Orion the Hunter on December evenings
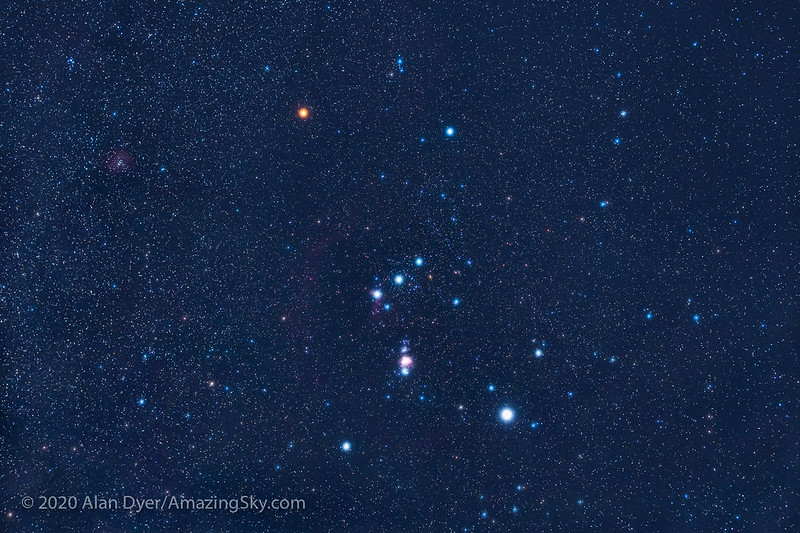
Tonight – or any December night – discover the well-known constellation Orion the Hunter. It’s vibrant and will be seen from inside smaller cities. And the three stars that make up Orion’s Belt – in a brief, straight row on the Hunter’s midsection – are very noticeable. When you have a dark sky, you may see one thing else: the starry band of the Milky Way – the edgewise view of our residence galaxy – working behind Orion.
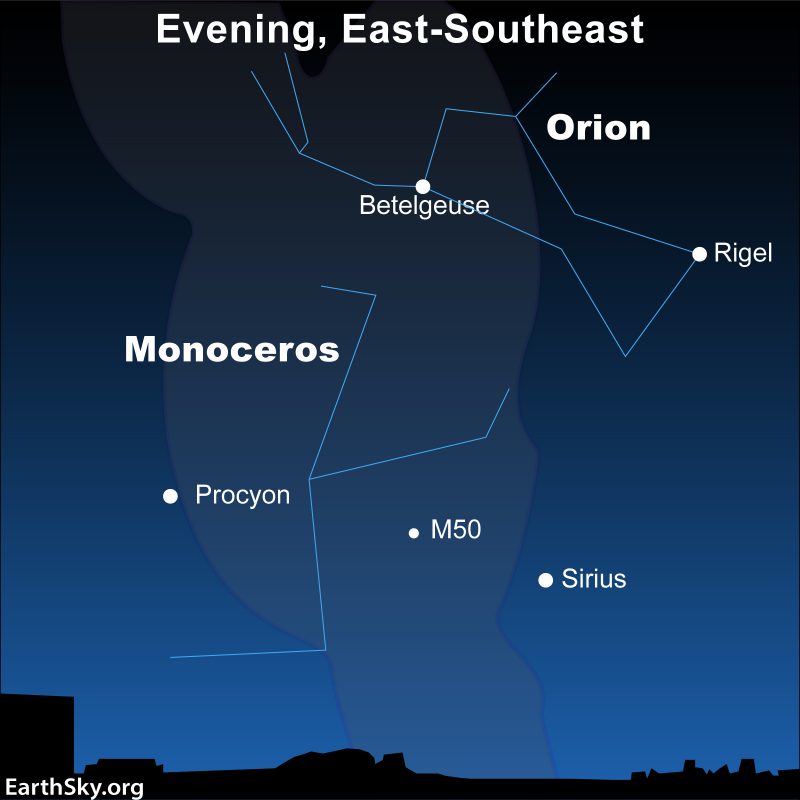
As seen from the Northern Hemisphere, after Orion rises, the three stars of Orion’s Belt jut kind of straight up from the horizon. Look on both aspect of the Belt stars for 2 very vibrant stars. One is the reddish star Betelgeuse. The opposite is vibrant, blue-white Rigel.
All through December, the constellation Orion is properly up by mid-evening (by that we imply by halfway between your native sundown and your native midnight). Like the entire starry sky, as Earth strikes across the sun, Orion rises earlier every night. And, by late December, Orion shall be seen at dusk or early night. That’s true for each the Southern and Northern Hemispheres.
Orion is a summer season constellation for the Southern Hemisphere.
However we within the Northern Hemisphere affiliate Orion with winter nights. That’s as a result of this constellation is up all through our lengthy December and January nights.

Use Orion to search out the Milky Way
As a result of so many individuals are conversant in Orion, this constellation is a good leaping off spot for locating the starry pathway of the Milky Way. You’ll want a dark sky to see the hazy arc of stars working behind the intense crimson star Betelgeuse.
Trying on the Milky Way in our sky is trying edgewise into the disk of our galaxy. We see the galaxy because the mixed glow of billions of stars. You would possibly know that – within the month of August – the Milky Way seems broad and vibrant through the night hours. At the moment of 12 months, within the night, all of us on Earth are gazing towards the star-rich center of the galaxy.
Now Earth has traveled in its orbit across the sun, and our night sky is mentioning in a distinct route. For those who see the Milky Way behind the constellation Orion this month, you would possibly suppose it’s very faint in distinction to the August Milky Way. It is fainter, as a result of now we’re trying towards the galaxy’s periphery. And now there are fewer stars between us and intergalactic space.
Backside line: Yow will discover one of the well-known constellations – Orion the Hunter – plus see the Milky Way tonight.
Read More: Orion’s Belt and the Celestial Bridge
Easily locate stars and constellations during any day and time with EarthSky’s planisphere.




