Comet burst virtually killed humanity 12,800 years in the past
About 12,800 years in the past – a geological blink of the attention – world temperatures out of the blue and dramatically plummeted. The icy circumstances of the Younger Dryas cooling period lasted greater than 1,200 years. Nevertheless it shouldn’t have occurred. Earth was warming when the cooling started. On June 25, 2024, scientists said they’ve discovered extra proof {that a} comet influence might need been chargeable for Earth’s sudden cooling.
The researchers published their peer-reviewed paper on Could 8, 2024, within the ScienceOpen journal Airbursts and Cratering Impacts. They stated bodily proof exhibits a 62-mile-wide (100-km-wide) comet exploded nearly the identical time humanity invented agriculture.
Beforehand revealed studies present human populations dropped dramatically on the similar second. The ensuing bottleneck virtually ended the human race. It took us greater than three centuries to start our restoration.
Unique supplies and microscopic metals litter Earth
As a result of the hypothetical comet by no means hit the bottom, proof for it comes from an abundance of tiny particles within the geological report. These micro-size bits of fabric – the metals iridium and platinum, unique magnetic micro-spherules, melt glass and miniscule nanodiamonds – cowl your complete globe. Scientists have discovered these particles within the layer of sediment that matches the beginning of the Youthful Dryas.
Emeritus Professor James Kennett of the College of California, Santa Barbara’s earth science division said the crew discovered sturdy proof supporting a cometary airburst:
There’s an entire vary of various shocked quartz, so we’ve to make a well-documented case that they’re certainly important for decoding cosmic influence, regardless that they’re not reflecting a conventional main crater-forming occasion. These are from very-low-altitude “landing” airbursts virtually definitely related to cometary influence.
Kennett is one in every of a number of authors of the brand new paper. The most recent publication is a part of a collection of scholarly works offering mounting proof a cosmic impactor altered humanity’s destiny. Kennett’s analysis even hints the comet strike sparked widespread adoption of agriculture.
Comet burst got here from a comet a minimum of 60 miles vast
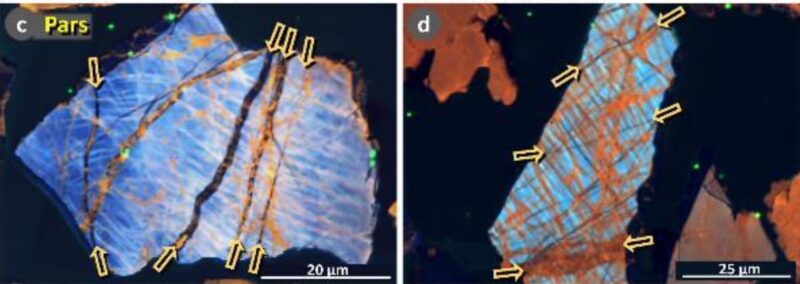
Whereas there’s proof of fallout from the comet’s atmospheric explosion all around the Earth – even in Australia – the newest paper focuses on three areas within the jap United States. All had been on the East Coast: Flamingo Bay, South Carolina; Parsons Island, Maryland; and Newtonville, New Jersey. A distance of 620 miles (1,000 km) separates the survey websites.
Of particular curiosity to the researchers are lamellae, tiny laminated layers of alternating supplies within the micro-size particles. Their abundance within the geologic report at 12,800 years in the past supplies sturdy proof for a Youthful Dryas comet influence. Kennett defined their significance:
Within the excessive type, similar to when an asteroid hammers into the Earth’s floor, all of the fractures are very parallel. When you concentrate on it, the pressures and temperatures that produce these fractures will differ relying on the density, entry angle, altitude of the influence and the impactor’s measurement.
With that in thoughts, the proof suggests the Youthful Dryas comet was about 62 miles (100 km) vast. That’s a lot bigger than the thing that killed the dinosaurs. The Chicxulub impactor – suspected of wiping out a lot of life on Earth – was possible an asteroid. The asteroid that took out the dinos was solely 6 miles (10 km) throughout. But as a result of it was a lot extra dense and really hit Earth, it was way more damaging.
The Youthful Dryas comet burst was extra just like the atmospheric explosion of a meteor over Tunguska in Russia in 1908. That object was possible simply 130 ft (40 meters) vast. However, it took out 830 sq. miles (2,150 sq. km) of forest. It additionally left no influence crater.
The Younger Dryas impact hypothesis stays controversial. There have been repeated makes an attempt to refute the conclusion. But the bodily proof in help of the thought continues to mount. On this video, the Prehistory Guys current the historical past of the proof – and objections to it – {that a} comet strike coincided with the beginning of the Youthful Dryas.
Megafauna extinction and the misplaced Clovis Tradition
The Youthful Dryas comet didn’t come down in a single piece. Researchers theorize it fragmented earlier than it exploded. A number of detonations are chargeable for the worldwide distribution of the microscopic particles the disastrous collision left behind. It modified the world endlessly; the analysis crew wrote:
The implications of this occasion, together with attainable world results on environmental ecosystems, glacial ice sheets, megafaunal extinctions and human populations, are but to be absolutely understood however have to be evaluated within the context of a geologically instantaneous and sure catastrophic occasion.
The airburst may additionally be the occasion that sealed the destiny of the North American Clovis culture. This toolmaking custom’s practitioners crafted distinctive shapes for his or her weapons. Research by different students exhibits a 52% decline in Clovis spearpoints on the similar time the suspected cosmic customer arrived.
The world’s megafauna had been already dying off about 40,000 years earlier than the Youthful Dryas set in. But there’s evidence within the fossil report the extinction course of sped up at the moment.
Nonetheless, not all scientists settle for the Youthful Dryas influence speculation as the reason for the cooling. Others imagine the jet stream shifted, inflicting polar ice to soften. And there’s proof the Atlantic meridional overturning circulation (AMOC) – which is at the moment at its weakest in 1,000 years – failed totally.
The AMOC could once more be on the verge of collapse.
Backside line: New proof suggests a celestial physique exploded in Earth’s ambiance 12,800 years in the past. The catastrophic comet burst could have cooled Earth’s local weather for round 1,200 years.
Via University of California, Santa Barbara
Read more: ECP contributor Yuri Beletsky’s best photos of Comet C/2014 Q1 (PANSTARRS)
Read more: Extinction of giant herbivores changed global landscapes




