This story is predicated totally on a press release from the European Area Company, on March 28, 2023. Edits by EarthSky.
Brightest gamma-ray burst
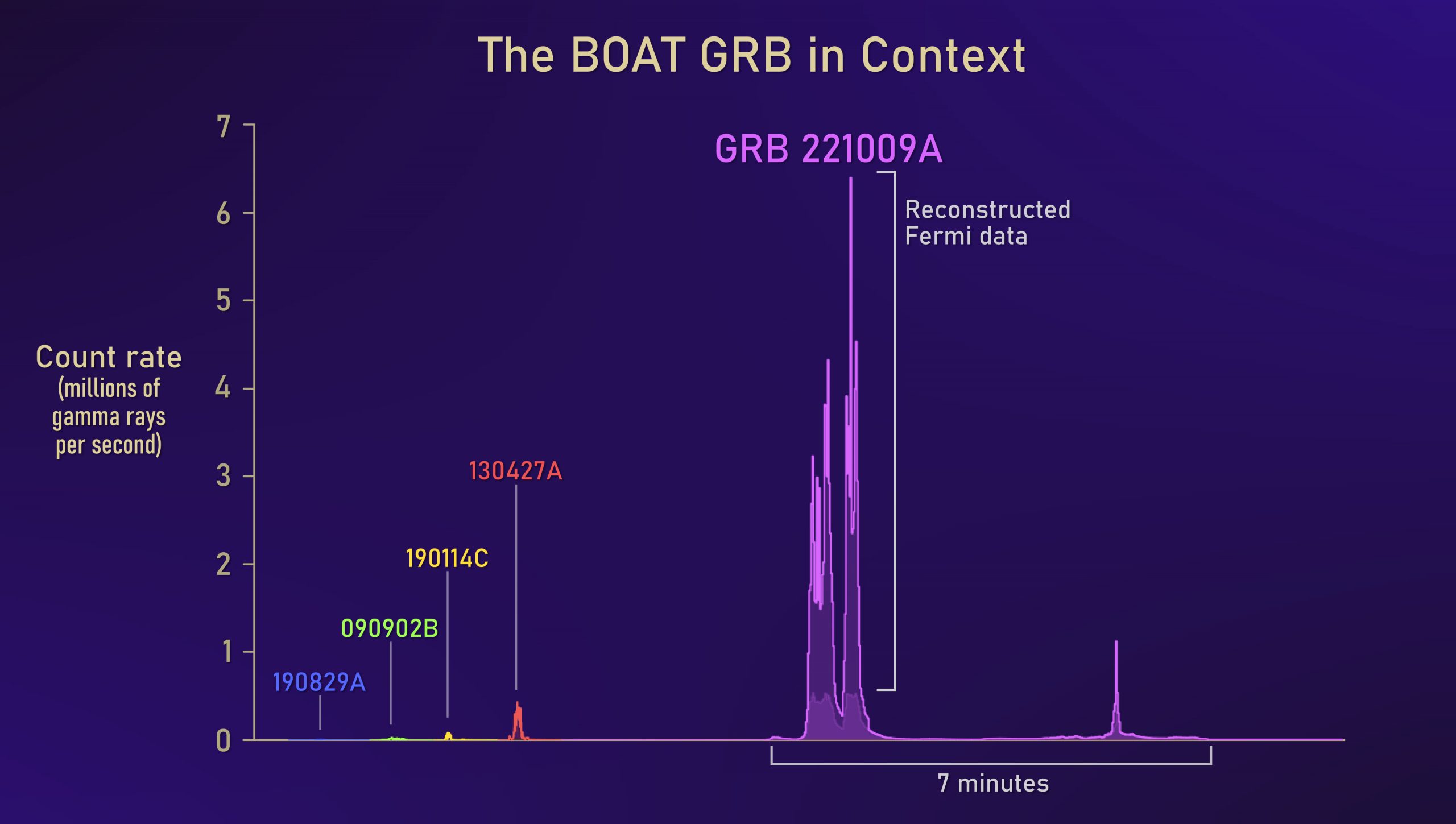
On October 9, 2022, the brightest gamma-ray burst (GRB) ever detected lit up screens throughout Earth. Nicknamed BOAT for brightest of all time, the blast is assumed to have been from a star turning into a black hole. It was so highly effective that it disturbed Earth’s ionosphere from 2.4 billion light-years away. And its x-ray radiation illuminated dust in our Milky Way galaxy, creating the obvious concentric rings seen within the picture above (the rise in dimension is mostly a perspective effect, with the biggest ring the closest to us). One of many scientists commented:
The distinction between your typical gamma-ray burst and this one is about the identical because the distinction between the sunshine bulb in your front room and the lit-up floodlights in a sports activities stadium.
Astronomers scrambled to level their telescopes on the gamma-ray burst, which is now often known as GRB 221009A. Many studied it. And astronomers said it supplied:
… an unprecedented have a look at the construction of the Milky Way and a brand new understanding of the sources of subatomic particles zipping by our planet.
Astronomers introduced their new findings on the Excessive Power Astrophysics Division assembly of the American Astronomical Society in Waikoloa, Hawaii, on March 28, 2023. A flurry of press releases from all over the world accompanied the presentation.
Last chance to get a moon phase calendar! Only a few left. On sale now.
All eyes on the brightest gamma-ray burst
However, as all the time, mysteries stay. Think about, for instance, that the gamma-ray burst is assumed to have come from a really huge star that exploded as a supernova, on the similar time collapsing to type a black hole. One thriller is that, as but, the particles from the explosion seems to have disappeared with out hint.
The gamma ray burst itself was first seen at Earth a number of months in the past. NASA’s Neil Gehrels Swift Observatory first detected X-rays from GRB 221009A on October 9, 2022. At first, the supply of the burst gave the impression to be in our Milky Way, not removed from the galactic heart.
However then Swift and NASA’s Fermi Gamma-Ray Space Telescope supplied extra knowledge, which quickly advised the supply was a lot farther away.
Observations from the European Southern Observatory’s Very Large Telescope then pinpointed the burst to a distant galaxy behind our personal.
Being a lot additional away, round 2 billion light-years as an alternative of a number of tens of 1000’s, meant that the GRB was exceptionally vivid: the brightest ever seen.

A 1-in-10,000-year burst
Statistically, scientists solely count on a gamma-ray burst as vivid as GRB 221009A to occur as soon as in many thousands of years. This burst might even be the brightest gamma-ray burst since human civilization started. Alicia Rouco Escorial, an ESA Analysis Fellow who research GRB, mentioned:
This has been a really eye-opening occasion. We now have been very fortunate to witness it.
Calculations present that for the few seconds it lasted, the blast deposited round a gigawatt of energy into Earth’s higher ambiance. That’s the equal of a terrestrial energy station’s vitality output. Erik Kuulkers, ESA Venture Scientist for Integral, one of many spacecraft that detected the GRB, mentioned:
So many gamma rays and X-rays had been emitted that it excited the ionosphere of the Earth.
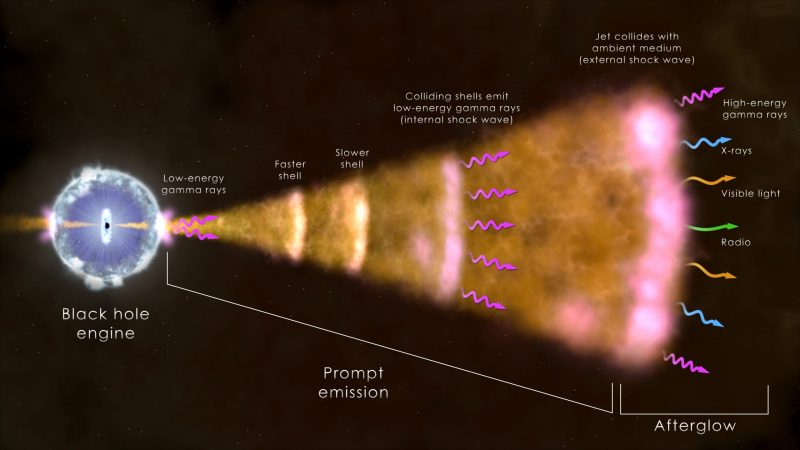
Finding out the GRB
The occasion was so vivid that even at this time scientists can see the residual radiation – the afterglow – and it’ll stay for a very long time. Volodymyr Savchenko, College of Geneva, Switzerland, who’s at the moment analyzing the Integral knowledge, mentioned:
We are going to see the afterglow of this occasion for years to return.
Scientists at the moment are bringing collectively the big quantity of information from completely different devices to grasp the unique explosion. Additionally they wish to know the way the radiation interacted with different matter on its journey by space.
Shockwave rings in dust clouds
One space that already yielded scientific outcomes is the X-rays that illuminated dust clouds in our galaxy. The radiation traveled by intergalactic space for round 2 billion years earlier than coming into our galaxy. It then encountered the primary dust cloud round 60,000 years in the past, and the final one about 1,000 years in the past.
Every time the X-rays encountered a dust cloud, it scattered some radiation, creating concentric rings that appeared to broaden outward. ESA’s XMM-Newton noticed these rings for a number of days after the GRB. The closest clouds produced the biggest rings just because they seem greater by perspective.
Andrea Tiengo of Scuola Universitaria Superiore IUSS Pavia in Italy analyzed the information with a group to seek out the gap to the dust clouds. Tiengo mentioned:
The primary cloud it hit seems to be on the very fringe of our galaxy, removed from the place galactic dust clouds are normally noticed.
Through the years, astronomers have proposed quite a lot of completely different properties for the dust grains. So, Tiengo and colleagues had been in a position to check them towards the X-ray knowledge. The mannequin that reproduced the rings extraordinarily nicely had dust grains composed principally of graphite. Additionally they used their knowledge to reconstruct the X-ray emission from the GRB itself, as a result of no instrument immediately noticed that individual sign.
A remaining thriller
However a thriller stays in regards to the object that exploded to create the GRB. Andrew Levan and colleagues used the Webb and Hubble space telescopes to search for the aftermath of the explosion … and located nothing. Levan mentioned:
That’s bizarre, and it’s not completely apparent what it means.
It might be that the star was so huge that following the preliminary explosion, it instantly shaped a black hole that swallowed the fabric that will historically make the gaseous cloud often known as a supernova remnant.
So, there may be loads of follow-up work as astronomers proceed to seek for the stays of the star that exploded. One factor they’ll search for is traces of heavy components reminiscent of gold, which scientists assume huge explosions can produce.
Backside line: The brightest gamma-ray burst of all time – or at the least thus far – blasted into the collective consciousness of earthly astronomers on October 9, 2022. It affected dust in our Milky Way galaxy and disturbed Earth’s ionosphere. The burst is assumed to have been born when a star exploded as a supernova, on the similar time collapsing to type a black hole. However, as but, the Webb and Hubble space telescopes have didn’t detect any supernova remnant.
Source: The Power of the Rings: The GRB 221009A Soft X-Ray Emission from Its Dust-scattering Halo
Source: Focus on the Ultra-luminous Gamma-Ray Burst GRB 221009A




