Saturn’s ocean moon, Enceladus, is attracting growing consideration within the seek for life in our solar system. Most of what we find out about Enceladus and its ice-covered ocean comes from the Cassini mission. Cassini ended its exploration of the Saturn system in 2017, however scientists are nonetheless working by way of its knowledge.
New analysis based mostly on Cassini knowledge strengthens the concept that Enceladus has the chemical substances crucial for all times.
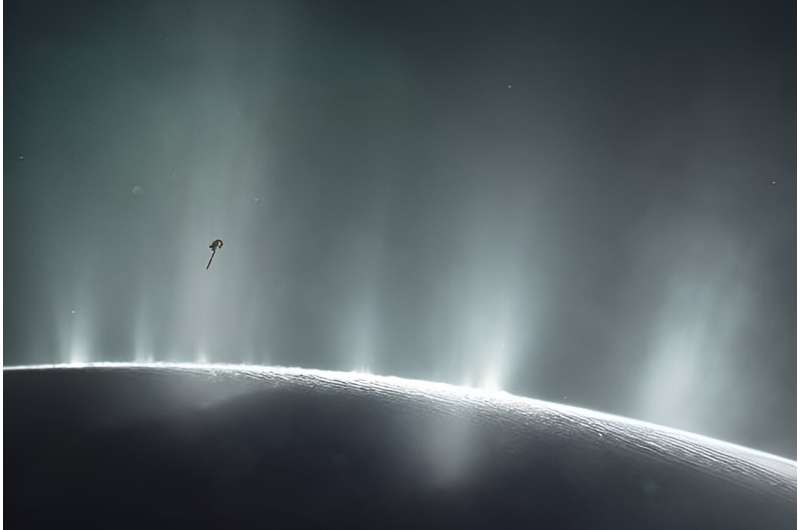
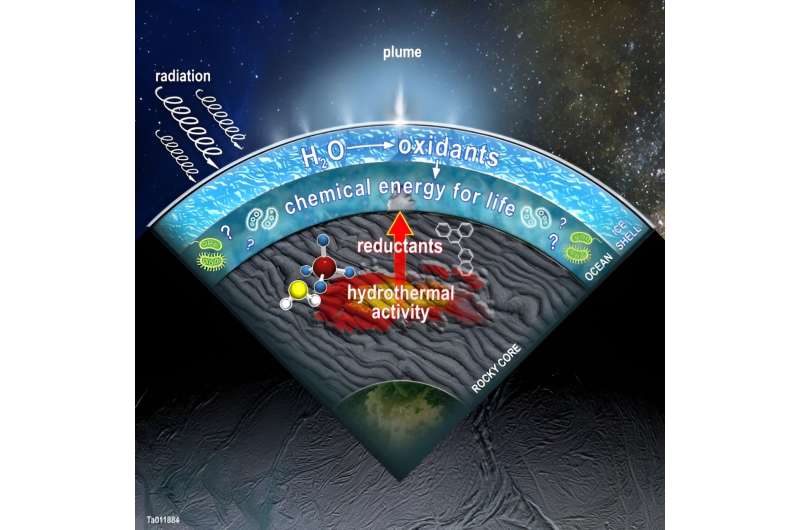
Throughout its mission, Cassini found geyser-like plumes of water erupting by way of Enceladus’ icy shell. In 2008, Cassini carried out a close-proximity flyby and analyzed the plumes with its Cosmic Mud Analyzer (CDA). The CDA confirmed that the water within the plumes contained a stunning mixture of volatiles, together with carbon dioxide, water vapor, and carbon monoxide. It additionally discovered hint quantities of molecular nitrogen, easy hydrocarbons, and complicated natural chemical substances.
However Cassini’s knowledge continues to be being analyzed, even six years after it accomplished its mission and was despatched to its destruction in Saturn’s environment. A new paper posted to bioRxiv titled “Observations of Elemental Composition of Enceladus According to Generalized Fashions of Theoretical Ecosystems” presents some new findings. The lead creator is Daniel Muratore, a post-doc on the Santa Fe Institute.
The work facilities on the invention of ammonia and inorganic phosphorous in Enceladus’ ocean. The researchers used ecological and metabolic idea and modeling to grasp how these chemical substances might make Enceladus amenable to life. “Other than speculating about threshold concentrations of bioactive compounds to assist ecosystems, metabolic and ecological idea can present a strong interpretative lens to evaluate whether or not extraterrestrial environments are appropriate with dwelling ecosystems,” the authors clarify.
A important element of ecological idea is the Redfield ratio. It is named after the American oceanographer Alfred Redfield. In 1934, Redfield revealed outcomes displaying that the ratio of carbon to nitrogen to phosphorous (C:N:P) was remarkably constant throughout ocean biomass at 106:16:1. Different researchers discovered that the ratio shifted barely relying on the world and the phytoplankton species current. Newer work refined the ratio to 166:22:1.
The precise numbers aren’t essentially the important level. Redfield’s conclusion is the important half. The Redfield ratio exhibits a exceptional unity between the chemistry of dwelling issues within the deep ocean and the ocean itself. He proposed that there is an equilibrium between ocean water and plankton vitamins that is based mostly on biotic suggestions. He described a chemical framework for vitamins and easy life.

“No matter its clarification, the correspondence between the portions of biologically accessible nitrogen and phosphorus within the sea and the proportions wherein they’re utilized by the plankton is a phenomenon of the best curiosity,” Redfield stated within the conclusion of his paper.
So, how does the invention of ammonia and phosphorous in Enceladus’ ocean relate to the Redfield ratio and Enceladus’ organic potential?
The Redfield ratio is widespread all throughout the Tree of Life on Earth. “Due to this seeming ubiquity, the Redfield ratio has been thought of a goal signature for astrobiological life detection, particularly on ocean worlds akin to Europa and Enceladus,” the authors of the brand new paper write. In terms of life, all we’ve got to go on is Earth. So it is smart to make use of foundational elements of life’s chemistry right here on Earth as a lens by way of which to look at different potential life-supporting worlds.
Evaluation of Cassini’s knowledge from Enceladus’ plumes exhibits a excessive degree of inorganic phosphate within the ocean. Different geochemical simulations based mostly on Cassini’s findings point out the identical. “These stories of phosphorus observe on the tails of earlier work figuring out quite a few elemental constituents of terrestrial life (C, N, H, O) from the Enceladus plume,” the authors clarify. Much more evaluation means that the ocean incorporates lots of the chemical substances frequent in dwelling organisms, like amino acid precursors, ammonium, and hydrocarbons.
So Enceladus’ ocean has a wealthy chemistry, and plenty of chemical substances replicate life’s chemical make-up. Specifically, there’s an rising speculation that Enceladus might assist methanogenesis. Earth’s Archaea carry out methanogenesis throughout a large swath of various environmental circumstances on Earth and have performed so for over three billion years, proving their survivability. Biochemical modeling means that Earth’s methanogens are appropriate with Enceladus’ ocean.
The researchers developed a brand new, extra detailed mannequin for methanogens on Enceladus to see if they might survive and thrive there. Their mannequin leaned closely on the Redfield ratio. They discovered that although phosphorous is current in excessive ranges within the moon’s ocean, the general ratio “could also be limiting to Earth-like cells.”
“Excessive standing shares of those vitamins might be per incomplete drawdown as a result of a small or metabolically gradual biosphere, a biosphere with a current origin of life,” or different causes that would trigger an imbalance.
So the place does that go away the prospects for all times on Enceladus?
We’re solely originally of biosignature science. We will establish particular person chemical substances, however from this nice distance away, we won’t precisely measure Enceladus’ total chemistry. Newer biosignature analysis, together with this paper, goals to establish how organic processes reorganize chemical components in telltale methods. By complete ecosystems, as Redfield did, scientists could uncover new biosignatures which can be much less ambiguous.
If we will try this, we could uncover that non-Earthly lifeforms reorganize chemical substances in totally other ways.
This analysis is a part of a brand new effort to detect greater than particular person chemical biosignatures, a few of which could be false positives. Methane, for instance, is usually a biosignature however can be produced abiotically. There are others, just like the not too long ago found phosphine on Venus.
Understanding ecosystems as a complete is the subsequent step. There is a bewildering variety of components to contemplate. Cell measurement, nutrient availability, radiation, salinity, temperature. On and on. However to grasp the general chemical atmosphere at Enceladus, Europa, or wherever else, we want extra detailed knowledge.
Fortunately, instrument science retains bettering, and upcoming missions to Europa will begin to paint a fuller image. Based on the authors, the subsequent step requires extra fulsome knowledge and a extra generalized strategy.
“We advise two priorities for additional astrobiological analysis to raised perceive the implications of those conclusions,” they write. “First, we echo earlier calls within the astrobiology literature to discover extra generalized notions of metabolism and physiology.” In addition they counsel that in search of direct parallels to terrestrial life within the type of biochemistry might not be the perfect technique for in search of life on Enceladus.
“Second, we suggest broadening the scope of Earth analog environments to incorporate these with excessive useful resource provide ratios mirroring that steered for Enceladus,” they clarify.
Our understanding of habitability grows incrementally, as this research clearly exhibits. There’ll doubtless be no revelatory moments the place we abruptly perceive it.
Nature has created an unlimited number of worlds, every with its personal chemistry. Whereas utilizing instruments just like the Redfield ratio as a lens is a technique of these worlds in all their distinctive glory, we won’t get tunnel imaginative and prescient.
Whereas most of what our imaginations dream up about life on different worlds is fanciful and unlikely, life might’ve discovered one other approach on Enceladus. There might be totally different ways in which life exists in and reorganizes chemical environments.
Extra info:
Daniel Muratore et al, Observations of Elemental Composition of Enceladus According to Generalized Fashions of Theoretical Ecosystems, bioRxiv (2023). DOI: 10.1101/2023.10.29.564608
Supplied by
Universe Today
Quotation:
Enceladus has all of the uncooked supplies for all times, researchers say (2023, November 8)
retrieved 8 November 2023
from https://phys.org/information/2023-11-enceladus-raw-materials-life.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any honest dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for info functions solely.




