The motion of cosmic ray particles throughout space, corresponding to electrons and protons, is influenced by the sun’s magnetic area, inflicting fluctuations within the depth of galactic cosmic rays (GCRs) reaching Earth in response to the solar cycle. During times of low solar exercise, such because the solar minimal, extra GCRs have been noticed to succeed in Earth in comparison with that for intervals of excessive solar exercise. This inverse correlation between the GCR-flux and solar exercise is called “solar modulation.”
Particularly, the depth of GCRs on Earth is affected by the lean angle of the heliospheric present sheet (HCS), a spiral floor separating the course of oppositely directed magnetic field lines originating from the poles of the sun. As the lean angle of the HCS will increase, the depth of cosmic rays on Earth decreases.
In keeping with the drift mannequin of GCR transport within the heliosphere, the negatively charged electrons in GCRs are likely to journey alongside the HCS to succeed in Earth if the magnetic area is directed away from the sun within the northern hemisphere, and in direction of the sun within the southern hemisphere. In distinction, the positively charged protons attain Earth from the heliospheric polar area, suggesting that GCR electrons are extra affected by solar modulation than the protons as they journey by way of the HCS to succeed in Earth.
Whereas earlier observations of cosmic ray particles made aboard space balloons and in space experiments present variations between the fluxes of positively and negatively charged GCR particles through the solar cycle, it’s unclear whether or not the particle cost performs any function within the anticorrelation between GCR depth and the lean angle of the HCS.
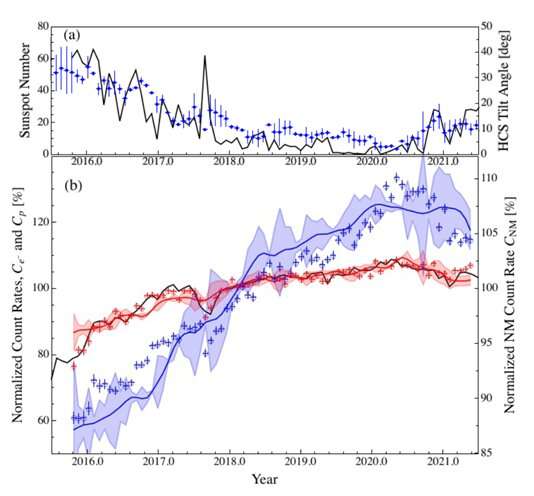
Now, in a current remark of GCR charged particles made with the CALorimetric Electron Telescope (CALET) onboard the Worldwide Area Station’s “Kibo” Uncovered Facility (EF) over a interval of six years, researchers have revealed that this anticorrelation is, in actual fact, extra distinguished for electrons than for protons.
The research, revealed in Bodily Assessment Letters, was co-led by three researchers from Japan, Affiliate Professor Yosui Akaike of the Waseda Analysis Institute for Science and Engineering (RISE) at Waseda College, Affiliate Professor Shoko Miyake of the Nationwide Institute of Know-how (KOSEN) at Ibaraki Faculty, and Professor Kazuoki Munakata of Shinshu College. It additionally included contributions from Professor Emeritus Shoji Torii from RISE.
“Utilizing CALET, we efficiently noticed a charge-sign dependent solar modulation of GCRs over six years,” says Akaike.
The researchers analyzed over 0.77 million electrons and 1.26 million protons collected in about 196 and 197 hours, respectively, over a six-year interval from 2015 to 2021, which coincided with the tip of solar cycle 24 and the start of solar cycle 25, the present solar cycle.
The findings indicated that through the low exercise state of the sun in direction of the tip of solar cycle 24, characterised by a discount within the variety of sunspots and HCS tilt angle, each electron and proton rely charges have been low however steadily rising. This development continued with the onset of solar cycle 25, reaching its peak in electron rely charge six months after the start of the cycle in December 2019.
Thereafter, each electron and proton rely charges steadily decreased because the sun’s exercise and HCS tilt angle elevated. Moreover, the outcomes confirmed that the variation within the rely charges of electrons was considerably increased than that of protons throughout this era, suggesting that electrons are extra inclined to the consequences of solar modulation, as predicted by the drift mannequin.
“This can be a clear signature of the drift impact dominating the long-term solar modulation of GCRs noticed with a single detector,” highlights Akaike.
Total, analyzing GCRs can shed vital gentle on the composition of the universe and the acceleration mechanisms of high-energy particles noticed in cosmic rays. Thus, the observations made by CALET may assist higher perceive the space climate and its results on the potential for potential life on the moon and different planets, like Mars.
Extra data:
O. Adriani et al, Cost-Signal Dependent Cosmic-Ray Modulation Noticed with the Calorimetric Electron Telescope on the Worldwide Area Station, Bodily Assessment Letters (2023). DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.130.211001
Supplied by
Waseda University
Quotation:
CALorimetric Electron Telescope (CALET) captures charge-sign dependent cosmic ray modulation (2023, June 8)
retrieved 8 June 2023
from https://phys.org/information/2023-06-calorimetric-electron-telescope-calet-captures.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any honest dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for data functions solely.




