A global group of researchers, led by scientists on the College of Toronto, has developed a brand new machine studying algorithm to assist reply one of many greatest questions of all: Are we alone within the universe? It’s one other use of synthetic intelligence (AI), wherein a pc performs duties people (or much less subtle computer systems) used to do. The researchers announced the information on January 30, 2023. They hope their new algorithm will streamline the seek for extraterrestrial intelligence, generally generally known as SETI. It may possibly discover potential alerts in knowledge that different strategies might need missed. And in reality, after taking a look at 820 preliminary stars, it has already discovered 8 potential alerts of curiosity.
The astronomers found the alerts in radio knowledge beforehand collected by the Robert C. Byrd Green Bank Telescope in West Virginia. The telescope collected the information as a part of the Breakthrough Listen initiative. Scientists had missed the tentative alerts in earlier examinations of the information.
The researchers published their work in a brand new peer-reviewed paper in Nature Astronomy on January 30, 2023. A preprint model of the paper can be obtainable from UC Berkeley SETI.
Along with the College of Toronto, the SETI Institute and Breakthrough Initiatives additionally issued their very own press releases.
New AI seek for aliens: Separating wheat from chaff
All through the historical past of SETI, interference from human-caused radio alerts has been a a persistent downside. Discovering precise extraterrestrial alerts – if they’re on the market – shouldn’t be a straightforward process. Peter Ma, an undergraduate on the College of Toronto and lead creator of the brand new paper, stated:
In a lot of our observations, there’s a number of interference. We have to distinguish the thrilling radio alerts in space from the uninteresting radio alerts from Earth.
Therefore, astronomers wanted a brand new technique of detecting radio alerts or different technosignatures, one that might “separate the wheat from the chaff” because it have been. That’s the place Ma and his group are available. They developed a brand new machine studying algorithm that may higher pick potential alien alerts from all of the background noise on Earth. This preliminary search combed by way of knowledge from 820 close by stars. The paper said:
Right here we current a complete deep-learning-based technosignature search on 820 stellar targets from the Hipparcos catalog, totaling over 480 hours of on-sky knowledge taken with the Robert C. Byrd Inexperienced Financial institution Telescope as a part of the Breakthrough Hear initiative.
The SETI Institute additionally quoted Ma:
In total, we had searched by way of 150 TB of knowledge of 820 close by stars, on a dataset that had beforehand been searched by way of in 2017 by classical strategies however labeled as devoid of attention-grabbing alerts.
Alien alerts vs. human-caused interference
So, how does this machine-learning instrument work? Principally, the researchers skilled the algorithm to distinguish between potential alien alerts and human-caused ones by simulating each kinds of alerts.
The brand new algorithm relies on comparisons of varied different machine-learning algorithms. The purpose is to lower false-positive charges and improve precision in detecting bonafide alerts. Steve Croft, challenge scientist for Breakthrough Hear on the Inexperienced Financial institution Telescope, added:
The important thing concern with any technosignature search is trying by way of this enormous haystack of alerts to search out the needle that is perhaps a transmission from an alien world. The overwhelming majority of the alerts detected by our telescopes originate from our personal expertise: GPS satellites, cellphones and the like. Peter’s algorithm provides us a more practical method to filter the haystack and discover alerts which have the traits we anticipate from technosignatures.
AI seek for aliens yields 8 ‘alerts of curiosity’
The algorithm could also be new and nonetheless being examined, but it surely has already found eight alerts of curiosity. The astronomers searched 820 close by stars from the Hipparcos catalogue for attainable technosignatures. And surprisingly, it has already discovered … one thing. The eight alerts seem to originate from the path of 5 of the celebs, starting from 30 to 90 light-years away. Researchers didn’t see them in earlier evaluation of the information, which didn’t use the machine studying method. Whereas not confirmed to be extraterrestrial, they’re actually attention-grabbing. Croft stated:
First, they’re current after we take a look at the star and absent after we look away, versus native interference, which is mostly all the time current. Second, the alerts change in frequency over time in a manner that makes them seem removed from the telescope.
They seem like alien alerts … however are they?
The researchers famous that the alerts have key characteristics that make them value a more in-depth look:
1. The alerts have been narrowband, that means they’d slim spectral width, on the order of just some Hz. Indicators brought on by pure phenomena are usually broadband.
2. The alerts had non-zero drift charges, which suggests the alerts had a slope. Such slopes might point out a sign’s origin had some relative acceleration with our receivers, therefore not native to the radio observatory.
3. The alerts appeared in ON-source observations and never in OFF-source observations. If a sign originates from a selected celestial supply, it seems after we level our telescope towards the goal and disappears after we look away. Human radio interference normally happens in ON and OFF observations because of the supply being shut by.
The alerts look like what scientists anticipate extraterrestrial alerts would possible be like. There’s one downside, although. Comply with-up observations – thus far, anyway – didn’t see them once more. The astronomers must detect them once more with a view to examine them extra carefully and attempt to decide if they really are from deep space or simply terrestrial interference. The paper states:
Our work additionally returned eight promising extraterrestrial intelligence alerts of curiosity not beforehand recognized. Re-observations on these targets have thus far not resulted in re-detections of alerts with related morphology.
Accelerating the seek for technosignatures
Despite the fact that these eight alerts are intriguing, but unconfirmed, they present that the brand new algorithm is working. Astronomers will have the ability to apply it to different datasets as nicely. As co-author Cherry Ng famous:
By poking the information with each method, we’d have the ability to uncover thrilling alerts. I’m impressed by how nicely this method has carried out on the seek for extraterrestrial intelligence. With the assistance of synthetic intelligence, I’m optimistic that we’ll have the ability to higher quantify the chance of the presence of extraterrestrial alerts from different civilizations.
Ma added:
With our new method, mixed with the following technology of telescopes, we hope that machine studying can take us from looking tons of of stars to looking tens of millions.
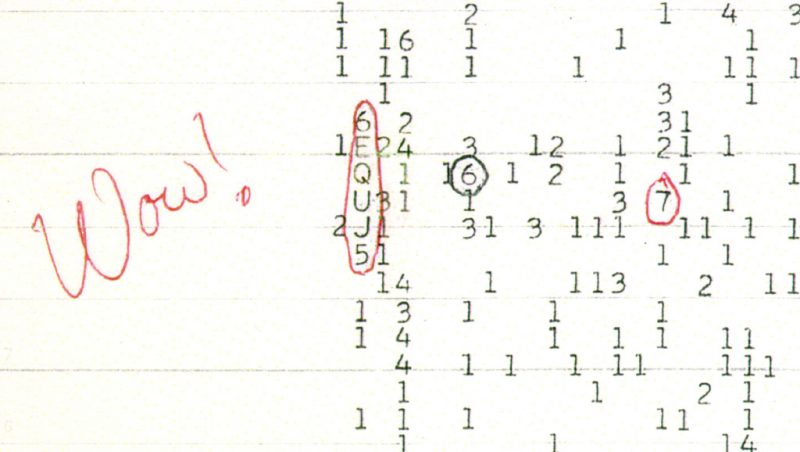
Extra promising than the Wow! sign?
Evaluation of the unique alerts is constant, nonetheless. Despite the fact that they could nicely transform one more case of earthly interference, they’re probably promising. Astronomer Michael Garrett on the Jodrell Financial institution Heart for Astrophysics, College of Manchester, said:
A cursory evaluate of the brand new paper recommend these are certainly promising alerts. They’re way more compelling than what is probably probably the most well-known SETI candidate, the Wow! sign, radio emission bearing the hallmarks of an extraterrestrial origin that was collected by an Ohio telescope in 1977. Realistically, it’s most probably that these eight new alerts have been generated by human expertise. However the true story right here is the effectiveness of AI and the strategies utilized by the group to dig out uncommon and attention-grabbing alerts beforehand buried within the noise of human-generated radio frequency interference, akin to cellphones and GPS.
The researchers will proceed to have a look at the celebs the place the alerts appeared to come back from, based on Breakthrough Initiatives Govt Director S. Pete Worden:
We’ll proceed to observe the celebs Peter noticed, and we’ll proceed to develop our use of synthetic intelligence to assist us attempt to reply humanity’s most profound query: Are we alone?
Astronomers beforehand detected Breakthrough Hear’s first candidate signal, known as BLCI, in 2020. It appeared to come back from the path of the closest star to the sun, Proxima Centauri, however was later traced to earthly interference.
Backside line: A global group of scientists stated {that a} subtle new AI seek for aliens has already discovered 8 potential alerts of curiosity from 5 close by stars.
Source: A deep-learning search for technosignatures from 820 nearby stars
Source (preprint): A deep-learning search for technosignatures of 820 nearby stars




