The Hyades star cluster is simply about 153 light-years away. At that brief distance away, it is seen with the unaided eye within the constellation Taurus. Its proximity provides skilled astronomers a better time observing it than many different objects of curiosity. Hyades incorporates lots of of stars with comparable ages—about 625 million years—comparable metallicities and comparable motions via space.
However one thing’s lacking from the Hyades cluster: white dwarfs. There’s an obvious lack of them, with solely eight of them within the cluster’s core. The place did they go?
The Hyades Cluster is fairly unremarkable. Learning it creates a benchmark in astronomers’ understanding of star clusters. Nevertheless it does have no less than one wrinkle, and that is its lack of white dwarfs. It is a stumbling block in understanding Hyades. Nonetheless, a brand new examine discovered one which was ejected from the cluster. And it is an ultra-massive white dwarf, one which nudges up in opposition to the mass restrict for such a stellar remnant. How does it slot in?
The brand new analysis is titled “An Extremely Massive White Dwarf Escaped From the Hyades Star Cluster.” It has been submitted to The Astrophysical Journal for publication and is presently accessible on the arXiv preprint server. The lead writer is David Miller from the Division of Physics and Astronomy on the College of British Columbia.
Open clusters like Hyades are solely loosely certain, and over time, they lose stars via interactions with fuel clouds, different clusters, and between cluster members. Miller and his co-researchers examined the shortage of white dwarfs in Hyades as a way to reconstruct the Hyades cluster. If they will establish stars which have been evicted, particularly white dwarfs on this case, they will piece collectively the cluster’s historical past.

Thankfully, the ESA’s Gaia spacecraft has been monitoring greater than 1 billion stars within the Milky Way, giving Miller and his colleagues a large compilation of knowledge to go looking via. The crew discovered three ultra-massive white dwarfs with kinematics indicating they might’ve left the Hyades cluster. The mass vary for 2 of them made it unlikely that they did come from Hyades, however not for the third one. That object “seems to be a high-probability escapee” from the cluster, the authors write.
White dwarfs are as huge because the sun however the measurement of the Earth. They’re made from electron degenerate matter and left their lifetime of fusion way back. The one vitality they emit is remnant thermal vitality.
White dwarfs are the tip state of about 97% of the celebs within the Milky Way. They’re ruled by the Chandrasekhar Restrict and may solely have about 1.44 solar plenty. In the event that they achieve extra mass than that, sometimes by siphoning it from a binary companion, they explode as Sort 1a supernovae, with the complete mass of the white dwarf dissipated into space.
Hyades’ escaped white dwarf is named an ultra-massive white dwarf. A lot of these white dwarfs have 1.10 or extra solar plenty. That is effectively beneath the Chandrasekhar restrict however effectively above the typical white dwarf mass of about 0.6 solar plenty. They’re essential outliers within the astrophysical examine of white dwarfs. Excessive-mass white dwarfs sometimes come from two progenitor stars in a binary pair, the place one of many white dwarfs siphons materials away from the opposite, growing its mass.
However the Hyades ultra-massive white dwarf has a mass of 1.317 solar masses and an age in keeping with solely a single progenitor. It is doubtlessly probably the most huge white dwarf to return from a single progenitor and can also be probably the most huge single progenitor star to be strongly related to an open cluster.
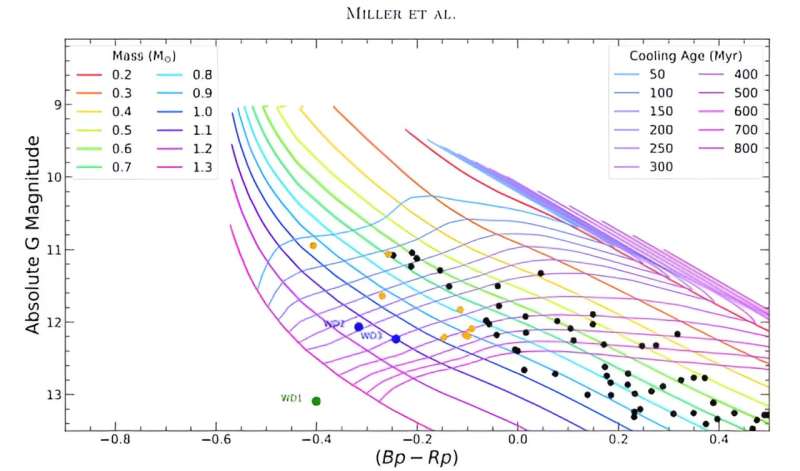
“Assuming a single-stellar evolution formation channel, we estimate a 97.8% likelihood that the candidate is a real escapee from the Hyades,” the researchers write.
Why is that this in any other case unassuming star important? As a result of it sometimes requires two progenitor stars, with one siphoning mass from the opposite, to create a white dwarf this huge.
“This offers a important observational benchmark for white dwarfs created from single progenitor stars, demonstrating that single stars can produce white dwarfs with plenty near the Chandrasekhar restrict,” the researchers clarify of their paper.
Although the Hyades is unremarkable in most methods, it is so shut that astronomers can detect older, cooler white dwarfs after which hint their origins with larger precision. This allowed the researchers to review the cluster in nice element. Because the Hyades is so unremarkable, the crew’s outcomes can prolong, to some extent, to open clusters usually.
“The mixture of the unremarkable nature of the Hyades cluster and the advantages of its proximity recommend that open star clusters could also be producing ultramassive white dwarfs, together with white dwarfs which push the Chandrasekhar restrict, extra generally than beforehand thought,” the authors write of their conclusion.
The Hyades is not troublesome to find within the sky. Orion’s Belt factors proper at it. If you wish to take a look, it is best seen from Northern Latitudes throughout November, December, and January. With the unaided eye, it seems like a “V” form made up of about 20 stars. Good binoculars enhance that quantity to about 100.
Extra data:
David R. Miller et al, An Extraordinarily Large White Dwarf Escaped From the Hyades Star Cluster, arXiv (2023). DOI: 10.48550/arxiv.2310.03204
Offered by
Universe Today
Quotation:
Extraordinarily huge white dwarf escaped from the Hyades star cluster, examine says (2023, October 12)
retrieved 12 October 2023
from https://phys.org/information/2023-10-extremely-massive-white-dwarf-hyades.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any honest dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for data functions solely.




