Together with your eye alone, binoculars, and a telescope, you may star-hop your solution to the great thing about globular star cluster M5, or Messier 5. With the unaided eye, M5 is barely detectable and seems to be a faint star. Binoculars present it a bit extra clearly. However flip a small telescope on it, and also you’ll see one of many most interesting globular clusters north of the celestial equator.
In contrast to most of the “faint fuzzies” within the night time sky – nebulas, galaxies and clusters that also seem as dim, blurry smudges even by way of telescopes – M5 is without doubt one of the finest globular clusters to watch. Burnham’s Celestial Handbook says that Admiral Smyth known as M5 a:
… Very good object … a noble mass, refreshing to the senses after trying to find faint objects.
However you want an honest telescope for the perfect views. In any other case, along with your eyes alone or binoculars, you would possibly describe it as Charles Messier did:
… A superb nebula which I’m certain incorporates no star.
In actuality, a whole lot of hundreds of stars pack tightly into the globular cluster M5, together with an uncommon variety of variable stars.
Globular clusters versus open clusters
Most of the brighter and bigger clusters seen from Earth are open star clusters. For instance, the Pleiades and the Hyades clusters are open star clusters. Open star clusters are born, and stay out their lives, throughout the galactic disk. They’re free collections of a number of hundred stars. After all, those we all know finest are comparatively close by, a couple of hundred light-years away.
In distinction, M5 is a globular star cluster. Globular clusters reside throughout the galactic halo – a sphere-shaped area of the Milky Way that extends above and under the galactic disk. If we liken the disk to a hamburger, then the bun could be the galactic halo. In actual fact, globular star clusters comprise a whole lot of hundreds of stars, tightly packed in a spherical ball.
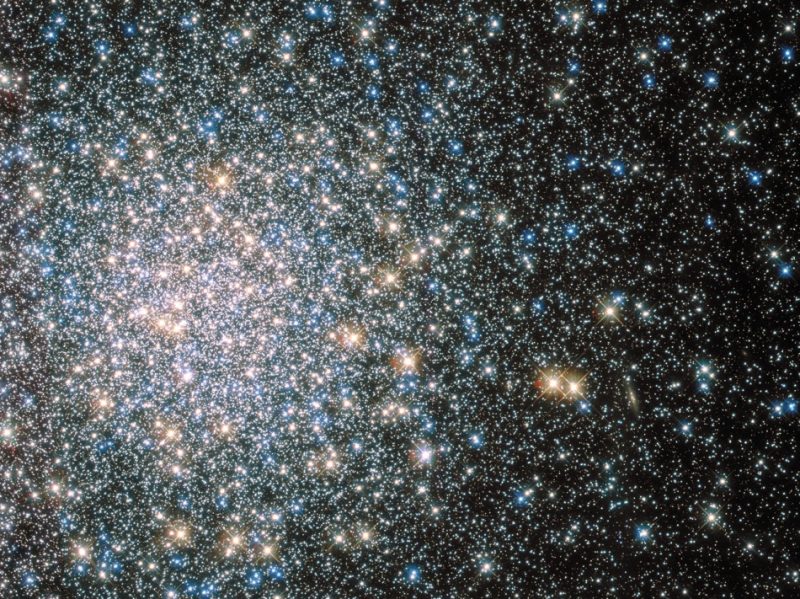

Globular clusters are historic
The actual fact is, globular clusters are our galaxy’s oldest members. In different phrases, they fashioned first, because the galaxy was forming. Spanning 165 light-years in diameter, M5 is without doubt one of the largest globular clusters recognized. Plus, it incorporates greater than 100,000 stars, or as many as 500,000, in accordance with some estimates.
And the comparatively younger stars of open clusters disperse after a whole lot of tens of millions of years. Nevertheless, the celebs in globular clusters stay carefully related after many billions of years.
In order you stare upon M5, you’re an object that’s round 13 billion years outdated, greater than twice the age of our solar system, and nearly as historic because the universe itself. Contemplating that M5 lies some 24,500 light-years distant, we will solely think about what this stellar metropolis would seem like if it was on the Pleiades’ distance of 430 light-years. Or think about what an inhabitant of a planet inside a globular cluster would see.
The right way to discover M5
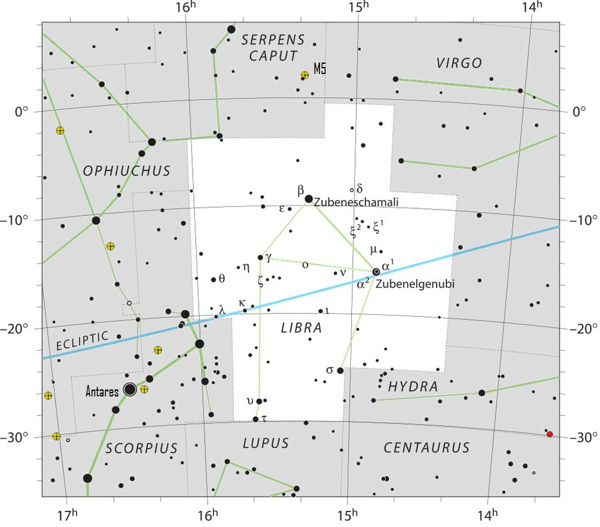
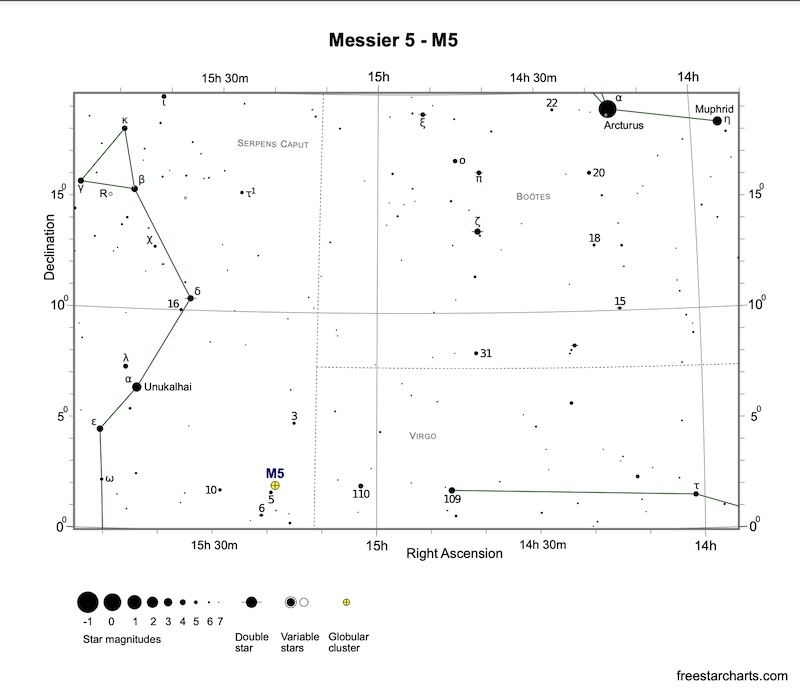
M5 is within the constellation Serpens Caput (the Serpent’s Head), so it’s seen all summer time. From the Northern Hemisphere, it’s seen within the night sky beginning in Could and reaches its highest level within the sky in July. Round September it’s passed by midnight.
Using a fist at arm’s length for a guide, M5 resides a great two fist-widths to the southeast of yellow-orange Arcturus, summertime’s brightest star. M5 can also be three fist-widths to the east of blue-white Spica, the brightest star within the constellation Virgo.
Plus, M5 is about one fist-width to the north (above) Zubeneschamali. So these stars offer you at the least a tough thought of M5’s whereabouts within the heavens.
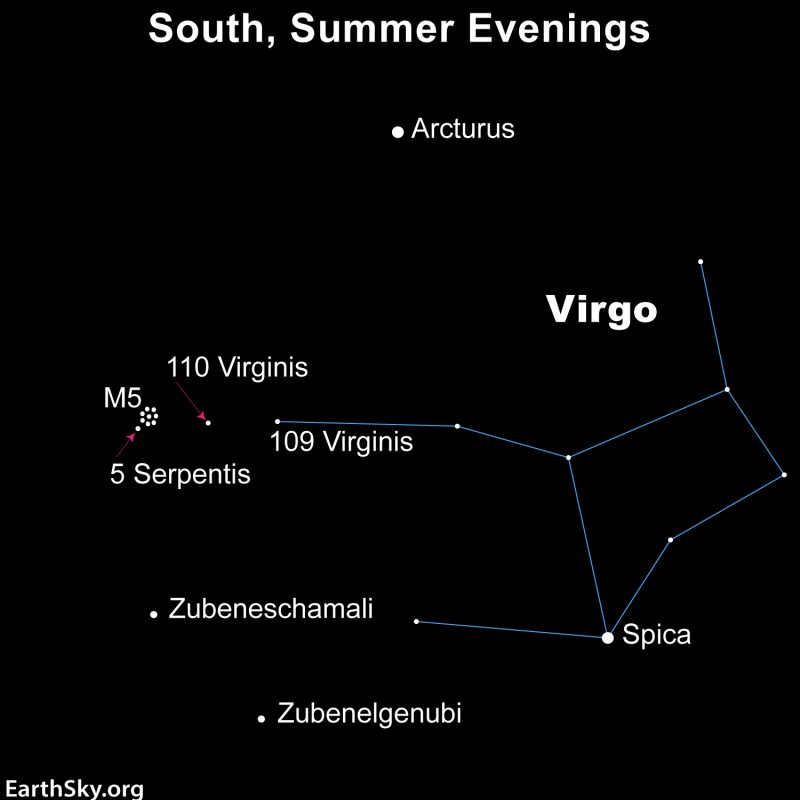
Practiced sky gazers star-hop to M5 by the use of two faint but seen Virgo stars: 109 Virginis and 110 Virginis. They draw an imaginary line from 109 Virginis by way of 110 Virginis, and go twice the space to land on the star 5 Serpentis. M5 is only one/3 of a degree to the northwest (higher proper) of this star. The space from 109 Virginis to M5 spans about eight levels of sky. For reference, the width of 4 fingers at arm’s size away approximates eight levels.
Variable stars in M5
As a matter of reality, astronomers have discovered greater than 100 variable stars on this globular cluster. By the best way, variable stars are those who range in brightness over a time frame. Most of the stars are RR Lyrae variable stars, a sort of star that pulses irregularly. A unique kind of variable star, a Cepheid variable, is brilliant and pulses recurrently, making them useful instruments for astronomers to find out distances. Scientists have additionally discovered Cepheid variables within the cluster. As well as, one SS Cygni class variable – or dwarf nova – and a faint eruptive star, additionally lies in M5.
Backside line: M5 is a superb globular cluster in Serpens Caput to discover with a small telescope.




