Each time one thing occurs with Betelgeuse, speculations about it exploding as a supernova proliferate. It could be cool if it did. We’re far sufficient away to endure no penalties, so it is enjoyable to think about the sky lighting up like that for months.
Now the red supergiant star has brightened by virtually 50%, and that has the hypothesis ramping up once more.
Betelgeuse will explode as a supernova. On that, there may be common settlement. However the query of when is much less sure. The star’s conduct is confounding. How can puny people discover out?
Betelgeuse is not solely a purple supergiant, it is also a pulsating semiregular variable star. Which means there’s some periodicity in its brightness adjustments, although the amplitudes can fluctuate. It has an roughly 400-day cycle the place its brightness adjustments. It additionally has a shorter 125-day cycle, one other 230-day cycle, and a whopping 2,200-day cycle, all decided by pulsations. All these cycles could make the star obscure clearly.
A few years in the past, Betelgeuse dimmed, and folks questioned what that meant. It seems that the star’s brightness did not really change. As an alternative, the star had ejected materials from its floor that cooled right into a dust cloud and blocked the sunshine. The episode is known as “The Nice Dimming.”

Now that it is brightening, it is attracting scientists’ consideration once more. They need to know what evolutionary stage it is in and what all this exercise signifies. New analysis reveals that it may explode as a supernova before anybody anticipated.
The brand new paper is “The evolutionary stage of Betelgeuse inferred from its pulsation durations,” and the primary creator is Hideyuki Saio from the Astronomical Institute, Graduate College of Science, at Tohoku College in Japan. Month-to-month Notices of the Royal Astronomy Society has accepted the paper for publication, and a model of the paper is on the market on the arXiv preprint server.
The juiciest components of latest analysis typically seize the headlines. No sense railing in opposition to that. That is how humanity rolls.
We’re not selecting on Dr. Eldridge. She’s not flawed. It is simply that the paper says that is just one doable final result. It outlines a number of others.
Of their paper, the authors say that Betelgeuse might be the Milky Way’s subsequent supernova, no matter which of their outcomes would possibly show to be true. “We conclude that Betelgeuse is within the late stage of core carbon burning, and a superb candidate for the following galactic supernova,” they write.
As a purple supergiant, Betelgeuse has left the primary sequence. All through its lengthy 8 to eight.5 million-year historical past, it used up huge portions of hydrogen by fusing it into helium and releasing the misplaced mass from that fusion as vitality. (Thanks Einstein.) Which means it is not fusing hydrogen into helium anymore just like the sun is. When stars like Betelgeuse lose mass, their gravity can not comprise their outward stress, and so they broaden right into a extra voluminous envelope. So regardless of dropping mass, they develop in dimension.
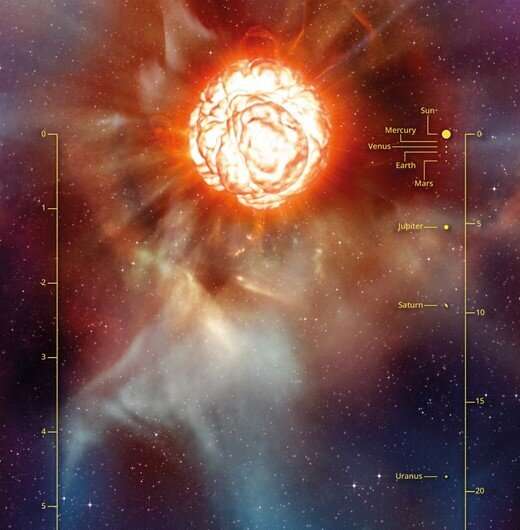
After stars like Betelgeuse go away the primary sequence and not fuse hydrogen into helium of their cores, issues change dramatically. Throughout the helium fusion stage that follows, carbon builds up of their cores. Then they start a core carbon-burning interval that produces different components. The authors of the brand new paper say that Betelgeuse is within the late phases of that interval.
However how late? How a lot time is left? There is not any actual reply for that but.
“Regardless of the comparatively small distance from Earth, and in some sense due to it, it has been troublesome to acquire tight constraints on the gap, luminosity, radius, present and Zero Age Predominant Sequence (ZAMS) plenty, and details about the inner rotational state and related mixing and therefore on the evolutionary state of Betelgeuse and when it would explode,” write the authors of a brand new evaluate of Betelgeuse. ZAMS is especially crucial to understanding the evolutionary stage of specific stars. It is elementary, although not solely accountable.
However the examine presents some stable potentialities.
The work is a mixture of observations and fashions that every go well with the observations in several methods. It is a difficult enterprise, which is why headlines claiming it may explode in tens of years are just a little deceptive. Nuance seldom attracts consideration.
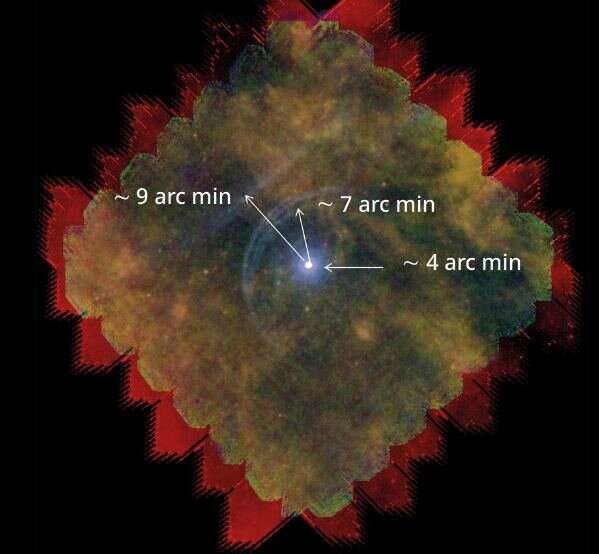
The core carbon-burning interval has a number of phases. The problem in figuring out when Betelgeuse will go supernova comes partly from figuring out which of these phases it is in. Betelgeuse pulses, ejects materials, rotates, and on high of that, is a runaway star rushing by way of space. Its distance from us can also be topic to debate. “Though it lies solely ~200 parsecs from Earth, and therefore will be spatially resolved with applicable instrumentation, uncertainties in its distance stay a crucial obstacle to deeper understanding,” the Betelgeuse evaluate explains.
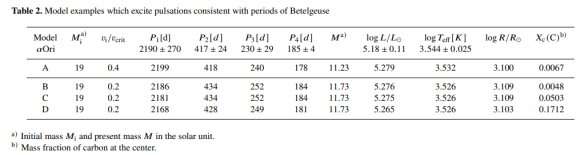
What’s attracted everybody’s consideration is these two sentences from the analysis: “Based on this determine, the core will collapse in a couple of tens years after the carbon exhaustion. This means Betelgeuse to be an excellent candidate for the following galactic supernova, which happens very close to to us.”
That is the determine they’re speaking about.
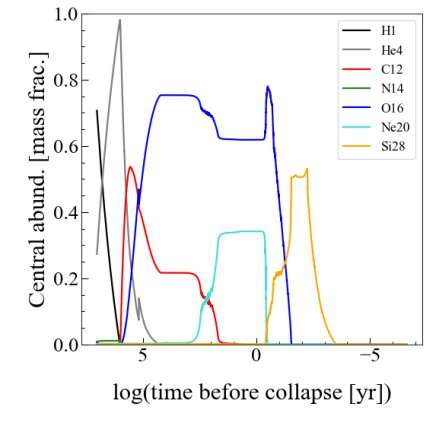
However what hasn’t attracted as a lot consideration is the next a part of the paper.
“In reality, it’s not doable to find out the precise evolutionary stage, as a result of floor situations hardly change within the late stage near the carbon exhaustion and past,” the researchers write. Astronomers can solely see the floor, nevertheless it’s what’s occurring deep contained in the star that tells the story.
The authors of the paper are actually saying that in accordance with observations, knowledge, and modeling, Betelgeuse may explode before thought. However—and that is crucial—they do not know what stage of core carbon-burning the star’s in. Carbon burning may go on for a very long time, in accordance with a number of the fashions that match the info.
However not everybody agrees that Betelgeuse is even within the core carbon-burning stage. The authors of the Betelgeuse evaluate say that the star remains to be within the helium phase. “Since core helium burning is way longer than subsequent burning phases, Betelgeuse is almost certainly in core helium burning. The pulsation interval probably constrains the radius and distance and the evolutionary state to core helium burning,” they write, whereas acknowledging that there are “arguments on the contrary.”
One other means the researchers tried to find out the timing of Betelgeuse’s supernova explosion is by matching its periodic pulsations with fashions of the identical.
When it lastly explodes—and no person disagrees with its eventual explosion as a supernova—it is not more likely to produce a lethal gamma-ray burst as some supernovae do. And whereas it’ll eject materials and produce highly effective X-ray and UV radiation, we’re too far-off to be affected. As an alternative, it’s going to be a light-weight present seen to everything of humanity, and that can change the Orion constellation perpetually. Scientists say it’s going to most likely go away behind a neutron star, perhaps a pulsar that will likely be seen for tens of millions of years. Your complete occasion, from begin to end, will likely be an unprecedented alternative to review stellar evolution, supernovae, and stellar remnants. Scientists will have the ability to work backwards from the explosion to all of the analysis carried out and all of the observations and knowledge and pinpoint the place they have been right and the place they have been flawed. Previous Betelgeuse will educate them rather a lot.
The shock wave from the supernova will arrive in about 100,000 years and will likely be simply deflected by our sun’s solar magnetosphere. The most important impact on Earth will likely be a rise in cosmic rays placing our higher environment.
Most of us will behold this calamitous explosion and sit in rapt awe of nature’s energy, we hope, whereas others will degenerate into bizarre conspiracy theories or quasi-religious, pseudo-scientific, cult-like reverence.
If, that’s, humanity remains to be round when the blessed occasion happens.
Extra data:
Hideyuki Saio et al, The evolutionary stage of Betelgeuse inferred from its pulsation durations, arXiv (2023). DOI: 10.48550/arxiv.2306.00287
Journal data:
arXiv
Supplied by
Universe Today
Quotation:
Betelgeuse is sort of 50% brighter than regular. What is going on on? (2023, June 6)
retrieved 6 June 2023
from https://phys.org/information/2023-06-betelgeuse-brighter.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any truthful dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for data functions solely.




