The Milky Way is our house galaxy within the huge universe, however the construction and composition of the Milky Way stay mysterious. The huge interstellar space between the billions of stars isn’t empty, however crammed with tenuous interstellar medium. The diffuse hydrogen fuel radiates a spectral line with a frequency of round 1420 MHz. Some dense hydrogen atoms collect to type clouds of molecular hydrogen, and newly born stars are fashioned within the dense cores; younger and brilliant stars can ionize the encompassing fuel.
Stars evolve from beginning to demise, and a few ultimately explode as supernovae, producing a remnant and a pulsar. The shock waves from the supernova explosion compress the interstellar fuel and speed up electrons to almost the pace of sunshine. These high-speed electrons cycle within the interstellar magnetic field, radiating faint radio waves. The galactic interstellar medium is key for the beginning and demise of many stars.
The 5-hundred-meter Aperture Spherical Telescope (FAST) constructed by China is essentially the most delicate single-dish radio telescope on this planet. As a result of it’s outfitted with a extremely delicate L-band 19-beam cryogenic receiver, it is a superb instrument for looking pulsars and exploring the galactic interstellar medium. A staff led by chief professor JinLin Han carried out the Galactic Airplane Pulsar Snapshot (GPPS) survey and located greater than 500 faint new pulsars which might be one order of magnitude fainter than the earlier identified pulsars.
Throughout the observations for pulsars, they concurrently recorded the spectral line knowledge, characterised by high sensitivity, excessive spectral decision and high spatial resolution, a particularly beneficial useful resource for finding out the construction of the Milky Way galaxy and the interstellar ecological cycle. They just lately accomplished the processing of the spectral line knowledge and printed the most recent outcomes of atomic and ionized fuel, magnetic fields and radio radiation in interstellar space within the Milky Way within the journal Science China Physics, Mechanics & Astronomy.
In its first knowledge launch, FAST detected the sky distribution of impartial hydrogen (HI) fuel in 88 sq. levels between the galactic longitude of 33° to 55° and the galactic latitude of ±2°. Although the superb calibration remains to be beneath means, the outcomes accessible are already essentially the most delicate for detection of HI fuel clouds so far, exhibiting unprecedented element in regards to the distribution of HI fuel.
John M. Dickey, emeritus professor on the College of Tasmania in Australia and the College of Minnesota in the USA, stated, “The advance in angular decision and sensitivity over all earlier surveys is spectacular… publication of this primary paper on the GPPS HI survey is a landmark accomplishment, worthy of celebration and worldwide consideration.”
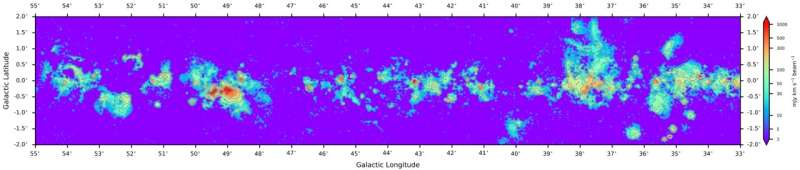
The ionized fuel of interstellar space is the final main part of the Milky Way that continues to be unexplored intimately. The staff processed the hydrogen radio recombination strains (RRL) within the GPPS spectral line knowledge in the identical sky space because the HI knowledge, revealing luminous areas ionized by bright stars and diffuse ionized fuel (DIG) of unknown origin. The information are indispensable for the research of the ecological cycle of fuel and star formation within the Milky Way.
Dr. Dana S. Balser, a scientist on the Nationwide Radio Astronomy Observatory, stated, “This GPPS RRL survey is essentially the most delicate survey so far and has adequate angular resolution to separate DIG emission from HII areas…. Giant, single-dish telescopes such because the FAST are the perfect to probe the DIG, the final main part of the Milky Way galaxy to be nicely characterised.”
The galactic magnetic fields that permeate the interstellar medium of the galaxy are extraordinarily tough to measure. The staff relied on the sensitivity of FAST to measure polarization and Faraday rotation of 134 faint pulsars within the galactic halo, and located that the magnetic area power within the galactic halo is about 2 microgauss.
Newly decided Faraday rotation measure knowledge from the GPPS survey provides proof for the magnetic area reversals alongside the spiral arms in farther areas of the Milky Way. With out FAST, the interstellar magnetic field in such a large area can be by no means detected.
The staff additionally examined the scanning observations by FAST for radio continuum radiation of the galaxy in an space of 5° × 7° within the sky. The outcomes affirm that two massive, faint radio-emission buildings (G203.1+6.6 and G206.7+5.9) are shell-type supernova remnants, certainly one of which was produced by a supernova explosion very near the sun at solely about 1,400 light-years.
“The delicate FAST observations can reveal unprecedented particulars of the Milky Way,” stated Jing Yipeng, an academician of the Chinese language Academy of Sciences at Shanghai Jiao Tong College. “The databases of impartial hydrogen and ionized hydrogen printed by these papers are beneficial assets for astronomers over the world.”
Extra info:
Tao Hong et al, Peering into the Milky Way by FAST: I. Beautiful Hello buildings within the inside Galactic disk from the piggyback line observations of the FAST GPPS survey, Science China Physics, Mechanics & Astronomy (2022). DOI: 10.1007/s11433-022-2040-8
LiGang Hou et al, Peering into the Milky Way by FAST: II. Ionized fuel within the inside Galactic disk revealed by the piggyback line observations of the FAST GPPS survey, Science China Physics, Mechanics & Astronomy (2022). DOI: 10.1007/s11433-022-2039-8
Jun Xu et al, Peering into the Milky Way by FAST: III. Magnetic fields within the Galactic halo and farther spiral arms revealed by the Faraday impact of faint pulsars, Science China Physics, Mechanics & Astronomy (2022). DOI: 10.1007/s11433-022-2033-2
XuYang Gao et al, Peering into the Milky Way by FAST: IV. Identification of two new Galactic supernova remnants G203.1+6.6 and G206.7+5.9, Science China Physics, Mechanics & Astronomy (2022). DOI: 10.1007/s11433-022-2031-7
John M. Dickey, The GPPS HI survey—A deeper view of the Milky Way galaxy, Science China Physics, Mechanics & Astronomy (2022). DOI: 10.1007/s11433-022-2030-x
Dana S. Balser, The diffuse ionized fuel within the Milky Way galaxy, Science China Physics, Mechanics & Astronomy (2022). DOI: 10.1007/s11433-022-2038-7
Offered by
Science China Press
Quotation:
FAST telescope reveals unprecedented particulars of the Milky Way (2022, December 13)
retrieved 13 December 2022
from https://phys.org/information/2022-12-fast-telescope-reveals-unprecedented-milky.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any honest dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for info functions solely.




