A mysterious remnant from a uncommon kind of supernova recorded in 1181 has been defined for the primary time. Two white dwarf stars collided, creating a brief “visitor star,” now labeled supernova (SN) 1181, which was recorded in historic paperwork in Japan and elsewhere in Asia. Nonetheless, after the star dimmed, its location and construction remained a thriller till a staff pinpointed its location in 2021.
Now, by laptop modeling and observational evaluation, researchers have recreated the construction of the remnant white dwarf, a uncommon incidence, explaining its double shock formation. In addition they found that high-speed stellar winds could have began blowing from its floor inside simply the previous 20–30 years. The work has been published in The Astrophysical Journal.
This discovering improves our understanding of the range of supernova explosions, and highlights the advantages of interdisciplinary analysis, combining historical past with trendy astronomy to allow new discoveries about our galaxy.
It’s the yr 1181 and in Japan the Genpei Struggle (1180–85) has lately begun. It can result in a shift in political energy from aristocratic households to the brand new military-based shogunate, which is able to set up itself within the coastal metropolis of Kamakura close to modern-day Tokyo.
A report of this tumultuous interval was compiled in a diary format within the Azuma Kagami. It chronicled not solely folks’s lives and key occasions (with various accuracy), however different every day observations, together with the looks of a brand new star.
“There are various accounts of this non permanent visitor star in historic data from Japan, China and Korea. At its peak, the star’s brightness was similar to Saturn’s. It remained seen to the bare eye for about 180 days, till it progressively dimmed out of sight. The remnant of the SN 1181 explosion is now very outdated, so it’s darkish and troublesome to seek out,” defined lead writer Takatoshi Ko, a doctoral pupil from the Division of Astronomy on the College of Tokyo.
The remnant of this visitor star, labeled supernova remnant (SNR) 1181, was discovered to have been created when two extraordinarily dense, Earth-sized stars, referred to as white dwarfs, collided. This created a uncommon kind of supernova, referred to as a Kind Iax supernova, which left behind a single, vivid and fast-rotating white dwarf. Aided by observations on its place famous within the historic doc, trendy astrophysicists lastly pinpointed its location in 2021 in a nebula in direction of the constellation Cassiopeia.
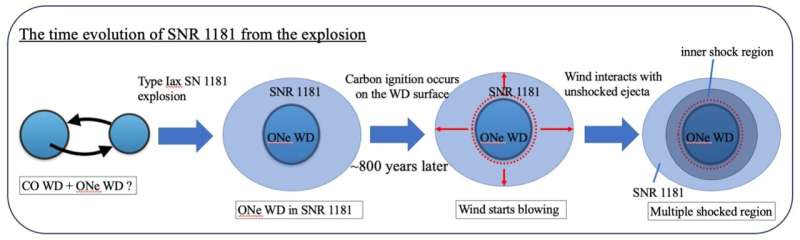
Resulting from its uncommon nature and site inside our galaxy, SNR 1181 has been the topic of a lot observational analysis. This steered that SNR 1181 is made up of two shock areas, an outer area and an inside one. On this new research, the analysis group analyzed the most recent X-ray knowledge to assemble a theoretical laptop mannequin to elucidate these observations, and which has recreated the beforehand unexplained construction of this supernova remnant.
The primary problem was that, in keeping with typical understanding, when two white dwarfs collide like this, they need to explode and disappear. Nonetheless, this merger left behind a white dwarf. The spinning white dwarf was anticipated to create a stellar wind (a fast-flowing stream of particles) instantly after its formation. Nonetheless, what the researchers discovered was one thing else.
“If the wind had began blowing instantly after SNR 1181’s formation, we could not reproduce the noticed dimension of the inside shock area,” stated Ko.
“Nonetheless, by treating the wind’s onset time as variable, we succeeded in explaining all the noticed options of SNR 1181 precisely and unraveling the mysterious properties of this high-speed wind. We had been additionally in a position to concurrently monitor the time evolution of every shock area, utilizing numerical calculations.”
The staff was very stunned to seek out that, in keeping with their calculations, the wind could have began blowing solely very lately, throughout the previous 20–30 years. They recommend this may occasionally point out that the white dwarf has began to burn once more, presumably as a result of among the matter thrown out by the explosion witnessed in 1181 falling again to its floor, rising its density and temperature over a threshold to restart burning.
To validate their laptop mannequin, the staff is now getting ready to additional observe SNR 1181 utilizing the Very Giant Array (VLA) radio telescope primarily based in central New Mexico state within the U.S., and the 8.2 meter-class Subaru Telescope within the U.S. state of Hawaii.
“The flexibility to find out the age of supernova remnants or the brightness on the time of their explosion by archaeological views is a uncommon and invaluable asset to trendy astronomy,” stated Ko. “Such interdisciplinary analysis is each thrilling and highlights the immense potential for combining numerous fields to uncover new dimensions of astronomical phenomena.”
Extra data:
Takatoshi Ko et al, A dynamical mannequin for IRAS 00500+6713: the remnant of a kind Iax supernova SN 1181 internet hosting a double degenerate merger product WD J005311, The Astrophysical Journal (2024). DOI: 10.3847/1538-4357/ad4d99
Supplied by
University of Tokyo
Quotation:
Elusive non permanent star described in historic paperwork recreated utilizing new laptop mannequin (2024, July 5)
retrieved 5 July 2024
from https://phys.org/information/2024-07-elusive-temporary-star-historical-documents.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any truthful dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for data functions solely.




