Can we predict earthquakes?
A pair of French researchers declare to have found the holy grail of seismology: a method of predicting main earthquakes hours earlier than we really feel them. If their discovery is actual, will correct and well timed earthquake prediction grow to be a actuality? Probably. It’s hopeful, as a result of well timed earthquake prediction would save lives and assist shield crucial infrastructure. So is it true? And, whether it is, can we use this discovery to foretell earthquakes?
Earthquake researchers Quentin Bletery and Jean-Mathieu Nocquet of Université Côte d’Azur in Géoazur, France, described their dramatic discovering this month (July 20, 2023) in a paper revealed within the journal Science.
Earlier than this, most consultants had mentioned earthquake prediction would by no means be doable as a result of there was no preliminary signal an earthquake would happen till the bottom really began shaking. However Bletery and Nocquet mentioned their evaluation of 90 previous earthquakes has advised that:
… massive earthquakes begin with a precursory phase of slip …
And so they mentioned the “precursory slip” phase comes inside two hours earlier than the earthquake itself occurs. That’s time sufficient for officers to offer warning in affected areas.
Is that this “slip” actual? That is still to be seen. The examine nonetheless must be confirmed. And different researchers will little doubt be making an attempt to duplicate and advance the work of Bletery and Nocquet.
What’s extra, even whether it is actual, will the discovering allow us to predict earthquakes? And, as Quentin Bletery told Scientific American:
[Our finding] doesn’t imply we all know the best way to predict earthquakes. But it surely implies that it’s bodily doable.
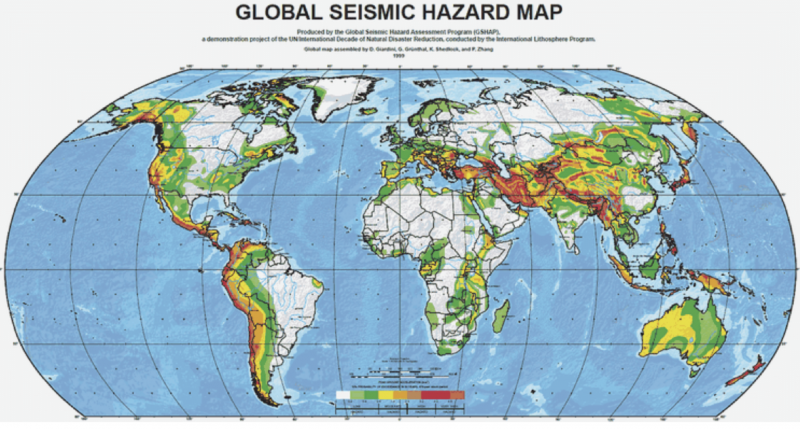
Why we didn’t assume we might
At current we are able to’t predict earthquakes, although geologists have sought a dependable earthquake prediction methodology for many years.
What’s wanted is a prediction that comes not minutes earlier than, however hours earlier than the earthquake. It’s solely on a timescale of hours that folks can transfer themselves out of the earthquake zone, or not less than to an open space, the place they’re not prone to be injured or killed by falling particles.
And there are different points, notably that making a system like that implied by the work of Bletery and Nacquet would require an costly retooling of the GPS system. If it really works in any respect, it’ll require the development of an intensive GPS sensor community alongside main earthquake rupture faults. As defined in an article accompanying the paper in Science, the methods in place to observe motion of earthquake faults aren’t at the moment delicate sufficient to detect warning indicators as they occur.
So implementing the strategies implied by this new discovery – if it’s actual – won’t be low cost.
Nonetheless, if it’s true, it’s a begin that might finally save thousands and thousands of lives. And the hope is that the invention by the 2 French researchers will ultimately result in dependable and well timed predictions. Even the prospect has seismologists anxious to know extra. Seismologist Richard Allen on the College of California, Berkeley, who was not concerned within the work, mentioned within the Science article:
It’s simply tantalizing. The entire concept of with the ability to predict the onset of [an] earthquake rupture is a extremely massive deal.

How did they uncover the ‘slip’?
So how did French earthquake researchers Quentin Bletery and Jean-Mathieu Nocquet make their discovery of a “slip” earlier than an earthquake? The researchers analyzed very exact historic GPS information displaying fault line motion in 5-minute increments. They particularly examined 48-hour durations earlier than 90 totally different main earthquakes.
They found a recurring sign that seems lengthy sufficient earlier than an earthquake happens that authorities could have time to concern a warning. Based on the article in Science:
They discovered that on common, horizontal actions of the stations exponentially accelerated in a course in step with sluggish fault slip close to the eventual earthquake nucleation point within the final two hours earlier than the earthquake ruptures.
These scientists say the indicators a serious earthquake is coming emerge from the background about 110 minutes earlier than the quake strikes.
To verify their discovery wasn’t only a random prevalence, the researchers additionally analyzed 100,000 48-hour home windows of GPS information that didn’t finish in main temblors.
Regardless of discovering a mannequin to forecast seismic exercise, the expertise to make use of the approach isn’t in place but. However the researchers consider it might be:
Though current instrumental capacities don’t permit us to establish precursory slip on the scale of particular person earthquakes, our remark means that precursory indicators exist and that the precision required to observe them shouldn’t be orders of magnitudes away from our current capabilities.
Extra particulars from GeologyHub
The favored YouTube channel GeologyHub says the paper may signify “an important scientific discovery within the area of geology through the previous 20 years.”
Within the GeologyHub video (under), the host presents a hypothetical instance of how earthquake prediction may save lives. Think about a 7.7-magnitude quake on the San Andreas Fault in California. A significant quake happens alongside it each 140 years on common. The prediction scheme would doubtless produce a handful of false alarms, in addition to saving maybe thousands and thousands of lives when the Large One lastly hits. Based on the GeologyHub video:
Throughout a mean 140-year interval one precise sign can be detected previous a serious earthquake together with a mean of seven to eight false positives.
That’s fairly nice.
Hypothetically, folks might be advised for every of those 110-minute home windows to easily transfer to a secure space which might face up to a doable earthquake, presumably in a area distant from the place massive objects might fall.
Has an earthquake ever been predicted?
Earlier than this new discovery, the USGS was adamant that any helpful prediction – any sooner than, say, a couple of minutes earlier than an earthquake struck – was unimaginable. USGS says on its FAQ page:
Neither the USGS nor another scientists have ever predicted a serious earthquake.
We have no idea how, and we don’t anticipate to know the way any time within the foreseeable future.
USGS scientists can solely calculate the chance {that a} important earthquake will happen in a particular space inside a sure variety of years.
There was a single case of what now seems to have been good luck, with regard to earthquake prediction. It occurred in Haicheng, Liaoning, China, on February 4, 1975. There’d been foreshocks, and far of the town had evacuated earlier than the earthquake, after an order from Chinese language officers. Then a magnitude 7.5 earthquake – a really sturdy earthquake – did strike. So there was a prediction, and it did save lives.
However the 1975 Haicheng earthquake “prediction” – which was primarily based on the previous foreshocks – later was deemed to be a fluke.
Backside line: A pair of French earthquake researchers declare to have found the holy grail of seismology: a method of predicting main earthquakes hours earlier than they occur.
Source: The precursory phase of large earthquakes




