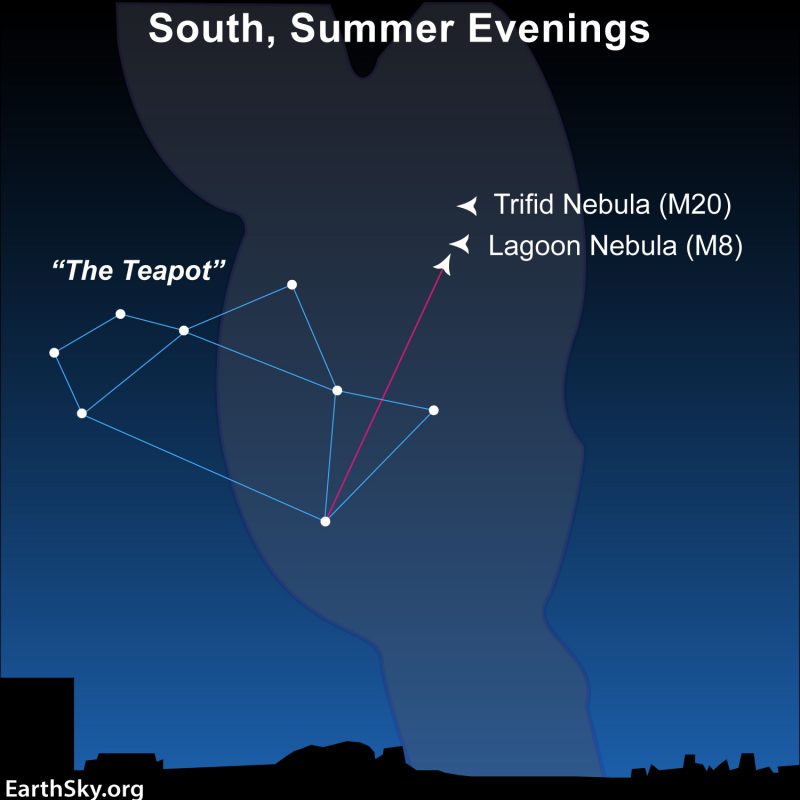
Strange binoculars beneath a dark sky can deliver the Lagoon Nebula to you from 5,000 light-years away. Search for it a couple of degrees above and to the correct of the Teapot asterism within the constellation Sagittarius. Messier 8 (M8) is the formal designation for this nebula. It’s a big fuel cloud inside our Milky Way galaxy, barely seen to the human eye beneath good situations, however wonderful with a darkish sky and a little bit of optical help.
Learn how to discover the Lagoon Nebula
To make sure, you may take pleasure in nice views of M8, however first it’s a must to discover it. Let’s begin with when to look. Within the Northern Hemisphere, mid-summer to mid-fall is right. In the event you’re within the Southern Hemisphere, you’ll need to look in mid-winter to mid-spring. Later, by early July every year, this object is crossing the meridian – showing highest within the sky – at midnight. And by early September, it’s crossing the meridian as darkness falls, making it prime for early night observations.
Subsequent, choose an evening near new moon and an observing spot that’s removed from interfering lights. Go to EarthSky’s Best Places to Stargaze page to discover a darkish sky location close to you.
Then, search for the constellation Sagittarius, which marks the path of the Milky Way’s middle. You’ll be trying southward within the night from Earth’s Northern Hemisphere. In the event you’re within the Southern Hemisphere, look northward, nearer to overhead, and switch the chart under upside-down. Desire a extra precise location for Sagittarius? Attempt utilizing Stellarium, which is able to allow you to set a date and time out of your precise location on the globe.
What you’ll see
The Lagoon Nebula spans an space of sky about 3 times the scale of the full moon. As the most important and brightest of plenty of nebulosities round Sagittarius, it’s extensively seen all through the Northern Hemisphere. As a result of its location within the sky (-24 levels declination), observers farther south see it even greater, which is healthier for observing.
The nebula is only a very faint patch to the unaided eye, nevertheless it takes on an rectangular form in binoculars. A brighter nucleus (the so-called “hourglass”) is seen on one aspect, separated by a darkish rift from an open star cluster on the opposite aspect. Whereas you’ll have seen pictures of the nebula with gorgeous coloration, these are attained through extremely technical long-exposure pictures. To the unaided eye, the faint nebulosity seems grayish, with little (if any) trace of coloration.

The science of the Lagoon Nebula
M8 is about 5,000 light-years away, and roughly 130 light-years in size. The Lagoon Nebula is an emission nebula, composed primarily of hydrogen. A lot of it’s ionized (heated or energized) by radiation from the close by younger and large star Herschel 36. It’s additionally a stellar nursery: a spot the place new stars are born. And an open star cluster – NGC 6530 – manufactured from sizzling, blue stars just some million years outdated lies on this area. Along with these younger stars, there are additionally many darkish Bok globules (darkish nebulae) of condensing fuel and dust. These are on their method to changing into protostars, and finally fully-fledged stars like these already shaped close by.
Early observations of the Lagoon
Whereas the title Lagoon would possibly conjure up a way of fantasy, there is no such thing as a recognized mythology related to this interstellar cloud. The title apparently refers back to the nebula’s look, with the darkish lane working via the cloud evoking a sandbar between two lagoons. Whereas seen to the unaided eye and subsequently actually seen all through historical past, there is no such thing as a recognized point out of this nebula till 1654, when Sicilian astronomer Giovanni Battista Hodierna recorded his observations of the star cluster throughout the nebula.
The realm was then noticed by a number of different astronomers, together with Charles Messier in 1764, after which it additionally turned referred to as Messier 8, or M8: the eighth object in Messier’s catalog.
In the event you’re seeking to make some observations your self, you might need to know that the Lagoon Nebula’s approximate middle place is RA: 18h 04m, declination: -24° 22′.
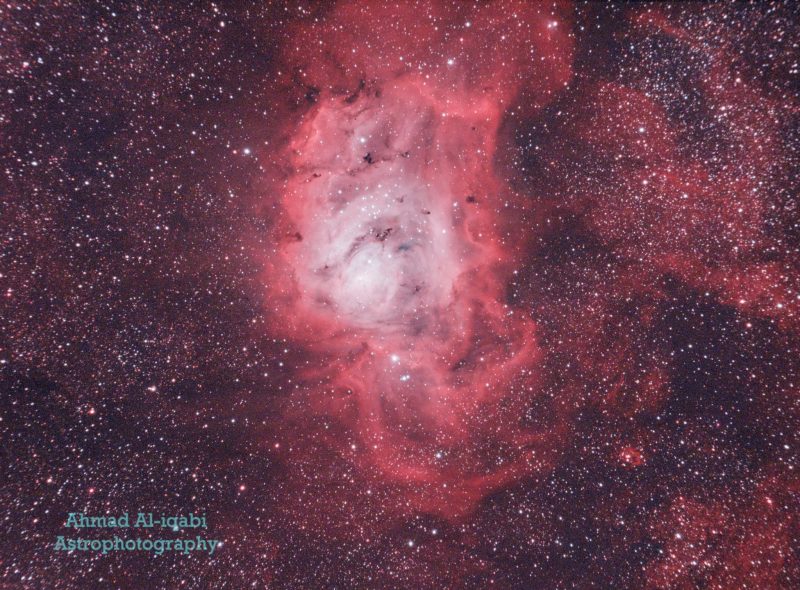

Backside line: The Lagoon Nebula, or Messier 8, is a big emission nebula within the constellation Sagittarius. You may discover it with binoculars.




