A global analysis staff led by UCLA astrophysicists has confirmed the existence of the faintest galaxy ever seen within the early universe. The galaxy, referred to as JD1, is among the most distant recognized thus far, and it’s typical of the sorts of galaxies that burned by means of the fog of hydrogen atoms left over from the Huge Bang, letting mild shine by means of the universe and shaping it into what exists in the present day.
The invention was made utilizing NASA’s James Webb Area Telescope, and the findings are revealed within the journal Nature.
The primary billion years of the universe’s life had been a vital interval in its evolution. After the Huge Bang, roughly 13.8 billion years in the past, the universe expanded and cooled sufficiently for hydrogen atoms to type. Hydrogen atoms take up ultraviolet photons from young stars; nevertheless, till the beginning of the primary stars and galaxies, the universe grew to become darkish and entered a interval generally known as the cosmic darkish ages.
The looks of the primary stars and galaxies a number of hundred million years later bathed the universe in energetic ultraviolet light which started burning, or ionizing, the hydrogen fog. That, in flip, enabled photons to journey by means of space, rendering the universe clear.
Figuring out the forms of galaxies that dominated that period—dubbed the Epoch of Reionization—is a serious objective in astronomy in the present day, however till the event of the Webb telescope, scientists lacked the delicate infrared devices required to check the primary technology of galaxies.
“Many of the galaxies discovered with JWST to date are brilliant galaxies which are uncommon and never considered notably consultant of the younger galaxies that populated the early universe,” mentioned Guido Roberts-Borsani, a UCLA postdoctoral researcher and the examine’s first creator. “As such, whereas essential, they aren’t considered the principle brokers that burned by means of all of that hydrogen fog.
“Extremely-faint galaxies equivalent to JD1, alternatively, are way more quite a few, which is why we consider they’re extra consultant of the galaxies that carried out the reionization course of, permitting ultraviolet mild to journey unimpeded by means of space and time.”
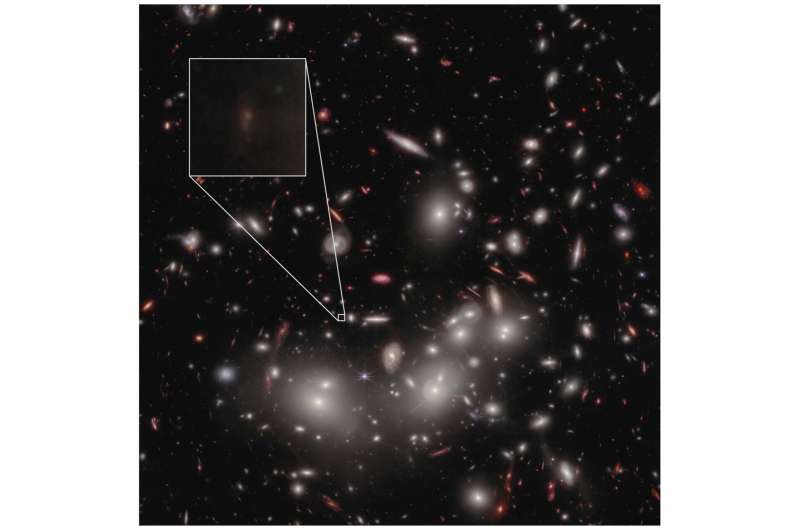
JD1 is so dim and so distant that it’s difficult to check with out a highly effective telescope—and a serving to hand from nature. JD1 is situated behind a big cluster of close by galaxies, referred to as Abell 2744, whose mixed gravitational power bends and amplifies the sunshine from JD1, making it seem bigger and 13 occasions brighter than it in any other case would. The impact, generally known as gravitational lensing, is much like how a magnifying glass distorts and amplifies mild inside its subject of view; with out gravitational lensing, JD1 would doubtless have been missed.
The researchers used the Webb Telescope’s near-infrared spectrograph instrument, NIRSpec, to acquire an infrared mild spectrum of the galaxy, permitting them to find out its exact age and its distance from Earth, in addition to the variety of stars and quantity of dust and heavy parts that it shaped in its comparatively brief lifetime.
The mix of the galaxy’s gravitational magnification and new photos from one other one of many Webb Telescope’s near-infrared devices, NIRCam, additionally made it doable for the staff to check the galaxy’s construction in unprecedented element and backbone, revealing three major elongated clumps of dust and gasoline which are forming stars. The staff used the brand new information to hint JD1’s mild again to its authentic supply and form, revealing a compact galaxy only a fraction of the dimensions of older galaxies just like the Milky Way, which is 13.6 billion years previous.
As a result of mild takes time to journey to Earth, JD1 is seen because it was roughly 13.3 billion years in the past, when the universe was solely about 4% of its current age.
“Earlier than the Webb telescope switched on, only a 12 months in the past, we couldn’t even dream of confirming such a faint galaxy,” mentioned Tommaso Treu, a UCLA physics and astronomy professor, and the examine’s second creator. “The mix of JWST and the magnifying energy of gravitational lensing is a revolution. We’re rewriting the ebook on how galaxies shaped and developed within the instant aftermath of the Huge Bang.”
The examine is revealed within the journal Nature.
Extra data:
Guido Roberts-Borsani et al, The character of an ultra-faint galaxy within the cosmic darkish ages seen with JWST, Nature (2023). DOI: 10.1038/s41586-023-05994-w
Offered by
University of California, Los Angeles
Quotation:
Astrophysicists affirm the faintest galaxy ever seen within the early universe (2023, June 1)
retrieved 1 June 2023
from https://phys.org/information/2023-06-astrophysicists-faintest-galaxy-early-universe.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any truthful dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for data functions solely.




