, “This supernova retains providing us surprises. No one had predicted that the compact object could be detected via an excellent sturdy emission line from argon, so it is form of amusing that that is how we discovered it within the JWST.”
Fashions point out that heavy argon and sulfur atoms are produced in nice abundance attributable to nucleosynthesis inside huge stars instantly earlier than they explode.
Whereas a lot of the mass of the exploding star is now increasing at as much as 10,000 km/second, and is distributed over a big quantity, the ionized argon and sulfur atoms have been noticed at near the middle the place the explosion occurred.
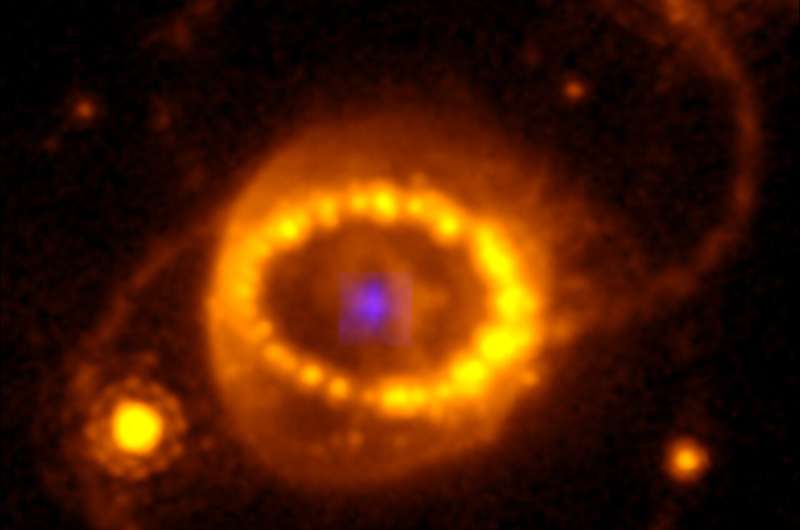
The ultraviolet and X-ray radiation which is assumed to have ionized the atoms was predicted in 1992 as a singular signature of a newly created neutron star.
These ionized atoms have been detected by James Webb’s MIRI and NIRSpec devices utilizing a method referred to as spectroscopy, the place gentle is dispersed right into a spectrum, enabling astronomers to measure gentle at totally different wavelengths to find out an object’s bodily properties, together with its chemical composition.
A UCL crew on the Mullard House Science Laboratory designed and constructed NIRSpec’s Calibration Supply, which permits the instrument to make extra exact measurements by offering a good, reference illumination of its detectors.
The brand new examine concerned researchers from the UK, Eire, Sweden, France, Germany, the USA, the Netherlands, Belgium, Switzerland, Austria, Spain and Denmark.
About Supernova (SN) 1987A
SN 1987A is essentially the most studied and greatest noticed supernova of all.
Exploding on February 23 1987 within the Massive Magellanic Cloud within the southern sky at a distance of 160,000 gentle years, it was the closest supernova because the final bare eye supernova noticed by Johannes Kepler in 1604. For a number of months earlier than it light SN 1987A might be seen with the bare eye even at this distance.
Much more importantly, it’s the solely supernova to have been detected through its neutrinos. That is extremely vital since 99.9% of the large power emitted on this occasion was predicted to be misplaced as these extraordinarily weakly interacting particles.
The remaining 0.1% seems within the growth power of the remnant and as gentle. Of the massive quantity (about 10 to the facility 58) of neutrinos emitted, about 20 have been detected by three totally different detectors across the Earth, from the collapse within the core of the star on February 23 at 7:35:35 UT.
SN 1987A was additionally the primary supernova the place the star which exploded might be recognized from photographs that had been taken earlier than the explosion. Apart from the neutrinos, essentially the most attention-grabbing results of the collapse and explosion is the prediction {that a} black hole or neutron star was created. This constitutes solely the central core of the collapsed star, with a mass of 1.5 instances that of the sun. The remaining is expelled with a velocity as much as 10% of the velocity of sunshine, forming the increasing remnant we observe instantly as we speak.
The ‘lengthy’ 10 second length of the neutrino burst indicated the formation of a neutron star, however regardless of a number of attention-grabbing indications from radio and X-ray observations, no conclusive proof for a compact object had been discovered till now, and was the primary remaining unsolved downside for SN 1987A.
An essential motive for this can be the big mass of dust particles that we all know was shaped throughout the years after explosion. This dust may block a lot of the seen gentle from the middle and subsequently disguise the compact object at seen wavelengths.
Two eventualities of neutron star
Of their examine the authors focus on two principal prospects: both radiation from the new, million diploma newly born neutron star or, alternatively, radiation from energetic particles accelerated within the sturdy magnetic discipline from the quickly rotating neutron star (pulsar). This is similar mechanism as operates within the well-known Crab nebula with its pulsar within the middle, which is the remnant of the supernova noticed by Chinese language astronomers in 1054.
Fashions of those two eventualities end in comparable predictions for the spectrum, which agree effectively with the observations, however are tough to tell apart. Additional observations with JWST and ground-based telescopes in seen gentle, in addition to the Hubble House Telescope, could possibly distinguish these fashions.
In both case, these new observations with JWST present compelling proof for a compact object, probably a neutron star, on the middle of SN 1987A.
In abstract, these new observations by JWST, along with the earlier observations of the progenitor and neutrinos, present an entire image of this distinctive object.
Extra info:
C. Fransson, Emission traces attributable to ionizing radiation from a compact object within the remnant of Supernova 1987A, Science (2024). DOI: 10.1126/science.adj5796. www.science.org/doi/10.1126/science.adj5796
Supplied by
University College London
Quotation:
Astronomers discover first sturdy proof of neutron star remnant of exploding star (2024, February 22)
retrieved 22 February 2024
from https://phys.org/information/2024-02-astronomers-strong-evidence-neutron-star.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any truthful dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for info functions solely.




