China efficiently launched the ultimate module of its Tiangong space station on Monday, inching nearer to completion by the tip of the yr and a landmark second within the nation’s space ambitions.
The world’s second-largest financial system has put billions into its military-run space programme, with hopes of ultimately sending people to the Moon.
China has come a great distance in catching up with the US and Russia, whose astronauts and cosmonauts have a long time of expertise in space exploration.
Here’s a take a look at the nation’s space programme, and the place it’s headed:
Mao’s vow
Quickly after the Soviet Union launched Sputnik in 1957, Chairman Mao Zedong pronounced: “We too will make satellites.”
It took greater than a decade, however in 1970, China launched its first satellite on a Lengthy March rocket.
Human spaceflight took a long time longer, with Yang Liwei changing into the primary Chinese language “taikonaut” in 2003.
Because the launch approached, issues over the viability of the mission induced Beijing to cancel a reside tv broadcast on the final minute.
But it surely went easily, with Yang orbiting the Earth 14 instances throughout a 21-hour flight aboard the Shenzhou 5.
China has launched seven crewed missions since.
Area station and ‘Jade Rabbit’
Following within the footsteps of the US and Russia, China started planning to construct its personal space station circling the planet.
The Tiangong-1 lab was launched in 2011.
In 2013, the second Chinese language lady in space, Wang Yaping, gave a video class from contained in the space module to youngsters internationally’s most populous nation.
The craft was additionally used for medical experiments and, most significantly, checks meant to arrange for the development of a space station.
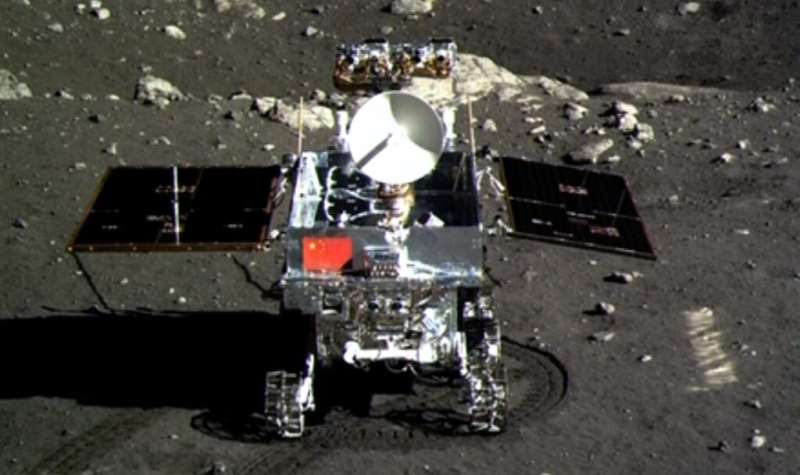
That was adopted by the “Jade Rabbit” lunar rover in 2013, which initially appeared a dud when it turned dormant and stopped sending alerts again to Earth.
It made a dramatic restoration, nevertheless, finally surveying the Moon’s floor for 31 months—effectively past its anticipated lifespan.
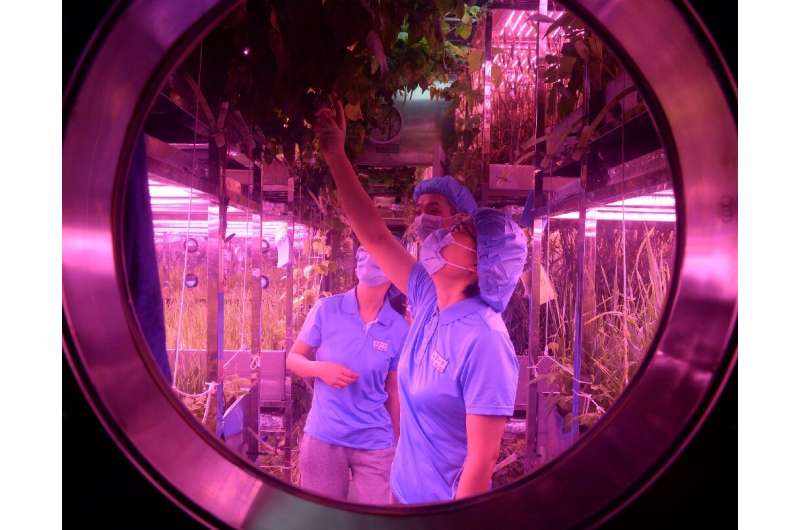
In 2016, China launched its second orbital lab, the Tiangong-2. Astronauts who visited the station have run experiments on rising rice and different crops in space.
‘Area dream’
Below President Xi Jinping, plans for China’s “space dream” have been put into overdrive.
Beijing is trying to lastly meet up with the US and Russia after years of belatedly matching their milestones.
Moreover a space station, China can be planning to construct a base on the Moon, and the nation’s Nationwide Area Administration stated it goals to launch a crewed lunar mission by 2029.
However lunar work was dealt a setback in 2017 when the Lengthy March-5 Y2, a strong heavy-lift rocket, did not launch on a mission to ship communication satellites into orbit.

That compelled the postponement of the Chang’e-5 launch, initially scheduled to gather Moon samples within the second half of 2017.
One other robotic, the Chang’e-4, landed on the far aspect of the Moon in January 2019—a historic first.
This was adopted by one which landed on the close to aspect of the Moon final yr, elevating a Chinese language flag on the lunar surface.
The unmanned spacecraft returned to Earth in December with rocks and soil—the primary lunar samples collected in 4 a long time.
And in February 2021, the primary pictures of Mars had been despatched again by the five-tonne Tianwen-1, which then landed a rover on the Martian floor in Might that has since began to discover the floor of the Pink Planet.
Palace within the sky
Tiangong—which means “heavenly palace”—is anticipated to be accomplished by the tip of the yr.
The Mengtian module launched Monday is the third and ultimate main element of the T-shaped station.
It carries various items of cutting-edge science gear, state information company Xinhua reported, together with “the world’s first space-based chilly atomic clock system”.
As soon as completed, Tiangong is anticipated to stay in low Earth orbit at between 400 and 450 kilometres (250 and 280 miles) above the planet for a minimum of 10 years—realising an ambition to take care of a long-term human presence in space.
It is going to be continuously crewed by rotating groups of three astronauts, who will conduct scientific experiments and assist check new applied sciences.
Whereas China doesn’t plan to make use of its space station for world cooperation on the size of the Worldwide Area Station, Beijing stated it’s open to international collaboration.
It’s not but clear how intensive that cooperation shall be.
© 2022 AFP
Quotation:
China’s ‘space dream’: A Lengthy March to the Moon and past (2022, October 31)
retrieved 31 October 2022
from https://phys.org/information/2022-10-china-space-moon.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any honest dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for info functions solely.




