The Rosetta orbiter spectrometer for ion and impartial evaluation (ROSINA) instrument orbited comet 67P to revolutionize our understanding of cometary materials composition. A key discovering of the satellite was to discover the composition of comet 67P/Churyumov-Gerasimenko. In a brand new report revealed in Science Advances, Ahmed Mahjoub and a workforce of planetary scientists within the Jet Propulsion Lab at CalTech, the House Science Institute Colorado, and the College of Bern in Switzerland, used the ROSINA information to check dust particles volatilized throughout a dust occasion in September 2016.
The scientists reported the detection of huge organosulfur species, on the comet‘s floor. They then performed laboratory simulations to point the formation of this materials from chemical reactions initiated by irradiating blended ices containing hydrogen sulfide. The outcomes highlighted the importance of cometary sulfur chemistry and its presence in precometary materials to facilitate the detection of organosulfur supplies in different comets and icy small our bodies by utilizing the James Webb Space Telescope.
Touchdown on a comet
When the Rosetta mission visited comet 67P, the satellite revealed remarkable insights to the various molecules on the comet. The researchers detected organics by utilizing a distant sensing instrument, seen and infrared thermal imaging spectrometry, and a collection of devices together with ROSINA, Ptolemy and the cometary sampling and composition experiment. The measurements made utilizing ROSINA supplied substantial data of the advanced organic chemistry in cometary supplies, alongside additional insights to the composition of the semi-volatile phases of comet 67P.
The measurements additional revealed the detection of ammonium salts. On this work, Mahjoub and colleagues mentioned the information gathered from the Rosetta probe and ROSINA throughout an occasion of enhanced dust influence on the instrument. They interpreted the information to disclose the presence of huge organosulfur molecules with low volatility embedded within the dust grains of comet 67P. The workforce accomplished in-lab simulations of the natural chemistry that started on the comet resulting from irradiation of easy ice mixtures within the presence or absence of hydrogen sulfide. The outcomes indicated the dominance of sulfur within the atmosphere, and a potential ice-chemistry origin to the sulfur-bearing species on the cometary materials.
The dust occasion
Previous to touchdown on the comet, Rosetta flew elliptical orbits throughout the previous few weeks of its mission with the pericenter altitude step by step lowered. On September 2016, the spacecraft reached its closest distance from the comet. It’s assumed that the space probe was hit by a piece of ice or dust previous to that, which led to the statement of high-density gasoline plumes for about 3 hours within the vicinity of the instrument.
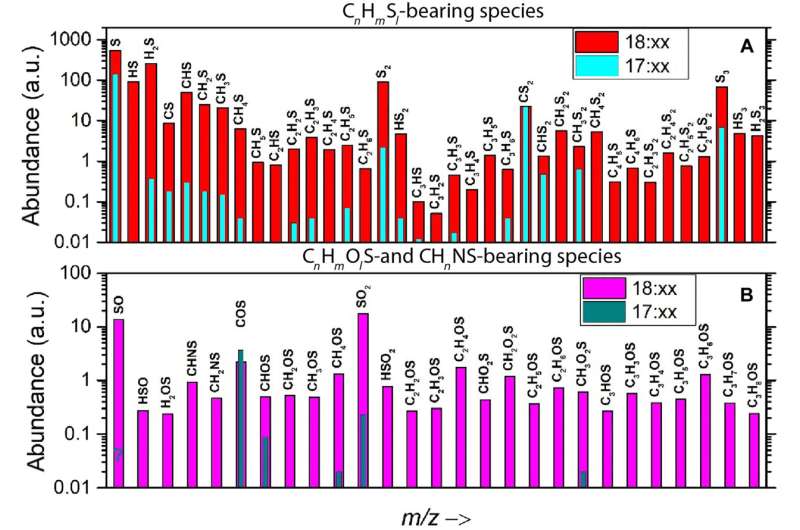
The measurements made through the research indicated the abundance of a wide range of sulfur-bearing molecules, previous to and after the dust occasion. The workforce performed mass spectrometry measurements to establish carbonyl sulfide and carbon disulfide as species that didn’t considerably enhance through the occasion resulting from their greater volatility, in comparison with sulfur dioxide, which elevated by about two orders of magnitude. The workforce additional monitored the presence of semi-volatile organo-sulfurous molecules on the floor of comet 67P.
Simulations within the lab
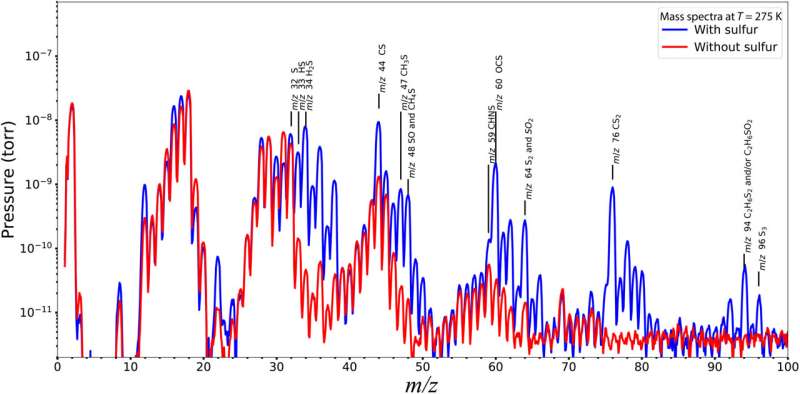
The ROSINA-double focusing mass spectrometer (ROSINA-DFMS) information obtained through the dust occasion confirmed sulfur chemistry to be extra advanced and various than hitherto identified or assumed through measurements within the undisturbed coma of the comet. Mahjoub and colleagues assumed this consequence to have resulted from the ice chemistry involving hydrogen sulfide. To discover this within the lab, the workforce carried out electron irradiation experiments on ice mixtures within the presence or absence of the molecules.
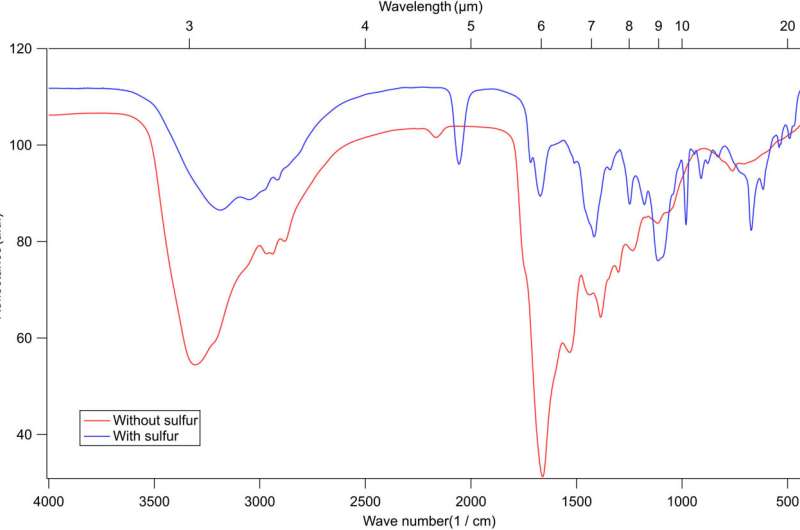
The experimental setup included a high-vacuum stainless-steel chamber, the place the workforce deposited ices on a gold substrate hooked up to a chilly finger of a helium cryostat via a gasoline, to arrange gasoline mixtures. The setup included an electron acquire within the chamber and a Faraday cup to watch the electron beam present. The workforce detected the evolving samples with a Fourier rework infrared spectrometer. Additional experiments highlighted the speedy dissociation of hydrogen sulfide within the setup, in comparison with methanol and water samples utilized in comparable experiments, to provide a excessive focus of reactive sulfur bearing radicals to predominantly have an effect on the chemistry within the ice movies.
Outlook
On this method, Ahmed Mahjoub and colleagues characterised natural heteropolymers in small interstellar icy grains and icy our bodies. They assumed hydrogen sulfide ice chemistry to be probably for the noticed species. They highlighted the presence of different pathways to kind organosulfur compounds within the diffuse interstellar medium, and within the solar nebula. Utilizing in-lab simulations, the scientists confirmed that sulfur-bearing natural compounds may very well be fashioned through sulfur ion bombardment of astrophysical ices containing carbon, oxygen, and nitrogen constituents.
The James Webb House Telescope included throughout this work can enhance the understanding of the chemistry of the solar system, together with comets, and asteroids. This instrument may help researchers to unveil the composition of a wide range of such interstellar our bodies alongside their similarities or variations, to grasp the formation and evolution of the solar system; the place sulfur chemistry is of curiosity. The destiny of sulfur has a key function within the evolution of comets and interstellar icy our bodies, though a lot of its function within the constructing blocks of the solar system stays to be identified. The aspect, nonetheless, holds promising capability to reply the origin and evolution of such icy small our bodies.
Extra data:
Ahmed Mahjoub et al, Advanced organosulfur molecules on comet 67P: Proof from the ROSINA measurements and insights from laboratory simulations, Science Advances (2023). DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adh0394
I. P. Wright et al, CHO-bearing natural compounds on the floor of 67P/Churyumov-Gerasimenko revealed by Ptolemy, Science (2015). DOI: 10.1126/science.aab0673
© 2023 Science X Community
Quotation:
Advanced organosulfur molecules on comet 67P: Proof from Rosetta orbiter and the lab (2023, June 30)
retrieved 1 July 2023
from https://phys.org/information/2023-06-complex-organosulfur-molecules-comet-67p.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any truthful dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for data functions solely.




