NASA’s Curiosity rover has been exploring the decrease slopes of Mount Sharp since 2014. Now, after three makes an attempt, the rover has reached one in every of its major locations: Gediz Vallis Ridge. Again when liquid water may nonetheless exist on Mars’ floor, historical rocky particles flows carried mud and rocks down the facet of the mountain to type this ridge. Curiosity captured a 360-degree panorama of its new environment on August 19, 2023. NASA announced the arrival of Curiosity on the ridge on September 18.
Curiosity rover arrives at Gediz Vallis Ridge
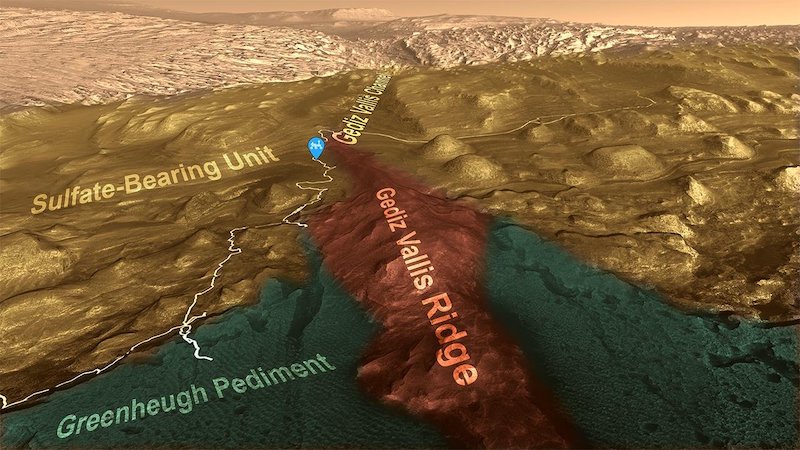
Gediz Vallis Ridge is a long-sought vacation spot for Curiosity. Moist particles flows from billions of years in the past fashioned this area. So it preserves an essential glimpse into what this a part of Mars was like when there was water and dirt. After three failed makes an attempt to achieve the ridge, Curiosity lastly arrived on August 14, 2023. That was sol 3,923 for the rover. One sol is a Martian day. Beforehand, the rover had encountered obstacles resembling sharp-edged “gator-back rocks and slopes that have been too steep to climb.
Ashwin Vasavada, Curiosity’s mission scientist at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, talked in regards to the accomplishment:
After three years, we lastly discovered a spot the place Mars allowed Curiosity to soundly entry the steep ridge. It’s a thrill to have the ability to attain out and contact rocks that have been transported from locations excessive up on Mount Sharp that we’ll by no means be capable of go to with Curiosity.
The ridge fashioned about three billion years in the past. On the time, Mars nonetheless had liquid water on its floor. This was one of many final moist intervals the planet skilled. Water on this space created mud, which flowed down the perimeters of the mountain, spreading out right into a fan form. The mud carried rocks and boulders of assorted sizes, some as massive as automobiles. Later, wind sculpted the piled-up particles into the ridge we see at this time.
You may drag your cursor round inside this 360-degree video to discover the view captured by Curiosity’s Mastcam whereas the rover was stopped subsequent to Gediz Vallis Ridge. Video through NASA/ JPL-Caltech/ MSSS/ UC Berkeley/ YouTube.
NASA posted in regards to the arrival on the ridge on X, exhibiting the brand new picture:
Nothing higher than stopping for a pic (or 136) after a difficult hike ?
To create this immersive panorama, my staff stitched collectively 136 pictures of this area referred to as Gediz Vallis Ridge. It may need taken me 3 years and 4 makes an attempt to get right here, however the science is price it. pic.twitter.com/FthK2VFnkJ
— Curiosity Rover (@MarsCuriosity) September 19, 2023
Curiosity rover sees a altering panorama
The upper up Mount Sharp, which is about three miles (5 km) tall, that you just go, the extra the panorama modifications. This displays the altering circumstances over time from when Gale crater – which the mountain is in the midst of – was a lake, to when it dried out. Curiosity has already discovered ample proof for the traditional lake (or sequence of lakes) and streams within the distant previous. The underside of the crater was as soon as the lakebed. As you ascend the mountain, issues get progressively drier.
The place the rover is now, nonetheless on the decrease slopes, there have been mud flows operating down the slopes of Mount Sharp. Gediz Vallis Ridge is without doubt one of the youngest geological options that Curiosity will see in its travels. It was additionally one of many final geological options to type on Mount Sharp. And now the rover can lastly see it up shut.
Historical muddy particles
Gediz Vallis Ridge is attention-grabbing to scientists for a few major causes. It accommodates historical remnants of the mud flows, which offer helpful clues about water in Gale crater on the time. Additionally, the particles flows transported many rocks and boulders. The rocks look darkish within the rover pictures and seem quite misplaced from the remainder of the panorama. The reason being that they originated from a lot increased up on the mountain. That is thrilling for the mission scientists, as they’ll now look at rocks from the higher components of the mountain that Curiosity can’t get to.
Geologist William Dietrich on the College of California, Berkeley, described the scene on the ridge:
I can’t think about what it might have been wish to witness these occasions. Big rocks have been ripped out of the mountain excessive above, rushed downhill, and unfold out right into a fan under. The outcomes of this marketing campaign will push us to higher clarify such occasions not simply on Mars, however even on Earth, the place they’re a pure hazard.
Altogether, Curiosity spent 11 days exploring Gediz Vallis Ridge. It took 136 pictures that have been later mixed into the panorama on the high of this submit. You may as well see the trail that the rover took going up the mountain. The rover had beforehand handed by a area referred to as Marker Band Valley. There, a skinny layer of darker rock stands out from the remainder of Mount Sharp. This is without doubt one of the areas the place Curiosity discovered clues in regards to the ancient watery history of Gale crater.
11 years of exploration
Curiosity safely landed in Gale crater on Mars at 10:31 p.m. Pacific Daylight Time on August 5, 2012. It has been busy ever since, seeing dust devils, seeing eclipses with the Martian moons, discovering proof for historical lakes and megafloods, detecting nitrogen and even discovering little Martian hoodoos.
Lear more about the Curiosity mission
Backside line: After three makes an attempt, NASA’s Curiosity rover has lastly reached a big ridge composed of historical mud and rocks. The ridge preserves a report of Mars’ moist previous.
Read more: Morning and afternoon on Mars, from Curiosity rover




